I’ve recently come across an interesting and amusing story entitled “Boost Your WiFi Signal Using Only a Beer Can” on discovery channel website. I’ve said to myself that I’ve got to try with my WiFi router. The interesting part is that my WiFi router (TP-LINK TL-WR940N) has 3 antennas, so I had to diligently drink three beer cans (LEO brand, the best local beer in Thailand). Once this was done, I had all that I needed, besides a pair of scissors, a utility knife and some double faced tape. The next step was to clean the beer cans, let them dry and cut the bottom and top of the beer cans as described on discover channel blog post. There is no dotted red line on LEO beer cans, but there are yellow horizontal lines that make this can perfect for the job. After less than 5 minutes of hard work, […]
Best Practices for Writing Safer C Code
Thomas Honold wrote an article published on EETimes giving 17 steps to safer C code. Not only this article provides tips to write safer C code, but I believe those steps are simply best practices when writing C code for embedded systems as they shorten the software life cycle by making it easier for a software team to write, debug and maintain code and by improving the software QA procedure. Here’s a summary of the 17 steps to achieve safer C code: Follow the rules you’ve read a hundred times: Initialize variables before use. Do not ignore compiler warnings. Check return values. Use enums as error types. Define an ENUM_MAX value at the end, so that the code to check the range does not have to be modified each time you add a new error code. Expect to fail Always assume there will be an error and set to default […]
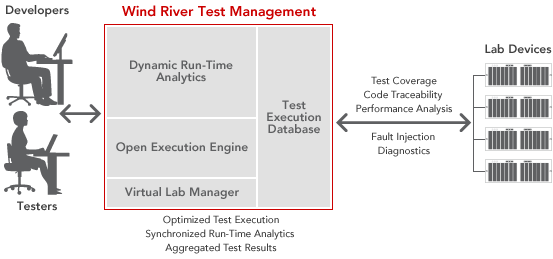
Embedded Linux QA with Wind River Test Management 4.0
Wind River has just announced the release of Winder River Test Management 4.0, a test suite specialized in testing embedded devices and allowing the test teams to optimize the testing effort by focusing resources on high-risk areas and deliver a high-quality embedded software solution on time. New Features and Enhancements New preconfigured test suite generators: The following new test suite generation methods are available: Create a test suite based on coverage and execution time: Selects test case instances that will generate the maximum coverage given a fixed time constraint . Create a test suite based on execution results: Selects test case instances that have run with specific final status values. Create a test suite based on requirements: Selects test case instances that are associated with specific requirement records to ensure that all requirements have a test associated with them and are thoroughly tested. Create a test suite based on defect […]
Bootloader to OS with Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a specification detailing an interface that helps hand off control of the system for the pre-boot environment (i.e.: after the system is powered on, but before the operating system starts) to an operating system, such as Windows or Linux. UEFI aims to provides a clean interface between operating systems and platform firmware at boot time, and supports an architecture-independent mechanism for initializing add-in cards. UEFI will overtime replace vendor-specific BIOS. It also allows for fast boot and support for large hard drives (> 2.2 TB). There are several documents fully defining the UEFI Specification, API and testing requirements: The UEFI Specification (version 2.3.1) describes an interface between the operating system (OS) and the platform firmware. It describes the requirements for the following components, services and protocols: Boot Manager Protocols – Compression Algorithm Specification EFI System Table Protocols – ACPI Protocols GUID Partition Table (GPT) […]
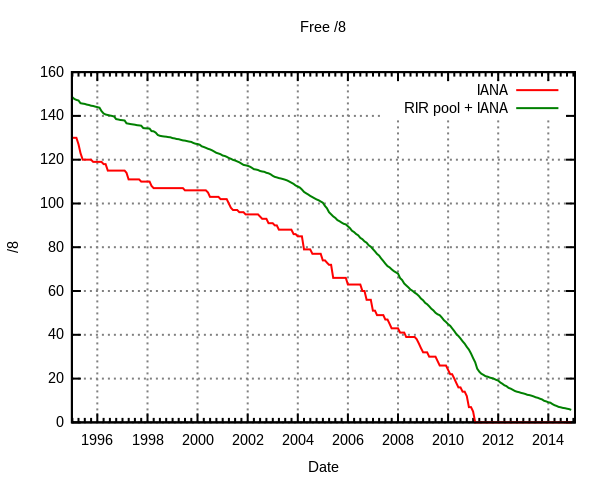
Is it IPv6 Time ? IPv6 Basics on Linux
The first time I worked on IPv6 was in 2000 in my master’s degree thesis where I started an implementation of Mobile IP based on IPv6 in Linux Redhat. Over a decade later, IPv6 has not really taken off, even though we hear stories about the IPv4 address space running out and I have yet to see an embedded device using anything else than IPv4. APNIC Ran out of IPv4 However, this may be about the change as on the 15th of April 2011, Japan Network Information Center (JPNIC) announced that APNIC (Asia Pacific Network Information Centre) ran out of IPv4 addresses. They will still try to make it last longer by reusing previously allocated IPv4 and an “IPv4 address transfer system” whose details will be made available later. You can also see a chart based on IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) data that shows this is a problem right […]
Boot Linux in 300 milliseconds
MakeLinux.com managed to boot Linux from the bootloader to console within 300ms using a customized (and minimal) version of Linux running on Beagleboard based on TI OMAP 3530 (Cortex A8) as per their Super Fast Boot project. Here’s the analysis of the boot sequence and timings: Logging starts at 70 ms from reset. Boot time from reset is 300 + 70 = 370 ms. Logging starts at 330 ms from power on. Cold boot time is 330 + 300 = 630 ms. Loading of 1.5 MiB Linux image from NAND takes 237 ms with throughput 6 MiB/s. Code execution takes 60 ms or 43M CPU cycles. (For other CPU frequency execution time is different, but the number of processor cycles is the same) The most time-consuming operation is coping firmware from NAND flash. They used a Linux 2.6.32 kernel from DVSDK 3.01, in a minimal configuration (900KB footprint), the boot […]
Setting Up an NFS Server in Ubuntu
You may need to setup an NFS server on Ubuntu to run and debug your program on your target platform or simply to share media files on the network composed of Linux clients. If you are using Windows clients, you would usually use SAMBA/CIFS, although it is possible to setup an NFS server in Windows as well using Windows Services for UNIX 3.5. Quick Guide to to setup an NFS server in Ubuntu without authentication. Install the required packages: # sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server nfs-common portmap Reconfigure and restart portmap: # sudo dpkg-reconfigure portmap # sudo /etc/init.d/portmap restart Edit /etc/exports: # sudo vi /etc/exports Add the directories to share with NFS and save the file, for example: /nfs 192.168.1.0/24(rw,no_root_squash,async) will give full read/write permissions to the nfs directory for computer in 192.168.1.0 subnet. Restart the NFS server: # sudo /etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server restart and reload the configuration: # sudo exportfs -a The […]
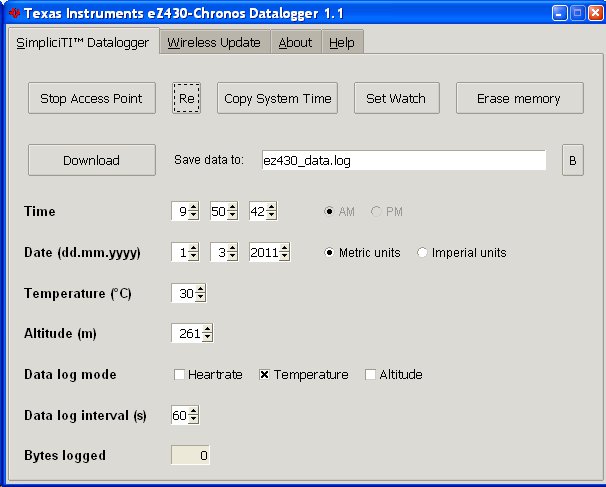
Temperature Data Logging with TI eZ430-Chronos Watch
I wanted to record 24-hour of temperature data with eZ430-Chronos devkit and draw the result in a spreadsheet to see how the temperature evolves during the day. Here are the instructions to do so. 1. Update firmware to Chronos Datalogger. In order to record temperature data in your eZ430-Chronos development kit, you’ll need to update the firmware to use Chronos Datalogger. First start the Chronos Control Center, click on the Wireless Update tab, click on browse to select the Chronos Datalogger firmware file matching your hardware. In my case, I selected C:\Program Files\Texas Instruments\eZ430-Chronos\Recovery\Chronos Watch\Applications\eZ430_Chronos_Datalogger_433MHz_1_5.txt. Then click on Update Chronos Watch. On the watch, press the # button several time to enter rFbSl mode and press the down button to start the wireless update. 2. Configure the watch for temperature logging. Now start Chronos Data Logger software, click on Start Access Point. On your watch, press the # button to […]