We just wrote about the Infineon XENSIV PAS CO2 Shield2Go board to measure carbon dioxide (CO2) levels last week, but I’ve just come across two more hardware with a CO2 sensor designed for makers, but based on Sensirion SCD40 sensor instead, and mostly designed to monitor indoor CO2 levels since high concentrations may impact your health negatively. The first one is the M5Stack UNIT CO2 that’s designed to be connected to one of the company’s Core modules through an I2C interface, and TeHyBug portable mini sensor device equipped with ESP8285 WiFi microcontroller, as well as optional AHT10 temperature & humidity sensor and BMP280 pressure sensor, besides the SCD40 sensor. M5Stack UNIT CO2 Specifications: Sensirion SCD40 sensor CO2 Measurement range – 400 ~ 2000 ppm CO2 Sampling accuracy – ±(50 ppm + 5% of reading) Temperature range – -10 – 60°C with 0.8°C accuracy Humidity range – 0 – 95% RH […]
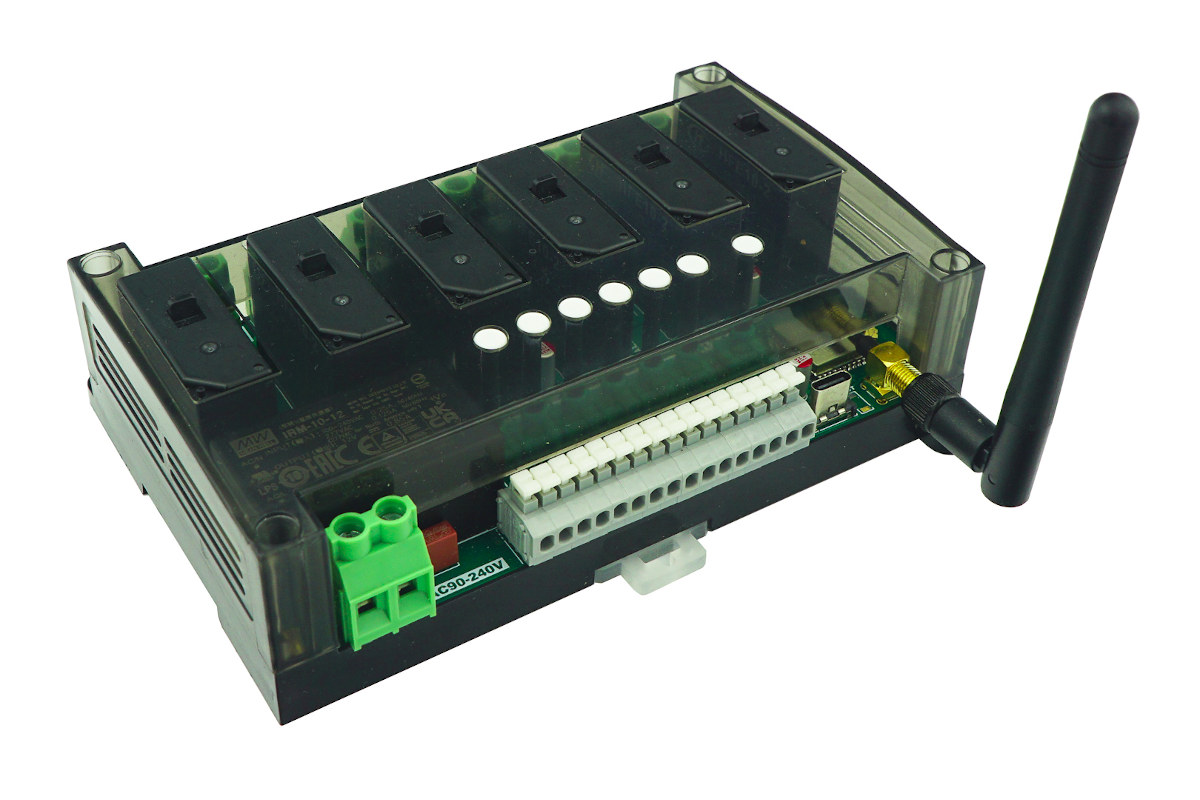
ESPHome compatible ESP32-S2 module offers six 32A latch relays in a DIN Rail enclosure
EasySensors “6Gang30AmpsLatchRelayEspHomeReady” (now that’s a product name!) is a DIN Rail mountable, ESP32-S2-based automation device featuring six 32A latch relays and supporting ESPHome open-source framework. The system also comes with two inputs for Dallas temperature sensors, two buttons for manual control of relays, a USB-C port for programming, as well as an external SMA antenna for WiFi connectivity. 6Gang30AmpsLatchRelayEspHomeReady specifications: Wireless SoC – Espressif ESP32-S2 Xtensa single-core 32-bit LX7 microcontroller @ up to 240 MHz with 320 kB SRAM, 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 (Matter-ready) Antenna – Embedded IPX to SMA adapter, 3dBi antenna I/Os 6x 32A latch relays with zero current idle consumption 2x Dallas temperature sensor pins with 5 kOhm pull-up resistors USB – 1x USB Type-C for programming via CP2102 USB to TTL chip Misc 6x control buttons, Reset button 6x status LED’s, 2x status LED’s Input Voltage – 85 to 305V AC Dimensions Board – 147 x […]
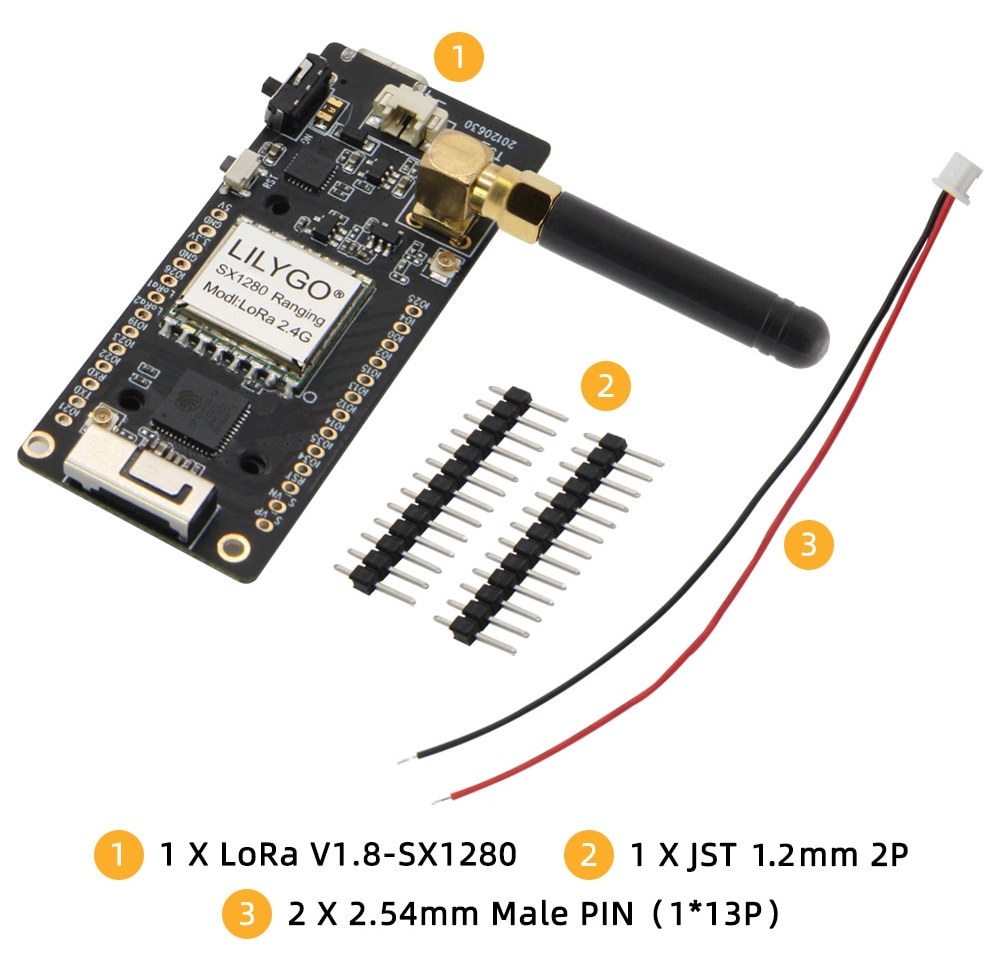
ESP32 board supports 2.4Ghz LoRa with SX1280 RF transceiver
We’ve seen plenty of ESP32 LoRa boards with the traditional 433 MHz, 868 MHz, or 915MHz frequencies, but I think LilyGO LoRa V1.8 (aka T3 V1.8) is the first ESP32 board that integrates a Semtech SX1280 transceiver for the 2.4GHz LoRa standard used for global coverage, notably maritime applications, and ranging. The ESP32 & SX1280 board also offers 26 pins for expansion, a microSD card for data storage, a 2-pin connector for batteries, a 0.96-inch OLED for information display, and comes with a 3D antenna and u.FL connector for WiFi and Bluetooth, and an SMA antenna for LoRa connectivity. LilyGO LoRa/T3 V1.8 specifications: SoC – Espressif ESP32 dual-core Xtensa LX6 processor with 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 4.2 Storage – 4MB SPI flash, microSD card slot Display – 0.96-inch OLED display with 128×64 resolution (SSD1306 I2C driver) Connectivity 802.11 b/g/n WiFi 4 up to 150 Mbps + Bluetooth 4.2 […]
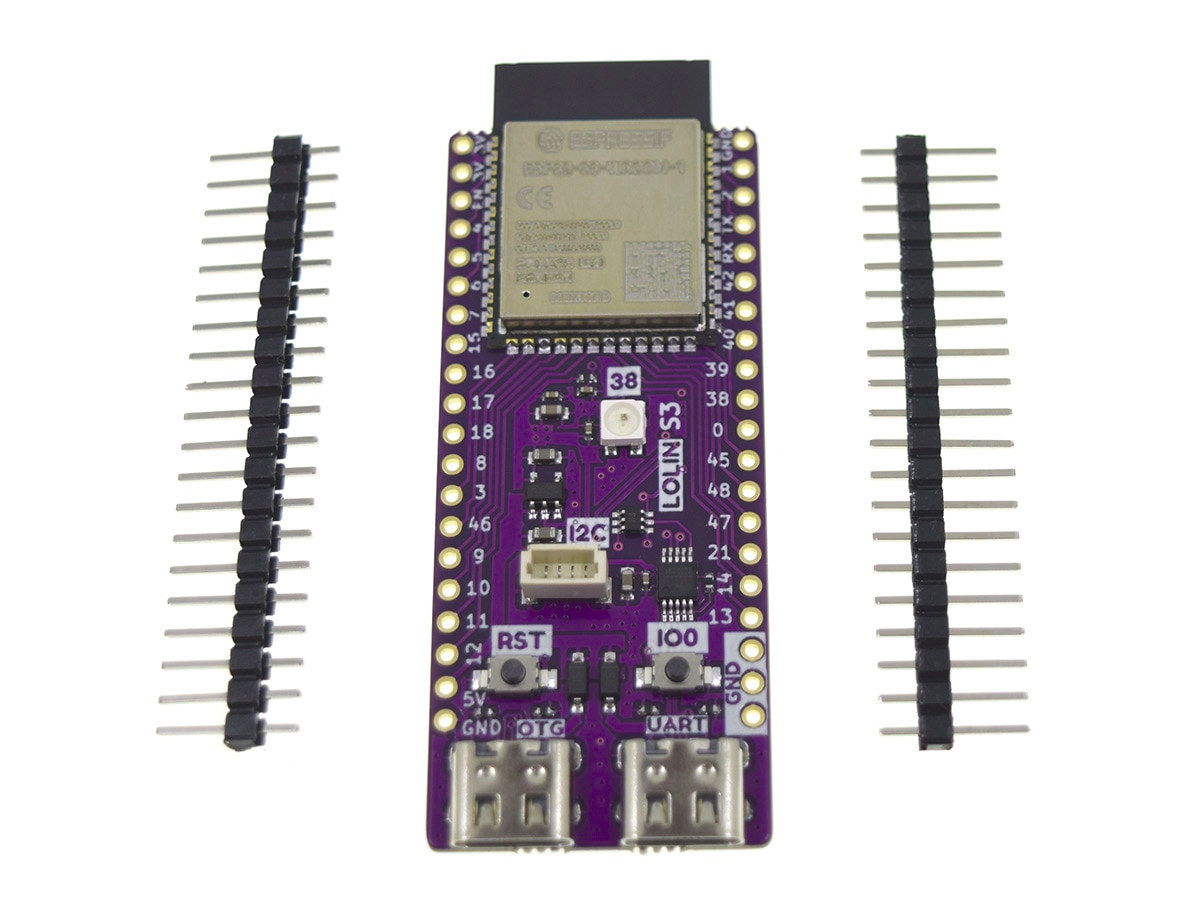
$7 Lolin S3 ESP32-S3 board ships with MicroPython firmware
Lolin S3 is the first ESP32-S3 board from the company, but instead of using the more compact D1 mini form factor, the board features a longer design with two rows of 20 pins offering up to 31 GPIOs. Based on ESP32-S3-WROOM-1 module, the board features 16MB QSPI flash, 8MB SPRAM, two USB Type-C OTG and UART ports, a Lolin I2C port, an RGB LED, as well as Reset and user buttons. Lolin S3 specifications: Wireless module – ESP32-S3-WROOM-1 module with: Espressif Systems ESP32-S3 dual-core Tensilica LX7 @ up to 240 MHz with vector instructions for AI acceleration, 512KB RAM, 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5.0 LE with support for long-range, up to 2Mbps data rate, mesh networking 16MB QSPI flash 8MB PSRAM PCB antenna USB – 2x USB Type-C ports, one OTG port, one UART port for programming and debugging Expansion 2x 20-pin headers with up to 31x GPIO, […]
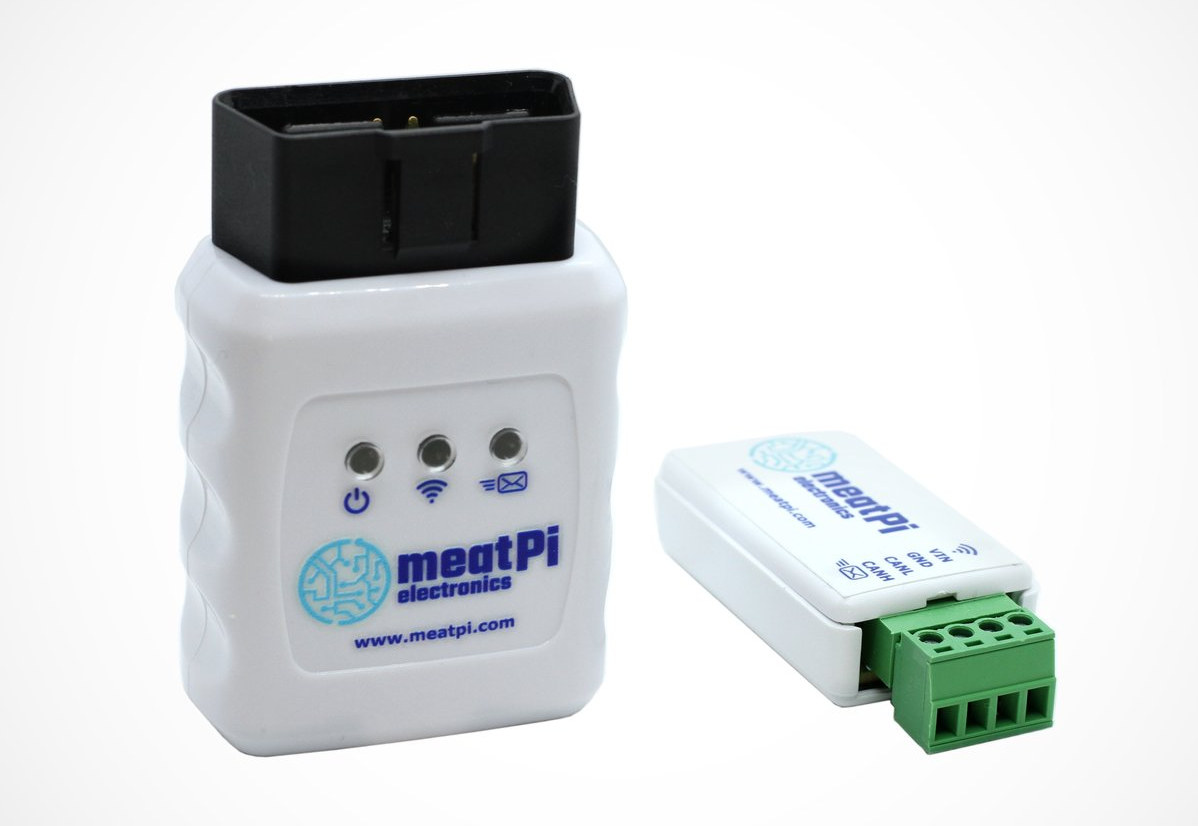
WiCAN ESP32-C3 CAN Bus platform is available in USB-CAN and OBD-II form factors (Crowdfunding)
WiCAN is an ESP32-C3 CAN bus adapter that works over USB, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth LE, and designed for car hacking and general CAN bus development. The device is available in USB-CAN and OBD-II form factors and comes with firmware that works with RealDash to create nice-looking dashboards with the data. RealDash can be installed on Android, iOS, and Windows 10 operating systems. WiCAN specifications: Wireless module – ESP32-C3-MINI-1 with ESP32-C3 RISC-V microcontroller with 2.4GHz WiFI 4 and Bluetooth 5.0 connectivity, 4 MB flash, PCB antenna CAN 2.0 A/B interface up to 1 Mbps Host interface WiCAN-OBD – OBD-II connector WiCAN-USB – Mini USB port for USB-to-UART up to 6 Mbps Power Supply WiCAN-ODB – 7.5V to 16V (Vbat) WiCAN-USB – 7.5V to 36V via screw-terminal connector Power Consumption – <= 1 mA in battery-saving mode The CAN Bus adapter also supports firmware updates over WiFi, and can be used either […]
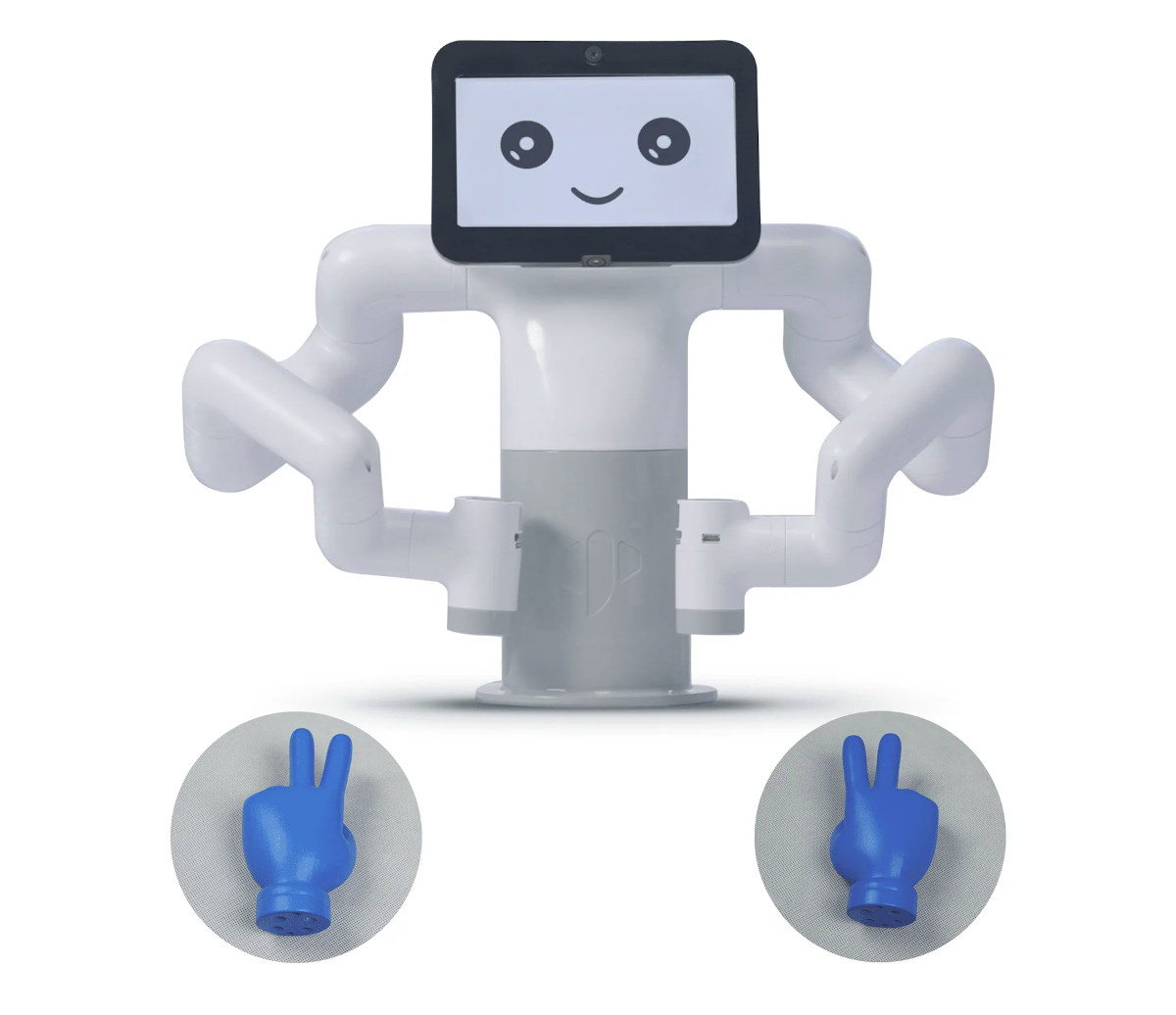
myBuddy 280 dual arm robot features Raspberry Pi 4 SBC and ESP32 controllers
Elephants Robotics myBuddy 280, aka myBuddy 280 Pi, is a dual-arm collaborative robot for education with a 7-inch display powered by Raspberry Pi 4 SBC, and also features three ESP32-based M5Stack core modules that help with the internal communication between the motors and the Raspberry Pi board. It builds upon the earlier myCobot 280 Pi robot with a single arm, with the same 280mm working range, but the new robot offers two arms, and a total of 13 degrees of freedom (DoF). The robot is also equipped with two 2MP HD cameras for computer vision, a standard 3.3V expansion I/O interface, a LEGO expansion interface, and can be fitted with a variety of adapters such as suction pumps, grippers, little hands (see below), etc… myBuddy 280 specifications: SBC – Raspberry Pi 4 (2GB or 4GB RAM) single board computer to control the display and communicate with the ESP32 modules IoT […]
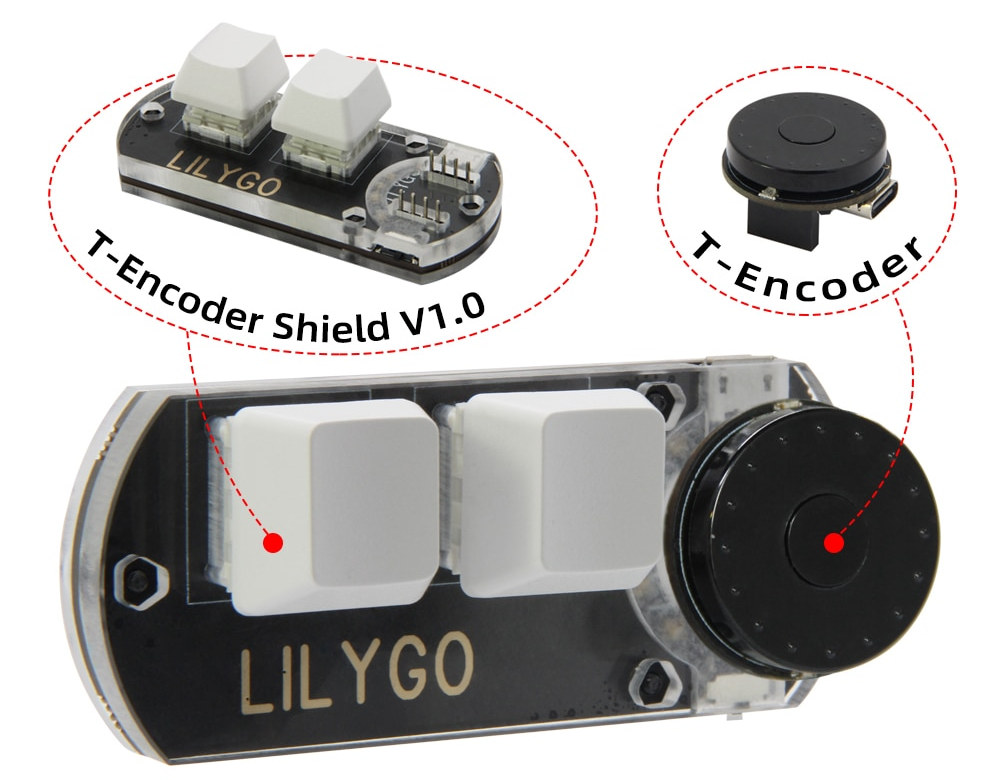
ESP32 board with rotary encoder gets 2-key keypad shield
LILYGO TTGO T-Encoder, a round-shaped ESP32 board with a built-in rotary encoder, has gotten a shield with a 2-key keypad based on WCH CH552 8-bit microcontroller. Launched several months ago, the TTGO T-Encoder is a USB-powered rotary encoder with ESP32 microcontroller offering WiFi and Bluetooth connectivity, and now, you can build a keypad with rotary encoder thanks to T-Encoder shield that features two mechanical switches and keycaps with RGB LED backlight. Since we missed it at launch, let’s check out the tiny TTGO T-Encoder board specifications first: System-in-Package (SiP) – Espressif ESP32-PICO-V3-02 with MCU – ESP32 Xtensa dual-core 32-bit Xtensa LX6 microcontroller up to 240 MHz, 448 KB ROM for booting and core functions, 520 KB SRAM for data and instructions, 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 4.2 BR/EDR + LE connectivity Memory – 2MB SPI PSRAM Storage – 8MB SPI flash Dimensions – 7×7 mm Antenna – Ceramic […]
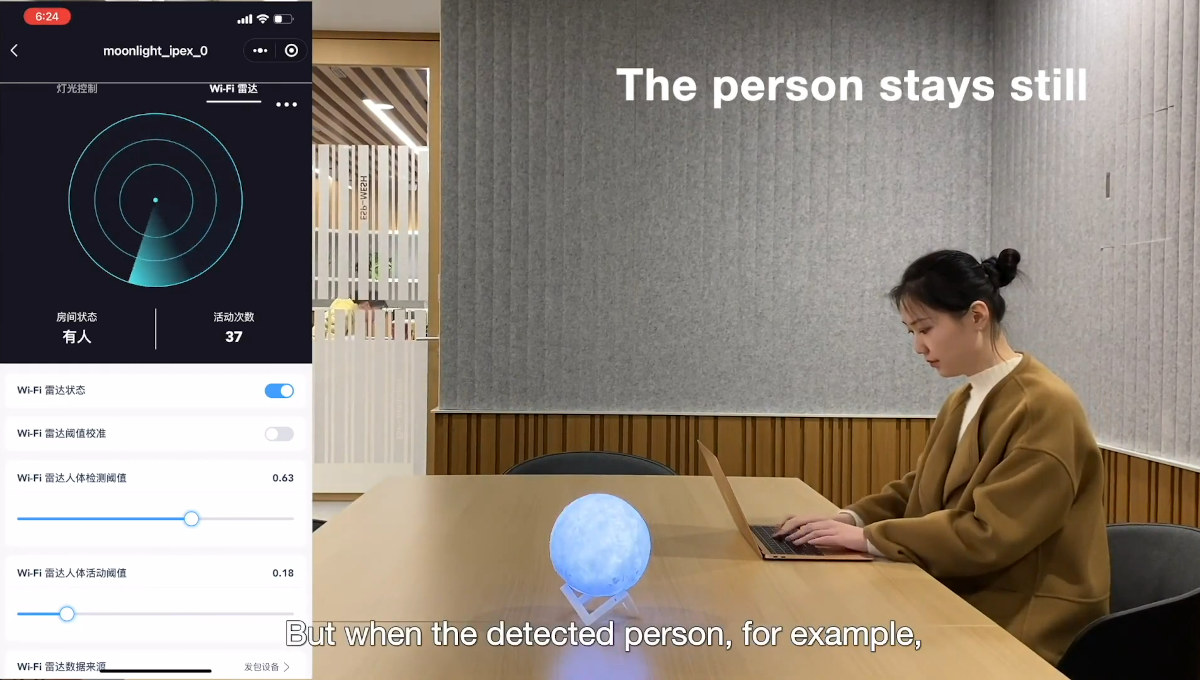
ESP-WIFI-CSI detects humans with WiFi signals only, no sensor needed
Espressif ESP-WIFI-CSI software relies on the disturbance in the force WiFi signals between one or more ESP32 boards and a router to detect whether humans are present in a room, or even indoor positioning, providing a cost-effective solution since no sensors are needed. Channel state information (CSI) leverages carrier signal strength, amplitude, phase, and signal delay indicators to reveal the signal scattering, reflection, and power attenuation phenomena that occur with the carrier as the transmission distance changes. This is typically used to measure the channel status of the wireless network in Wi-Fi communication, but it’s also possible to analyze and study the changes in CSI to detect movements such as walking and running of people or animals, and Espressif claims it can also capture subtle movements caused by small movements such as breathing and chewing of people or animals in a static environment. ESP-WIFI-CSI implementation works with all ESP32 series […]