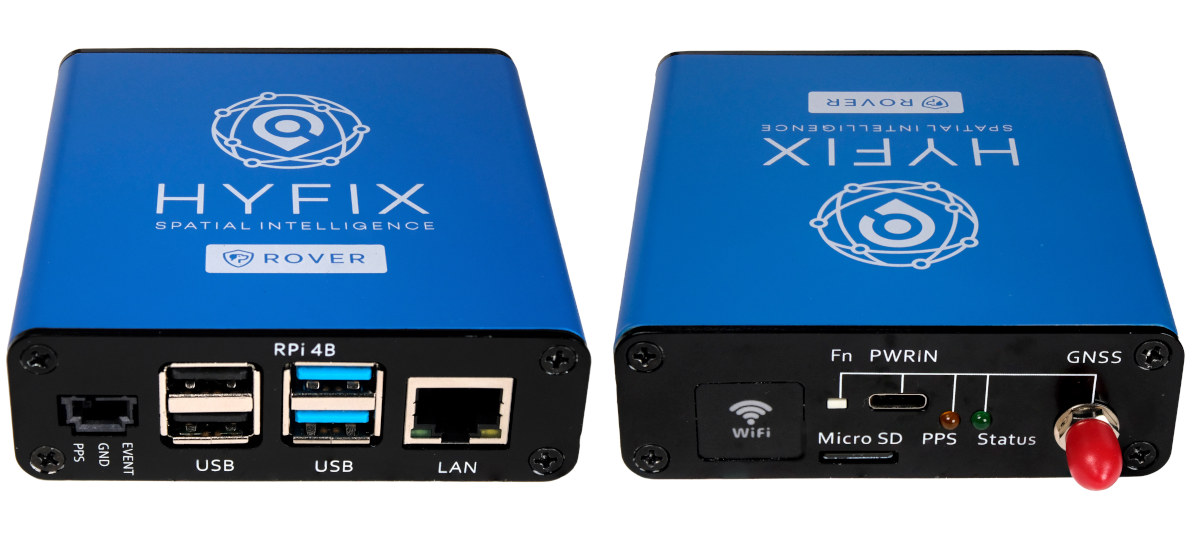
HYFIX’s RTK Rover is an affordable, centimeter-accurate RTK (Real-time Kinematic) GNSS receiver with either a USB interface or/and Ethernet connectivity with the latter relying on a Raspberry Pi 4 SBC. As a reminder, RTK relies on traditional GNSS networks like GPS and works with a Base station at a fixed location and a Rover station that can be fitted to a drone or mobile robot in order to determine the position with up to one-centimeter accuracy. The RTK Rover from HYFIX is equipped with a dual-band LC29H GNSS module from Quectel and an onboard IMU sensor that tracks position through dead reckoning when GNSS connectivity is lost. RTK Rover specifications: MiniPCIe card with Dual-Band L1/L5 RTK Receiver (Quectel LC29H) Antenna – External antenna (6x5x2 cm) connected to SMA connector Sensor – IMU Interfaces USB Type-C port for power and serial Interface Ethernet Rover Kit only – Gigabit Ethernet and USB ports […]
UniHiker review – A Linux-based STEM education platform with IoT and AI support, Micro:bit edge connector
DFRobot’s UniHiker is a STEM educational platform that was originally launched in China, but now UniHiker is now available worldwide through the DFRobot shop. The company has sent us a UniHiker sample for review, so let’s unpack the kit and learn how to use the UniHiker platform. The main component of the kit is the Linux-powered UniHiker board which features a 2.8-inch resistive touchscreen display and a BBC Micro:bit edge connector, so we can use expansion boards for the Micro:bit board. Let’s start unboxing it together. UniHiker unboxing DFRobot sent us the UniHiker platform by DHL. The package is a familiar-looking DFRobot box in orange color and comes with a plastic box to safely store the UniHiker board and accessories after use. The plastic box contains another plastic box with the board, some 3-pin and 4-pin cables for Gravity ports, and a USB Type-C cable. The UniHiker is like a […]
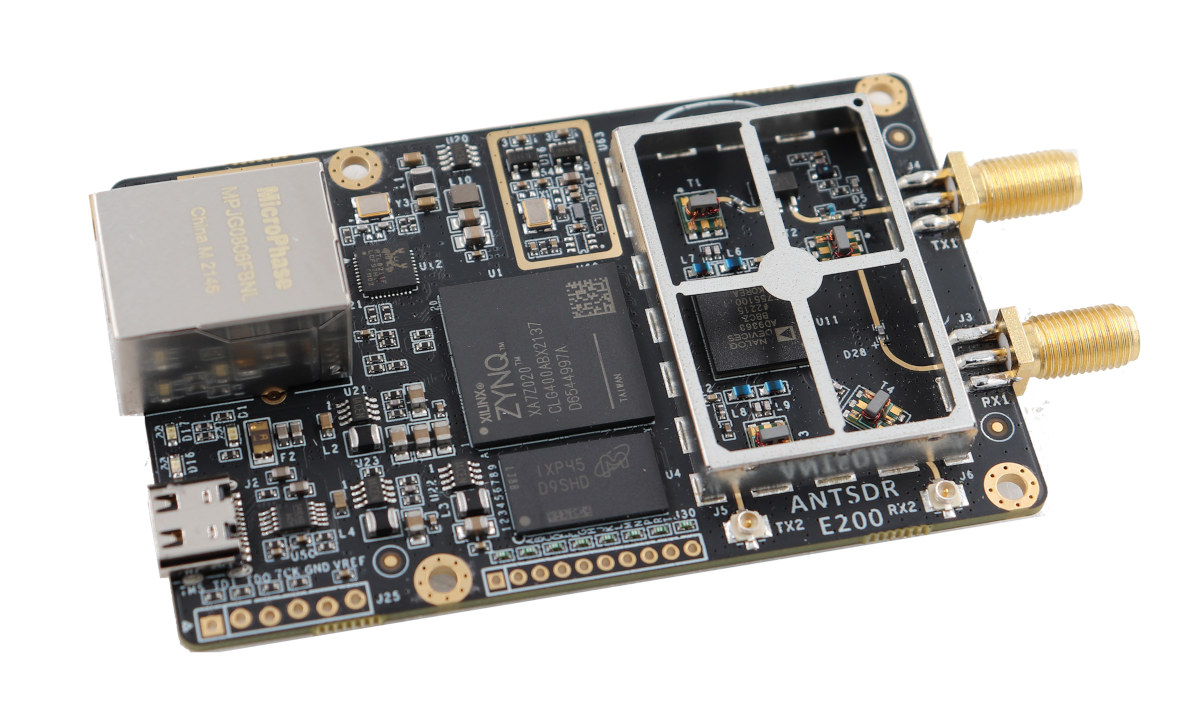
AntSDR E200 – Gigabit Ethernet connected SDR with Xilinx Zynq SoC FPGA supports 70 MHz – 6 GHz range (Crowdfunding)
We’ve just written about the uSDR M.2 SDR module on Crowd Supply, but it turns out the crowdfunding platform is hosting another SDR (Software-Defined Radio) project with the AntSDR E200 board equipped with an AMD Embedded Zynq 7020 SoC FPGA and an Analog Devices AD9363 or AD9361 RF chipset, and providing Gigabit Ethernet connectivity to the host. The board can operate in the 70 MHz – 6 GHz range with the AD9361 chipset, and the 325 MHz – 3.8 GHz range with the AD9363, supports 2×2 MIMO with two SMA antenna connectors and two U.FL connectors, and also features expansion interfaces for GPIOs. AntSDR E200 specifications: SoC FPGA – AMD Embedded/Xilinx Zynq 7020 dual-core Arm Cortex-A9 processor and FPGA with 85K logic cells, 4.9Mb Block RAM, 220 DSP slices System Memory – 512MB DDR3 Storage – 256 Mbit QSPI flash for firmware; microSD card slot (bottom side) RF Chipset – […]
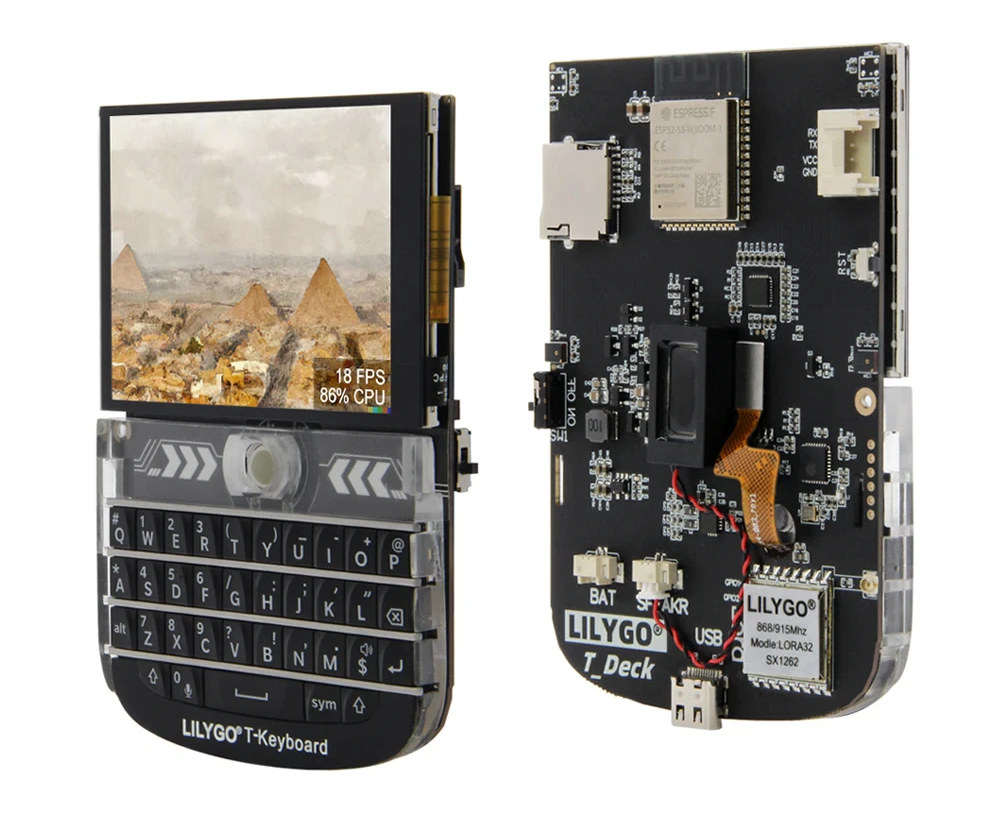
ESP32-S3 board features 2.8-inch display, Blackberry-like keyboard, and optional LoRaWAN connectivity
LILYGO T-Deck is a development kit with an ESP32-S3 WiFi and BLE module, a 2.8-inch display with touchscreen support, a Blackberry-like keyboard based on ESP32-S3, and optional LoRaWAN connectivity through an SX1262 LoRa module. It looks ideal for text-based messaging, but the devkit also includes two microphones and a speaker so audio communication must be possible. Other features include a MicroSD card slot, a Grove connector (UART) for expansion, and support for a LiPo battery with USB charging. LILYGO T-Deck specifications: ESP32-S3-WROOM-1 wireless module SoC – ESP32-S3FN16R8 dual-core Tensilica LX7 microcontroller @ up to 240 MHz with 2.4 GHz 802.11n WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5.0 LE connectivity Memory – 8MB PSRAM Storage – 16MB SPI flash PCB antenna Storage – MicroSD card slot Display – 2.8-inch IPS display with 320×240 resolution; ST7789 SPI display controller Audio – Built-in speaker using MAX98357A amplifier, 2x MEMS microphones Wireless 2.4 GHz 802.11n WiFi […]
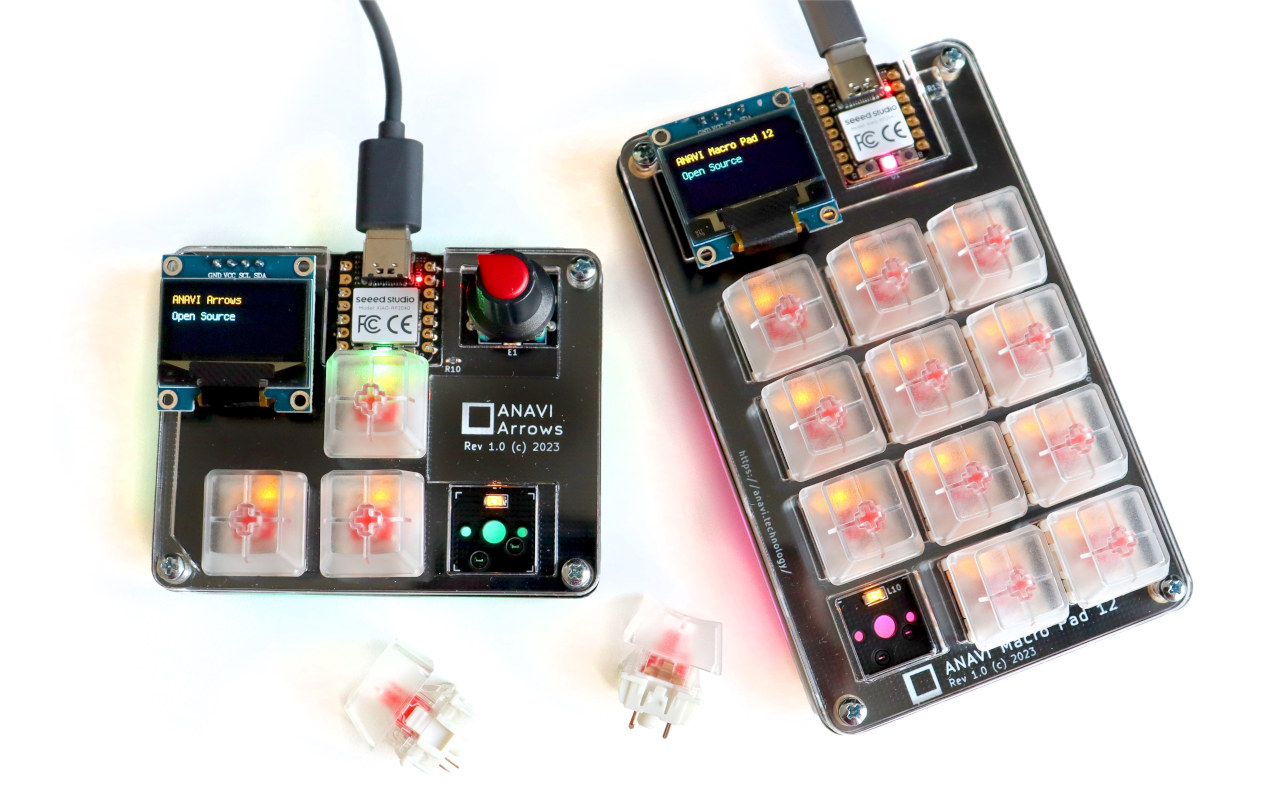
ANAVI launches CircuitPython-programmable Macro Pad 12 & Arrows mechanical keyboards (Crowdfunding)
ANAVI Technology has launched two more open-source hardware mechanical keyboards based on the Raspberry Pi RP2040 microcontroller, equipped with an OLED display, and programmable with CircuitPython: the ANAVI Macro Pad 12 with 12 keys and the ANAVI Arrows with four keys and a rotatory encoder. The new mechanical keyboards follow ANAVI Macro Pad 10 & Knobs input devices equipped with the same Seeed Studio XIAO RP2040 MCU module running the KMK firmware written with CircuitPython, but with different form factors and features. ANAVI Macro Pad 12 specifications: MCU module – Seeed Studio XIAO RP2040 with Raspberry Pi RP2040 dual-core Cortex-M0+ microcontroller @ up to 133 Mhz with 264KB SRAM, 2MB SPI flash, USB Type-C port Keys – 12x Gateron red, linear, non-clicky mechanical switches and transparent keycaps with yellow LED backlighting Display – OLED display connected to I2C slot (can be replaced with another I2C module) Host interface – USB […]
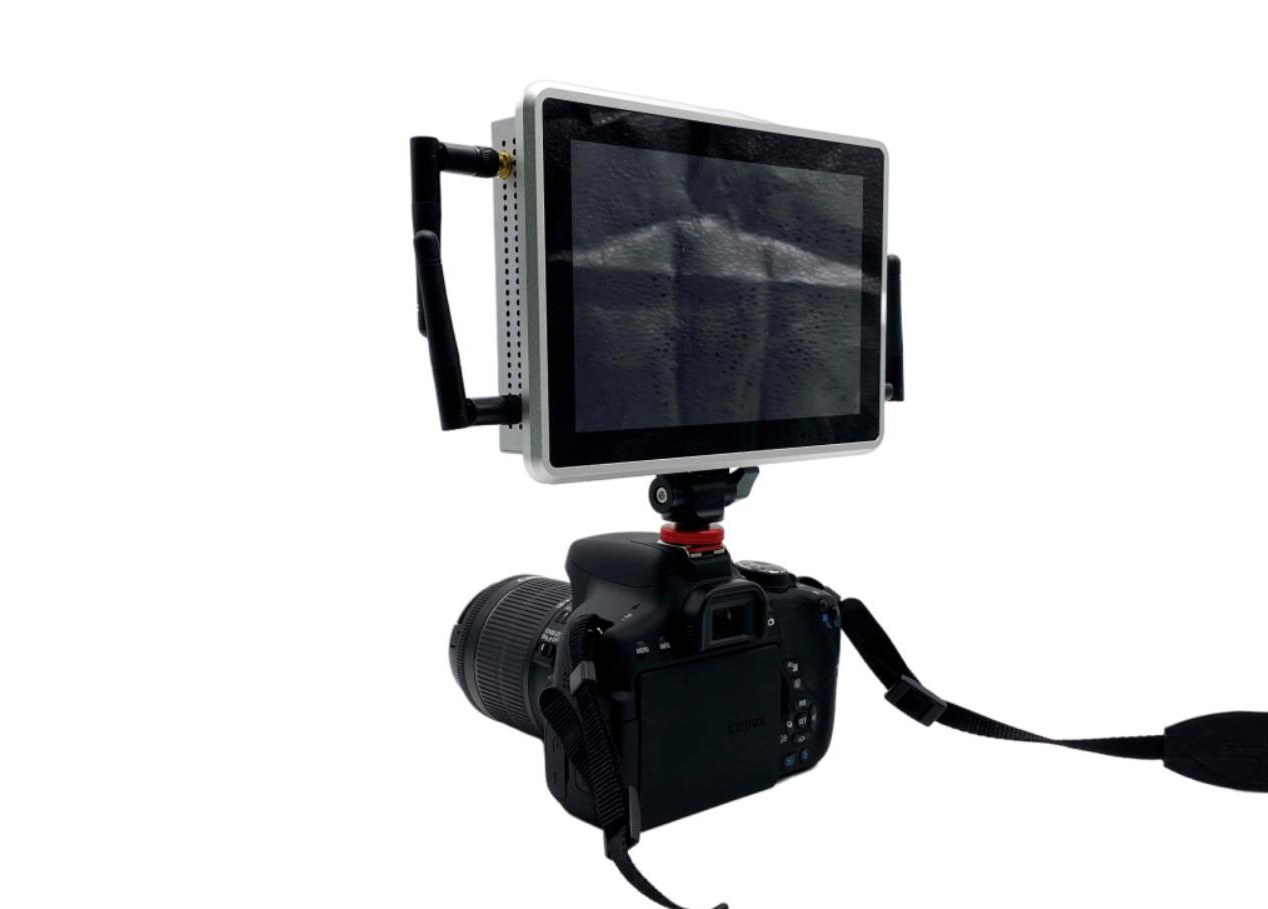
Mekotronics A58 – A 7-inch display with Rockchip RK3588 SoC and a DSLR camera mount for live streaming
Mekotronics A58 7-inch smart display is powered by a Rockchip RK3588 SoC with up to 16GB RAM and 128GB eMMC flash, and ships with a DSLR camera mount to enable video broadcasting and live streaming on social platforms. In the past, we’ve covered several Rockchip RK3588-powered Arm mini PCs by Mekotronics such as the R58, R58X, and more recently the R58X-Pro and R58X-HDD models, but the company has now leveraged its experience with the platform by launching a 7-inch smart display that can be used for live-streaming, but as we’ll see from the specifications below can also find many other uses. Mekotronics A58 specifications: SoC – Rockchip RK3588 octa-core processor with four Cortex-A76 cores @ 2.4 GHz, four Cortex-A55 cores @ 1.8 GHz, an Arm Mali-G610 MP4 GPU, a 6TOPS NPU, 8K 10-bit decoder, 8K encoder System Memory – 4GB, 8GB, or 16GB LPDDR4X Storage 32GB, 64GB, or 128GB eMMC […]
PiccoloBASIC – A BASIC interpreter for the Raspberry Pi Pico board
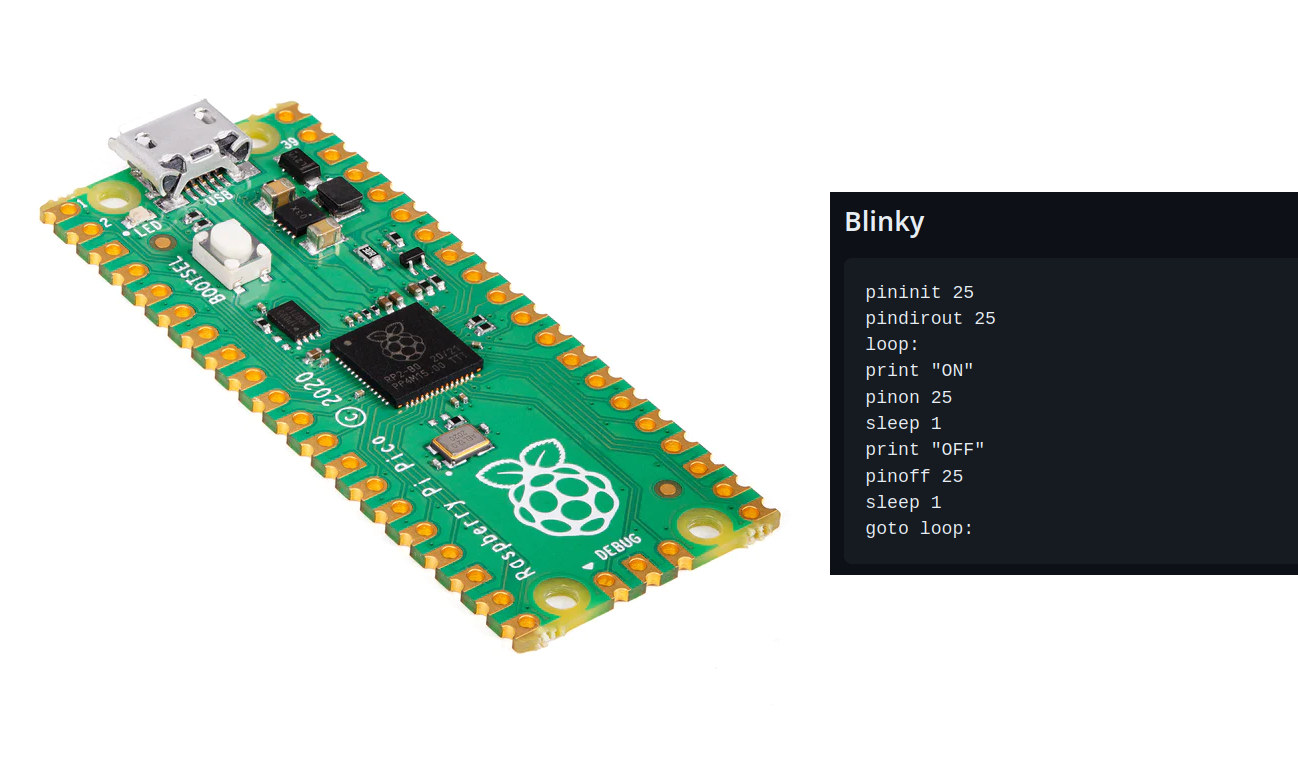
PiccoloBASIC is an open-source BASIC interpreter for the Raspberry Pi Pico development board that’s based on “uBASIC: a really simple BASIC interpreter” by Adam Dunkels and relying on Arm’s LittleFS fail-safe filesystem for microcontrollers. If my memory serves me well, my first computing experience was at school using a Thomson TO7 computer that we programmed with BASIC. I don’t think the language is still used in practical applications, but we can still see some BASIC projects pop up from time to time such as a BASIC interpreter for the Arduino Zero boards. Gary Sims, owner of the Gary Explains YouTube channel, has now ported a BASIC interpreter to the Raspberry Pi Pico. The project is still work in progress, but currently implemented features include: Let, if, print, for, goto, gosub String variables (let z$=”hello”) Floating point numbers and variables (let z#=1.234) Builtin functions [zero, randint, not, time] Sleep, delay, […]
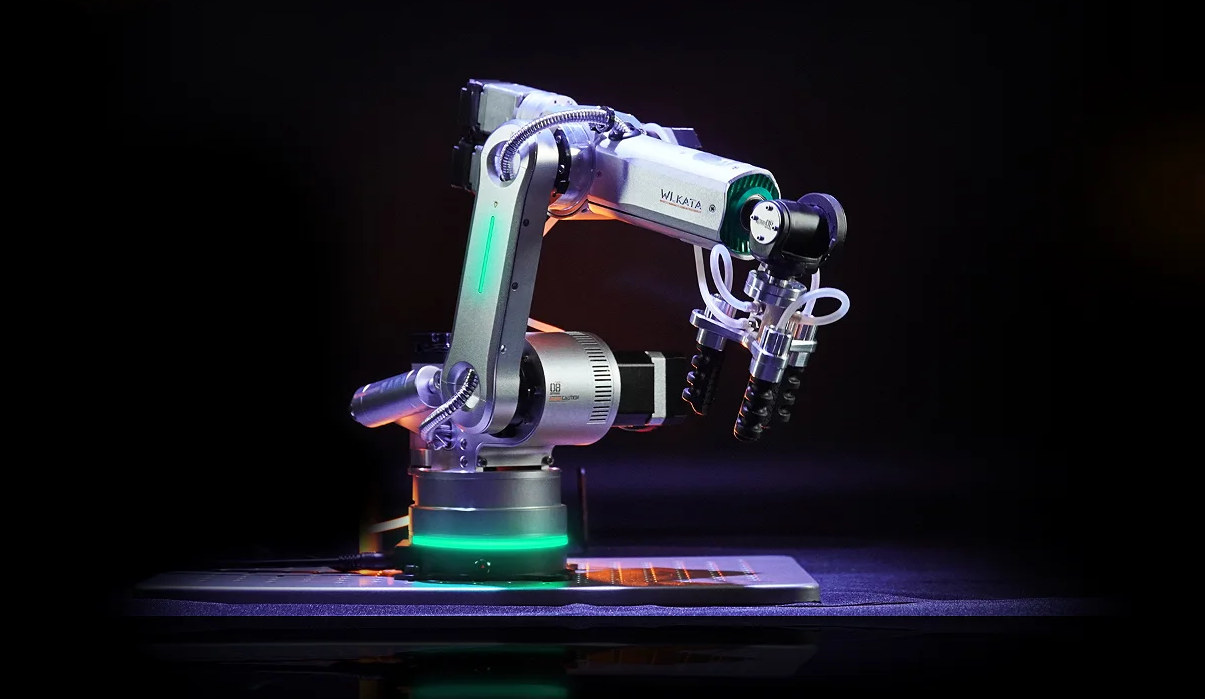
WLKATA Robotics Haro380 is a high precision industrial 6-Axis mini robotic arm (Crowdfunding)
WLKATA Robotics’ Haro380 is a high-precision industrial 6-axis mini robotic arm that can carry a payload of up to 500 grams and designed for education, engineering projects, and light manufacturing. We’ve covered some desktop robotic arms in the past such as the myCobot 280 Pi, but the HARO380 goes a step further with 0.05mm repeatability, a 6-axis harmonic reducer, and zero backlash. It is an upgraded version of the company’s entry-level Mirobot robotic arm introduced in 2019. Haro380 specifications and key features: Control board Unnamed MCU Base interface – RS485, DC power, expansion interface, USB interface I/Os – 2x digital inputs, 2x digital outputs Emergency switch Supply voltage – 24V DC Temperature Range – 5 to 40°C Humidity – 20 to 75% RH non-condensing 6-axis harmonic reducer Magnetic end effectors Repeatability – +/- 0.05 mm Max payload – 500 grams Reach – 380 mm Control interfaces – USB to serial, […]