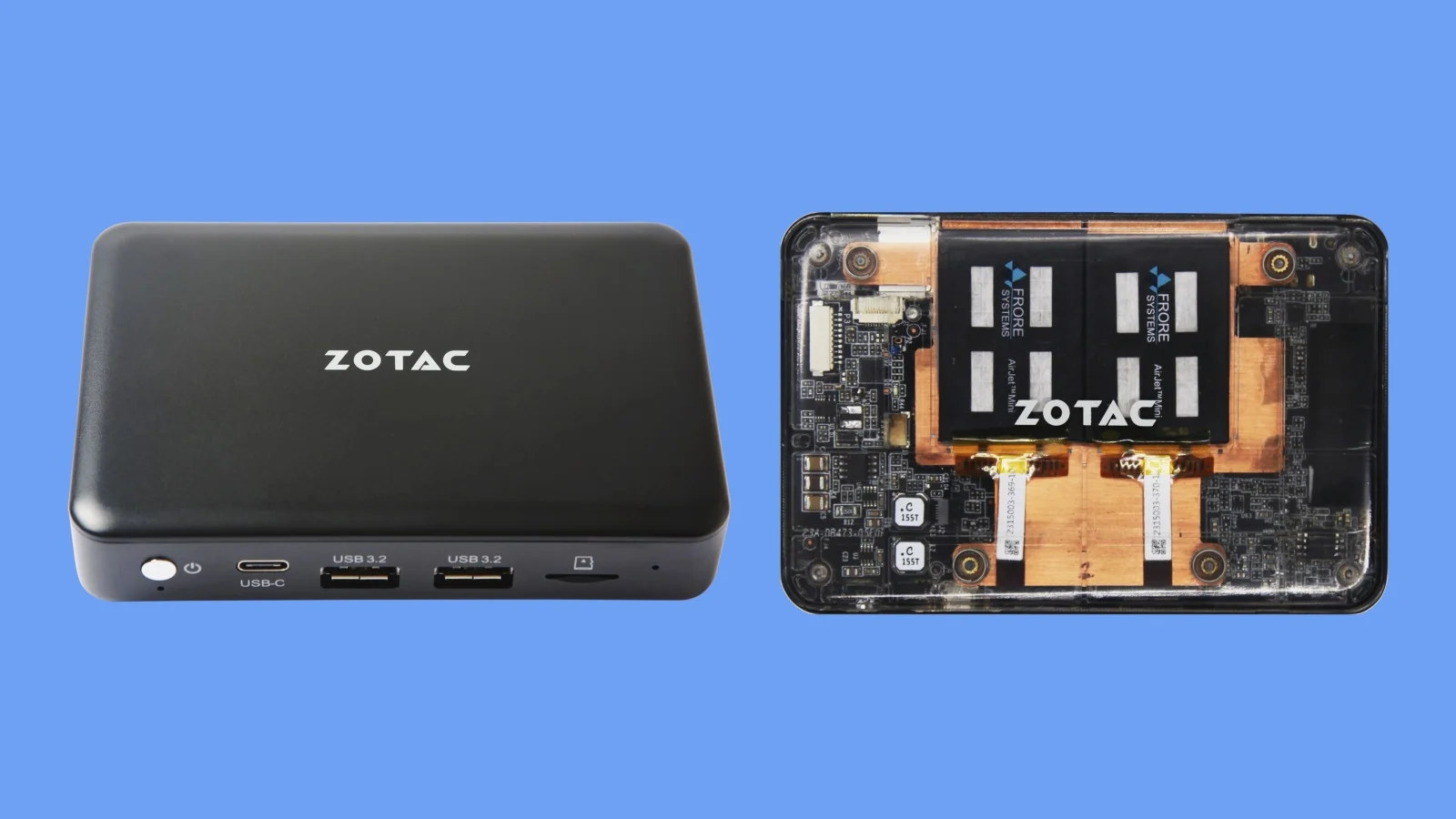
ZOTAC PI430AJ Pico is the first mini PC equipped with (two) Airjet solid-state active cooling chips introduced at CES 2023, doing without the metal case required by typical fanless systems, and instead relying on a plastic case. The PI430AJ Pico is powered by a recent 7W Intel Core i3-N300 octa-core Alder Lake-N processor coupled with up to 16GB LPDDR5 RAM and an M.2 NVMe SSD up to 1TB capacity. The mini PC is showcased at COMPUTEX 2023 with a transparent cover to showcase the two FRORE Systems Airjet mini PC, but it will eventually be sold with a black plastic enclosure. ZOTAC PI430AJ Pico preliminary specifications: SoC – Intel Core i3-N300 octa-core processor up to 3.8 GHz with 6MB cache, 32EU Intel UHD Graphics Gen 12 @ 1.25 GHz; TDP: 7W System Memory – Up to 16GB LPDDR5 Storage – Up to 1TB M.2 NVMe SSD, microSD card slot Video […]
SONOFF TX Ultimate Review – A smart touch wall switch with innovative features
SONOFF has been producing a wide range of new products over the years, and since the beginning of the year, the company introduced various new products and features including the iHost Smart Home Hub local hub which no longer requires cloud connectivity. The one we are going to review is the Ultimate Smart Touch Wall Switch (also known as the SONOFF TX Ultimate). SONOFF stated that they wanted to provide a new experience with their smart switch. Initially, we couldn’t imagine what new experiences a smart switch could offer. When we think of SONOFF, we usually associate it with affordable smart switches that are durable and perform as expected, not stylish or feature-rich devices. However, the SONOFF TX Ultimate comes as a complete package with light, color, sound, and touch. SONOFF has also expanded the touch area, so there’s no need to worry about missing the button while pressing it. […]
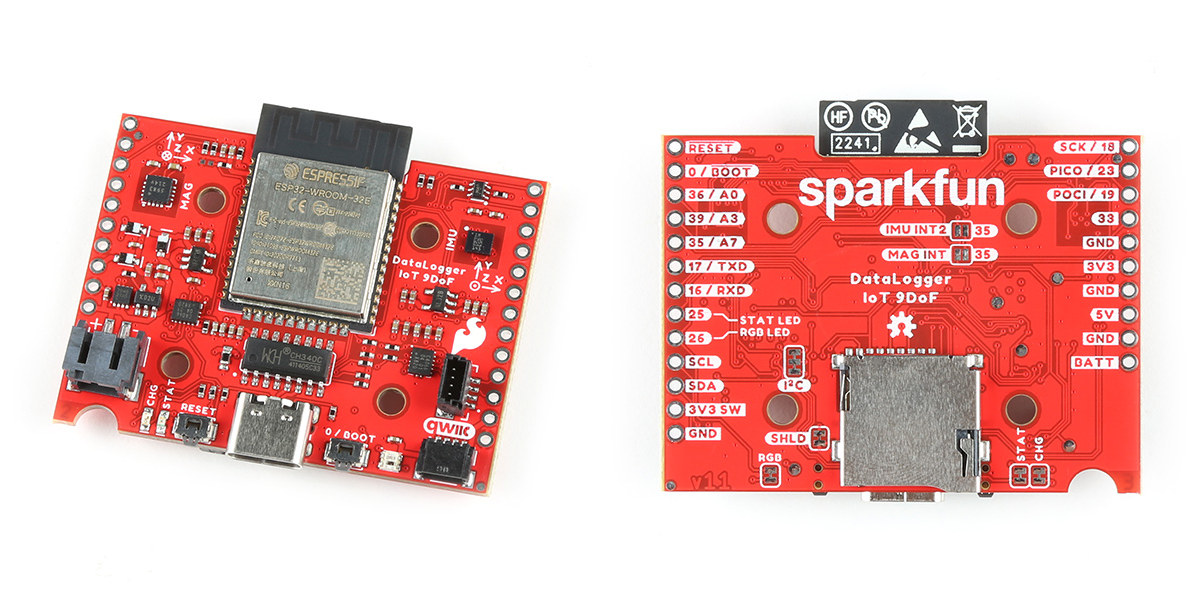
SparkFun “Datalogger IoT – 9DoF” no code platform supports over 50 Qwiic sensor modules
SparkFun “DataLogger IoT – 9DOF” is an ESP32-based data logger board that transfers data to a microSD card or wirelessly to the cloud and comes with firmware that can automatically detect over 50 Qwiic modules without any programming required from the user making it a so-called “no code platform“. The board comes with a 9-axis IMU sensor + magnetometer, and two Qwiic connectors, and the data is stored in CSV or JSON formats on a microSD card or sent to IoT cloud platforms such as Amazon AWS IoT, Microsoft Azure, or Mathworks ThingSpeak using protocols like MQTT or HTTP. SparkFun “Datalogger IoT – 9DoF” specifications: Wireless module – ESP32-WROOM-32E: ESP32 dual-core microcontroller 4MB flash 2.4 GHz WiFi and Bluetooth LE connectivity, built-in PCB antenna Storage – MicroSD card slot Sensors 6-axis IMU accelerometer & gyro (ISM330DHCX) Magnetometer (MMC5983MA) 2x Qwicc I2C connectors for additional sensors USB – 1x USB Type-C […]
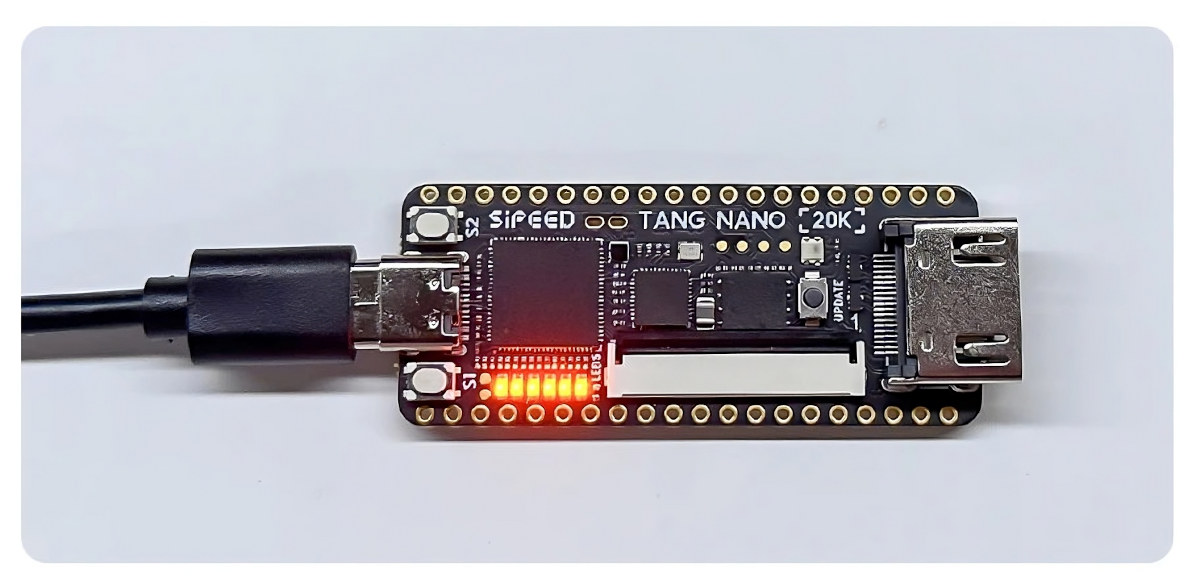
$25 Sipeed Tang Nano 20K FPGA board can simulate a RISC-V core, run Linux, retro games
The Sipeed Tang Nano 20K is a low-cost FPGA development board based on Gowin GW2AR-18 FPGA with 20,736 logic cells and 64Mbit RAM, which coupled with 64MBit QSPI flash provides enough resources to simulate a 32-bit RISC-V core booting Linux or playing retro games in an emulator. The FPGA board comes with a USB-C port for power and to load the FPGA bitstream through a BL616 microcontroller that also acts as a USB to serial chip, an HDMI port and an RGB LCD interface for video output, two user buttons, and two rows GPIOs to connect peripherals such as gamepads (through adapters). Sipeed Tang Nano 20K specifications: FPGA – Gowin GW2A-LV18QN88C8I7 with 20,736 logic units (LUT4) 15,552 flip-flops (FF) RAM 41,472 shadow SRAM (S-SRAM) 828K block SRAM (B-SRAM) Numbers of B-SRAM – 46 64Mbit 32-bit SDR SDRAM 48x 18×18 multipliers 2x PLLs 8x I/O Bank Onboard debugger – Bouffalo Labs […]
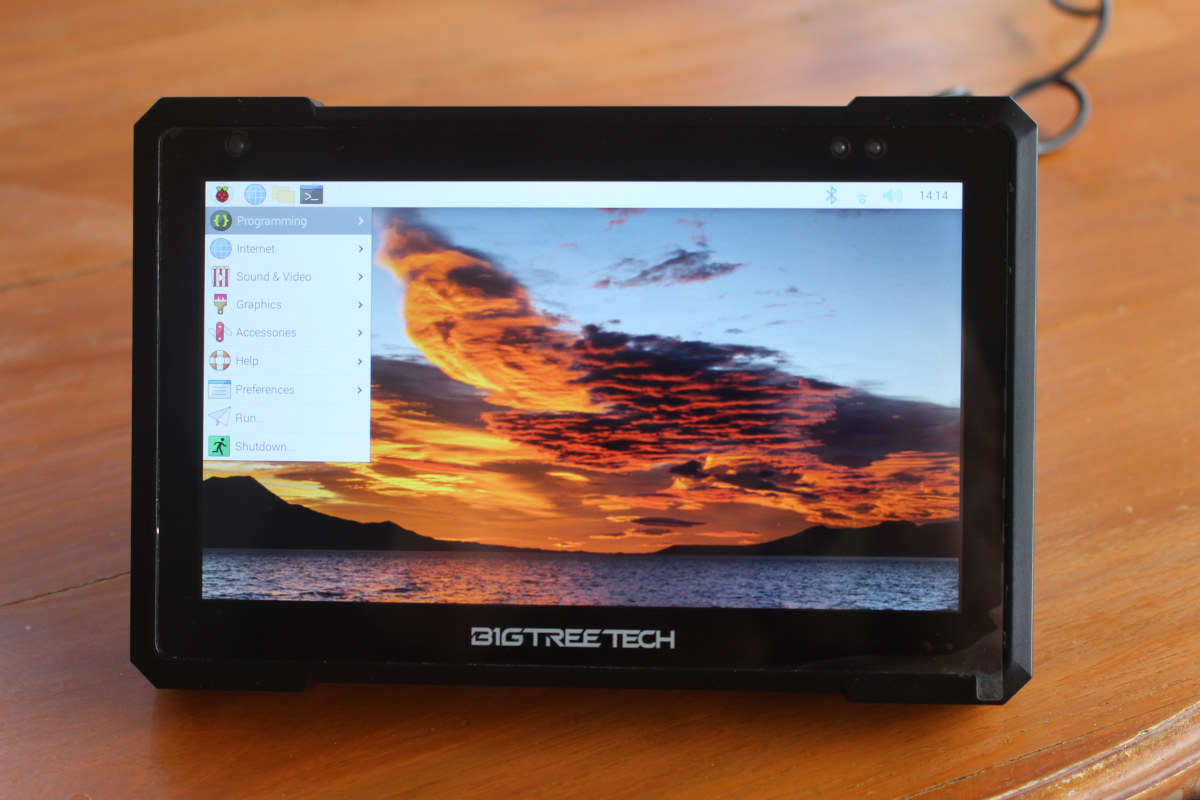
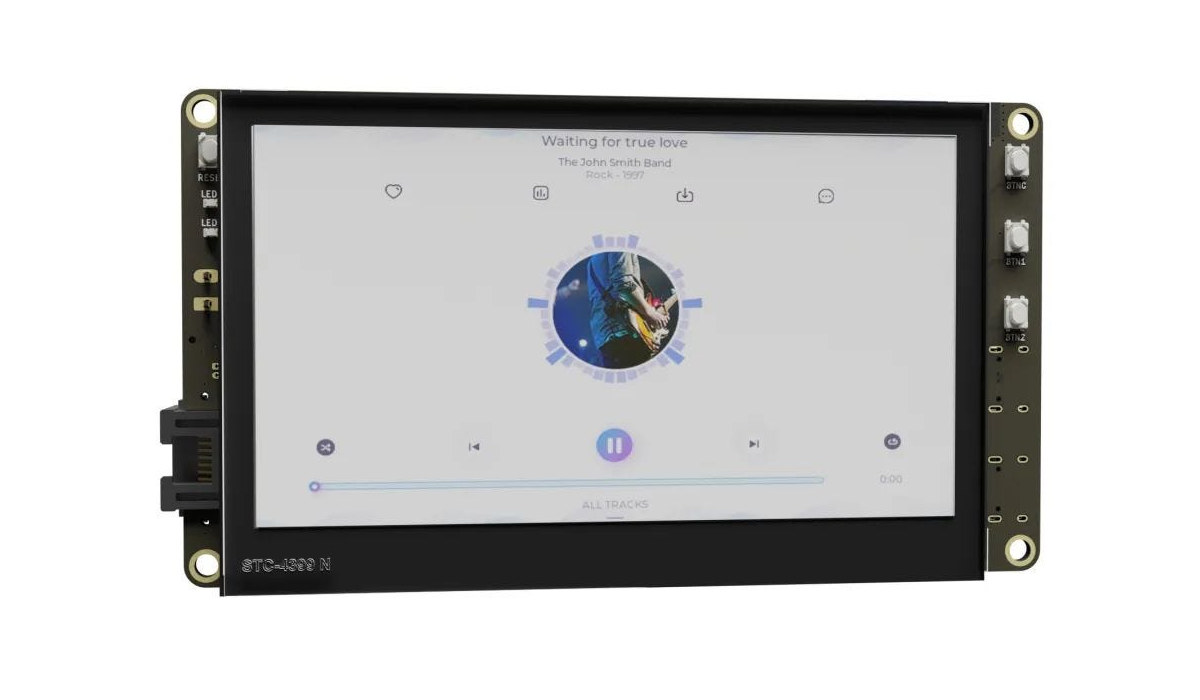
Using BTT Pad 7 touchscreen display with Raspberry Pi CM4
The BTT Pad 7, or BIGTREETECH Pad 7 in full, is a 7-inch touchscreen display that ships with the CB1 Allwinner H616 system-on-module compatible with Raspberry Pi CM4. The display is mostly designed for 3D printers with its SPI and CAN Bus interfaces, but it can also be used as a standard tablet PC. So today, I’ll switch the CB1 with a Raspberry Pi CM4 Lite module and report my experience doing the conversion and using it as a Raspberry Pi CM4 tablet PC running Raspberry Pi OS, and test it with a 3D printer with Klipper in another post later on. Installing a Raspberry Pi CM4 (Lite) module in the BTT Pad 7 We’ll need the Pad 7, a Raspberry Pi CM4, and a few tools. The first step is to remove the red heatsink by loosening four screws with a 2.0mm hex key, as well as the cover […]
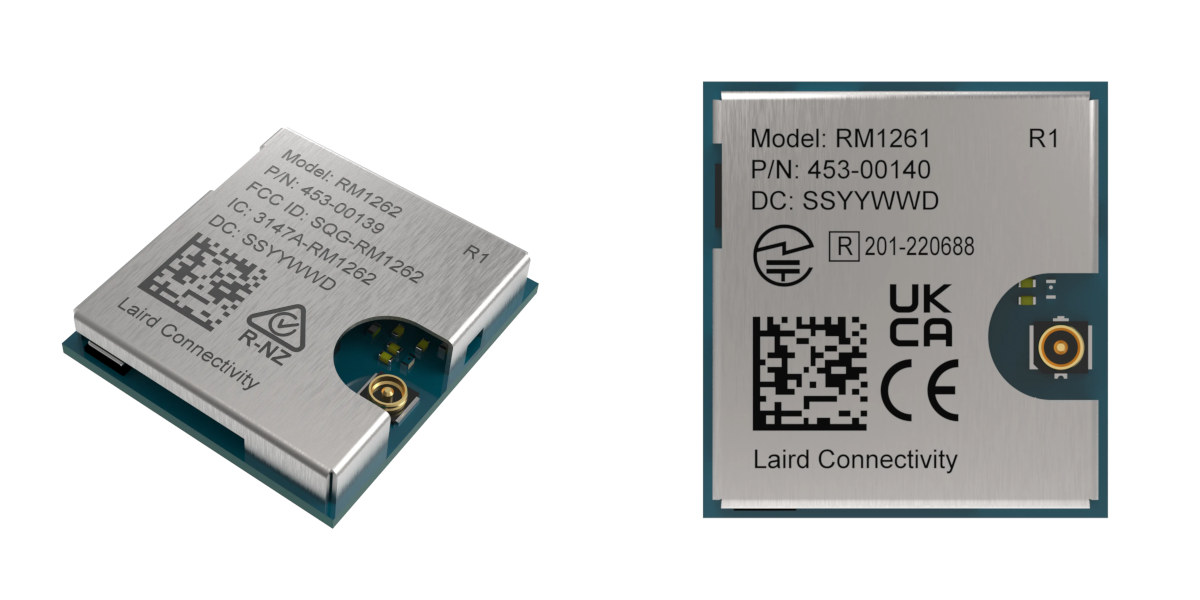
Laird RM126x LoRaWAN modules and development kits feature Silicon Labs EFR32 MCU, support P2P communication
Laird Connectivity has launched the RM126x series of ultra-low power LoRaWAN modules with the RM1261 based on SX1261 RF transceiver compliant with regulations in Europe, UK, Taiwan, Japan, India, and other countries, and the RM1262 based on Semtech SX1262 for USA, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, etc… The RM126x modules partially achieve their low power consumption through the use of a Silicon Labs EFR32 series microcontroller, and should be integrated into products for industrial, agriculture and forestry, smart cities, utilities monitoring, transportation, logistics, supply chain, healthcare monitoring, and retail. Laird RM126x specifications: MCU – Silicon Labs EFR32 Arm Cortex-M33 microcontroller with 512KB flash, 32KB SRAM LoRa connectivity RF transceiver – Semtech SX1261 or SX1262 Data rates LoRa 125kHz LoRa 250kHz LoRa 500kHz FSK 50kbps (as per RP002-1.0.3 ) Frequency Range (1) – 863 MHz – 870 MHz Frequency Range 2 – 902 MHz – 928 MHz LoRa Version Class – Version […]
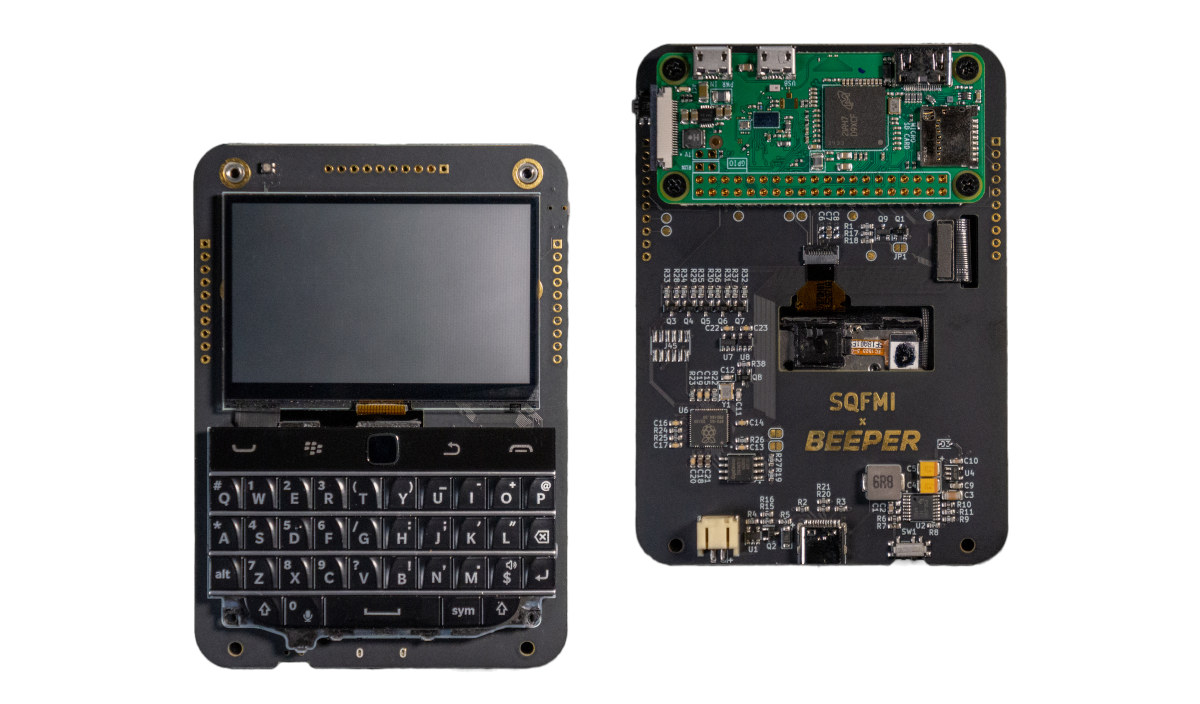
BeepBerry handheld Linux computer drives 2.7-inch display with Raspberry Pi Zero W
Good news! The PocketCHIP handheld Linux computer is back! OK, not quite but that’s what the Raspberry Pi Zero-powered BeepBerry reminds me of with a Blackberry-like keyboard, a small 2.7-inch display, and a 2,000mAh LiPo battery for power. The BeepBerry is another open-source hardware design from SQFMI, who previously did the Watchy ESP32 E-Ink smartwatch, that runs Raspberry Pi OS Lite on the Raspberry Pi Zero/Zero W, and also includes a Raspberry Pi RP2040 to handle the keyboard and peripherals. BeepBerry specifications: SBC – Raspberry Pi Zero board with a Broadcom BCM2835 ARM11 processor @ 700 MHz, VideoCore IV GPU, or Raspberry Pi Zero W with WiFi and Bluetooth Storage – MicroSD card slot Display – Ultra-low power high contrast 2.7-inch Sharp Memory LCD with 400 x 200 resolution User input – QWERTY tactile keyboard w/ backlight and touchpad based on Solder Party BB Q20 Keyboard USB – USB-C programming […]
$25 Renesas “HMI Board” features RA6M3 microcontroller for RT-Thread & LVGL development
The Renesas HMI board is a Renesas RA6M3 Cortex-M4F development board with a 4.3-inch LCD developed in collaboration with the teams behind the RT-Thread RTOS project and LVGL open-source graphics library. Besides a color display for HMI (Human Machine Interface), the board also features a microSD card for data storage, Ethernet and WiFi connectivity, Arduino headers and PMOD connectors for expansion, a microphone and a speaker, a CAN bus terminal block, and two USB-C ports for debugging and power. Renesas HMI board specifications: MCU – Renesas RA6M3 (R7FA6M3AH3CFB) Arm Cortex-M4F microcontroller @ 120MHz with 2MB Flash, 640KB RAM, TFT controller, 2D accelerator, and JPEG decoder. Storage – MicroSD card slot Display – 4.3-inch LCD (RGB 888) Audio – Microphone and speaker Networking Low-profile 10/100M Ethernet RJ45 port RW007 SPI WiFi module by Shanghai Ruiside Electronic Technology USB – 2x USB Type-C ports Serial – 2-pin CAN bus terminal block Expansion […]