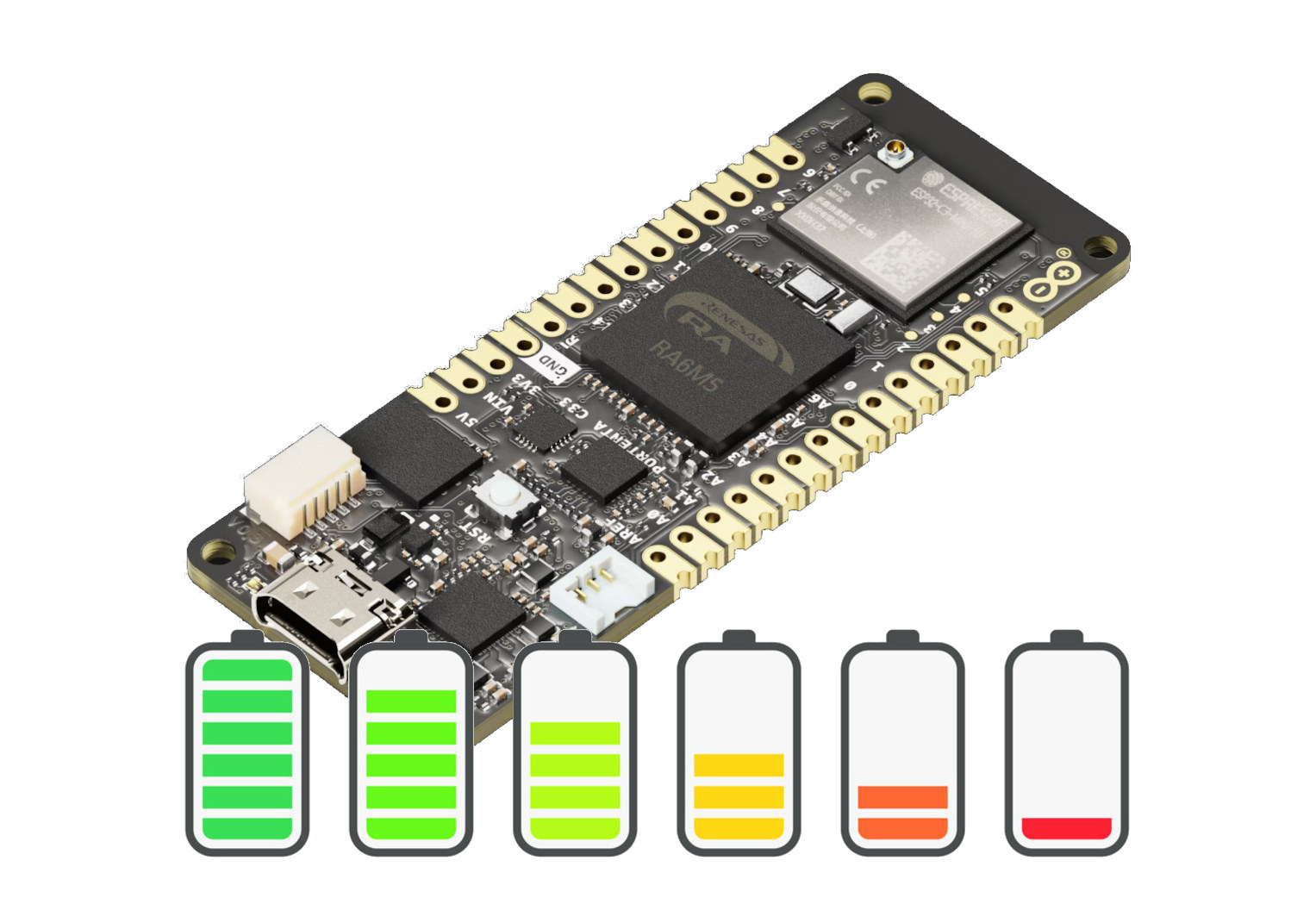
Arduino has released a new power management library designed for Arduino Pro modules to help users monitor battery usage, fine-tune charging parameters, and optimize the power consumption of their Arduino code by notably enabling sleep and standby modes on supported devices. Currently, the Arduino Portenta H7 boards, the Arduino Portenta C33, and the Nicla Vision module are supported by the new power management library. The company explains some boards consume under 100 microamperes in deep sleep mode enabling months or even years of continuous runtime on a single charge, so making use of those features is important to lower the power consumption of battery-powered IoT devices and wearables. Arduino power management library key features: Battery monitoring – Reports battery metrics such as voltage, current, percentage, and temperature. Battery health tracking – Monitors battery health with detailed insights into temperature and reported capacity. Charging control – Monitors and adjusts charging parameters […]
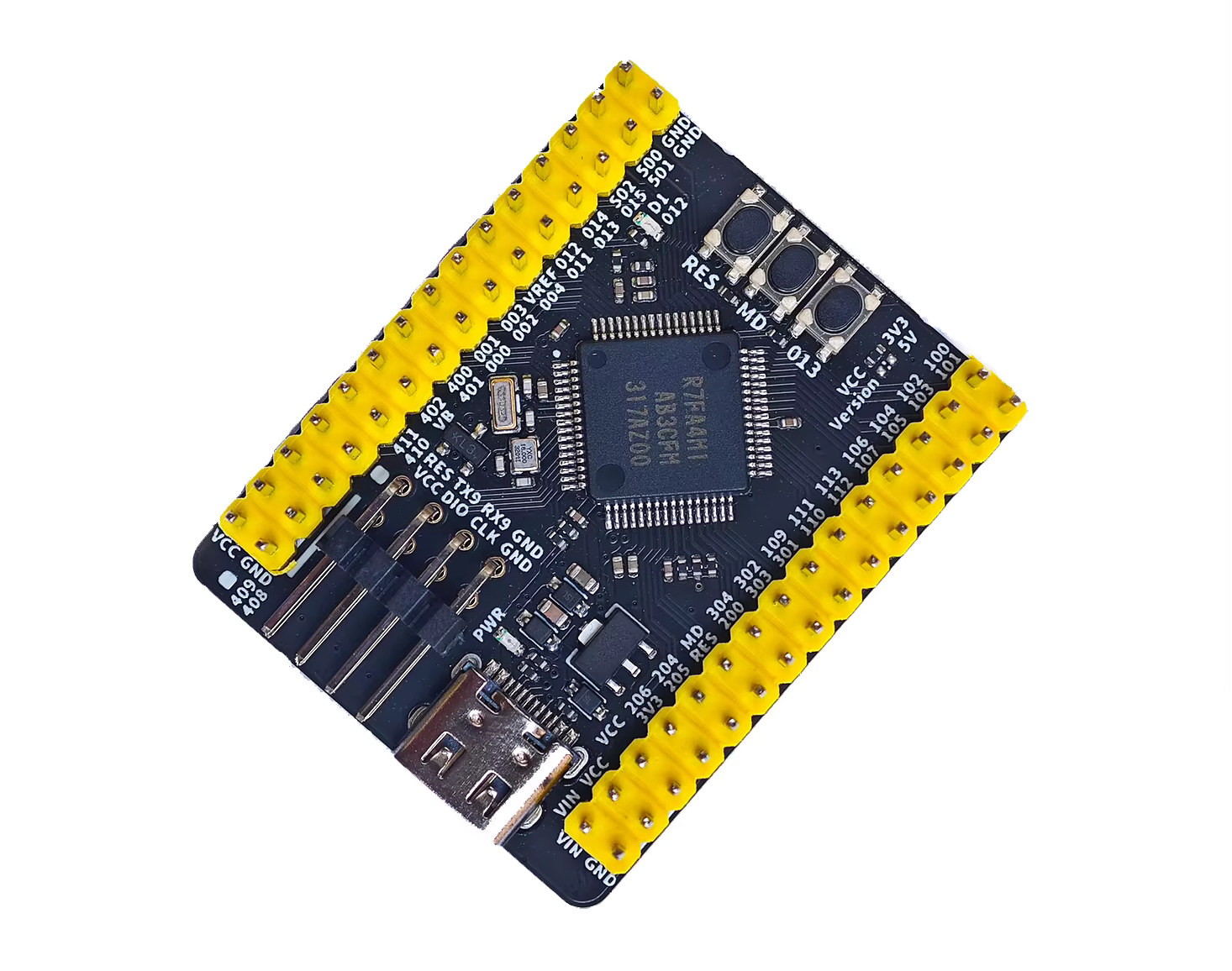
WeAct RA4M1 – A small board with plenty of GPIOs that’s software-compatible with the Arduino UNO R4
Last week, we covered the Maker Go RA4M1-R4 development board, an inexpensive “clone” of the Arduino UNO R4 Minima with some small modifications like support for up to 50V DC input and a 3.3V/5V switch for I/Os. But today, I’ve come across a smaller and cheaper Renesas RA4M1 board that’s also software compatible with the Arduino UNO R4. Meet the WeAct RA4M1. The WeAct RA4M1 is mostly a breakout board for the Renesas R7FA4M1AB3CFM Arm Cortex-M4F microcontroller with two 30-pin GPIO headers, a USB-C port for power and programming, and three buttons. It offers a middle ground between the Arduino UNO R4 Minima and the tiny XIAO RA4M1 USB-C board. WeAct RA4M1 specifications: Microcontroller – Renesas RA4M1 Arm Cortex-M4F MCU @ 48 MHz with 32KB SRAM, 256KB flash USB – 1x USB Type-C port for power and programming Expansion 2x 30-pin headers with GPIO, VIN, VCC, GND 3.3V or 5V […]
Maker Go RA4M1-R4 core board is a cheap Arduino UNO R4 Minima clone taking up to 50V DC input
The Maker Go RA4M1-R4 core board is another Arduino UNO R4 Minima clone but offered at a price point much lower than the original and the Waveshare R7FA4 Plus A (another clone) since it shows up for only $0.99 on AliExpress with free shipping. Note that the ultra-low price is because of a “Welcome deal” on AliExpress, and the regular price is $7.76, so not everyone may get it for $1. About $8 is still cheap compared to the $20 (18 Euros) asked for the official Arduino UNO R4 Minima board. Let’s look at the clone in more detail to find out if they’ve made any changes to the board. Maker Go RA4M1-R4 core board specifications: Microcontroller – Renesas RA4M1 Arm Cortex-M4F MCU @ 48 MHz with 32KB SRAM, 256KB flash USB – 1 x USB Type-C port for power and programming Expansions – Arduino UNO female + male headers […]
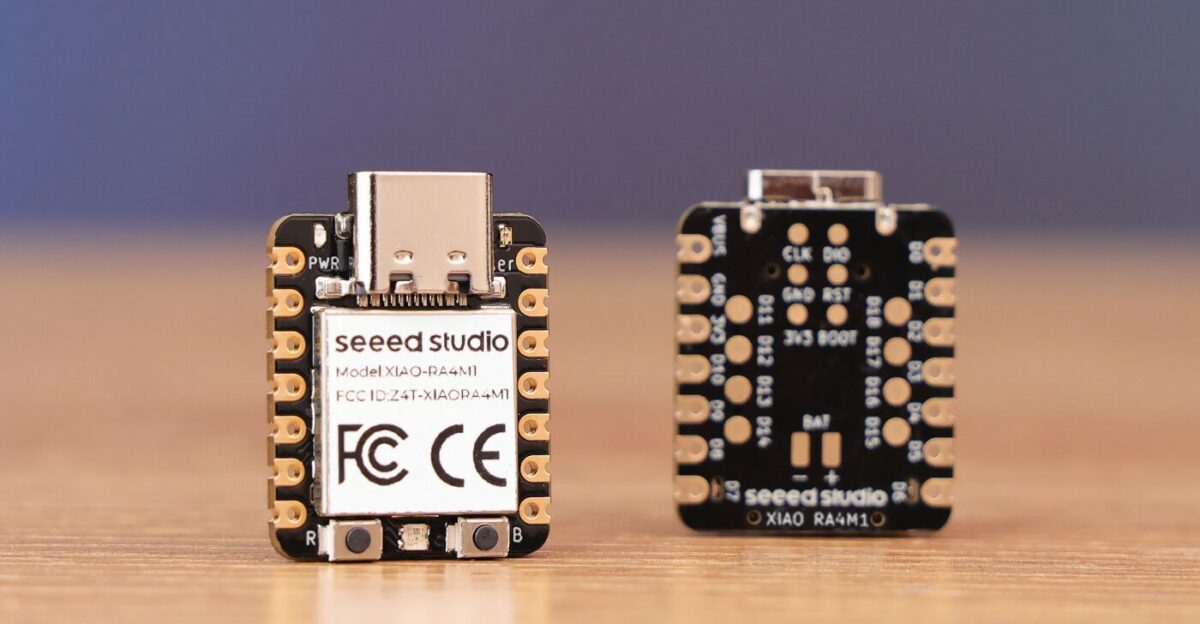
XIAO RA4M1 stamp-sized Renesas RA4M1 USB-C board features 14-bit ADC, 12-bit DAC, CAN Bus interfaces
Seeed Studio has added yet another member to their XIAO board family with the XIAO RA4M1 powered by Renesas’ RA4M1 32-bit Arm Cortex-M4 MCU. This compact board includes 256KB Flash, 32KB SRAM, a 14-bit A/D converter, a 12-bit D/A converter, a CAN bus interface, and onboard charging circuitry. It’s designed for low-power, battery-powered applications. The company started the XIAO family with the Seeeduino XIAO (Microchip SAMD21G18) in 2020, and since then they’ve made several other variants with different processors including the XIAO RP2350, XIAO RP2040, XIAO ESP32C3, XIAO ESP32S3, XIAO ESP32C6, and the nRF52840-based XIAO BLE. Feel free to check them out if you are interested in these boards. XIAO RA4M1 specifications: Microcontroller – Renesas RA4M1 (R7FA4M1AB3CFM) as found in Arduino UNO R4 CPU – Arm Cortex-M4F operating at up to 48 MHz Memory – 32KB SRAM Storage 256 KB code flash memory 8 KB data flash memory USB – 1x […]
Arduino to switch from Arm Mbed to Zephyr RTOS
Following Arm’s decision to stop supporting Mbed from July 2026 onwards, Arduino has now decided to use Zephyr RTOS instead of Arm Mbed for Arduino boards that rely on the latter including Arduino GIGA, Arduino Nano 33 BLE, Arduino Nano RP2040 Connect, as well as Arduino PRO boards/solutions such as the Portenta, Nicla, and Opta families. Note that Arduino UNO, MKR, and Nano families are not impacted by the change since their Arduino Core implementation does not rely on Mbed. The change is not going to happen overnight as software development takes time, and Arduino plans to release the first beta based on ZephyrOS by the end of 2024. and a rollout for various boards starting in 2025 long before Arm Mbed is phased out for good. Arduino is not new to the Zephyr project as the company became a Silver member last year, and they were aware that Arm […]
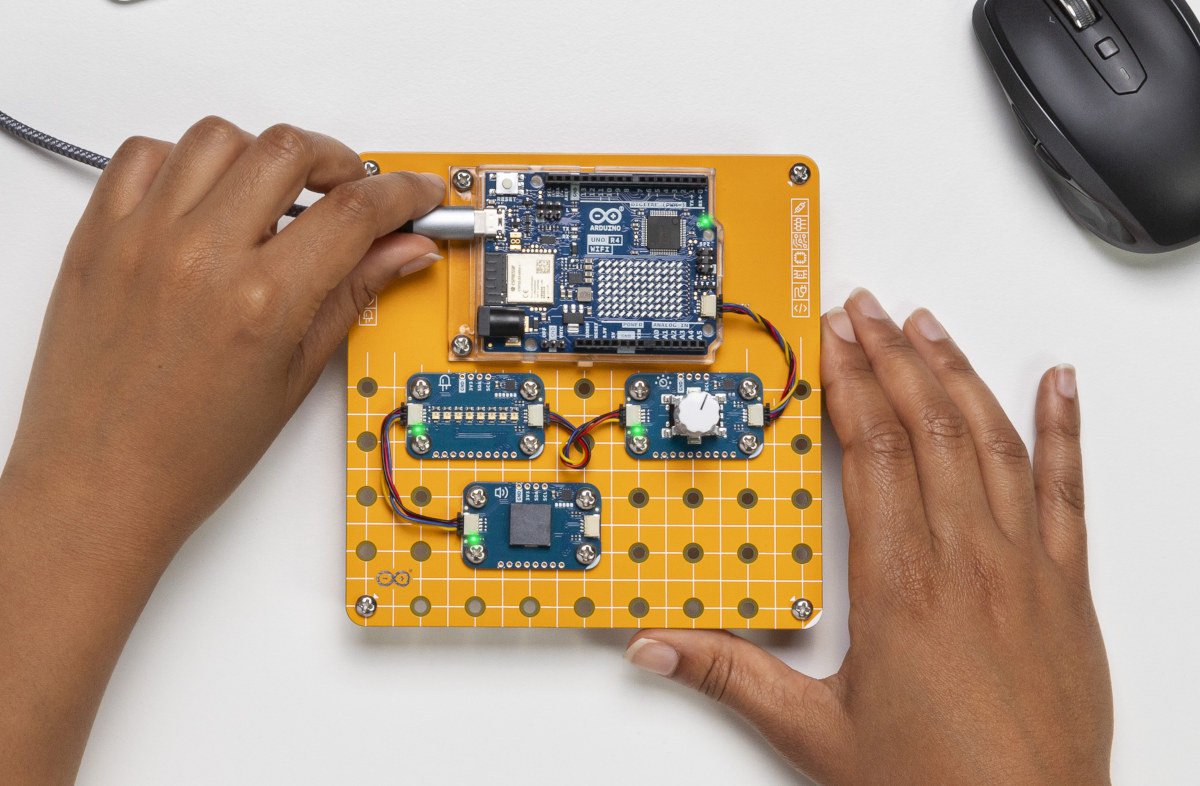
Beginner friendly Arduino Plug and Make Kit features Arduino UNO R4 WiFi and Modulino I2C modules
Arduino has just launched a “Plug and Make” kit designed for beginners with an Arduino UNO R4 WiFi board, several “Modulino” modules, a “Modulino” base to neatly attach the UNO R4 and modules, and various cables, spacers, screws, and nuts. When thinking about Arduino projects, breadboards or even soldering may come to mind, but the new Arduino Plug and Make Kit does not require any of those. No breadboard, jumper wires, or soldering needed. Users can simply connect the modules to the Arduino board through Qwiic cables, neatly attach everything together on the provided base, and follow one of the seven projects complete with step-by-step instructions provided with the kit. The Arduino Plug and Make Kit content Arduino UNO R4 WiFi board 7x Modulino I2C nodes Modulino Knob* – Encoder for value adjustments Modulino Pixels* – 8x LC8822-2020 RGB LEDs Modulino Distance – STMicro VL53L4 Time-of-Flight (ToF) proximity sensor to […]
Renesas SLG7EVBFORGE FPGA dev board is built around ForgeFPGA SLG47910V low-density FPGA
Renesas SLG7EVBFORGE FPGA dev board, built around SLG47910V is Renesas’ first low-density FPGA in the ForgeFPGA family. The FPGA includes 1120 LUTs, 1120 flip-flops, 5kb of distributed memory, 32kb of block RAM, and a 50 MHz on-chip oscillator with a phase-locked loop (PLL). With robust features, low power consumption, and affordable pricing this FPGA can be used in applications in sensor data aggregation, consumer electronics, and portable computing devices. The SLG47910V FPGA gets connected to a ZIF socket to the development board, this design choice puts out a clear sign that upcoming Forge family FPGAs will support this dev board. Additionally, it features Pmod connectors and configurable power sources. The dev board can be programmed via OTP Non-Volatile Memory or SPI interface and additional features get managed through Renesas’ Go Configure Software Hub. Previously we have written about similar low-power low-cost FPGA boards like the Sipeed Tang Mega 138K, the […]
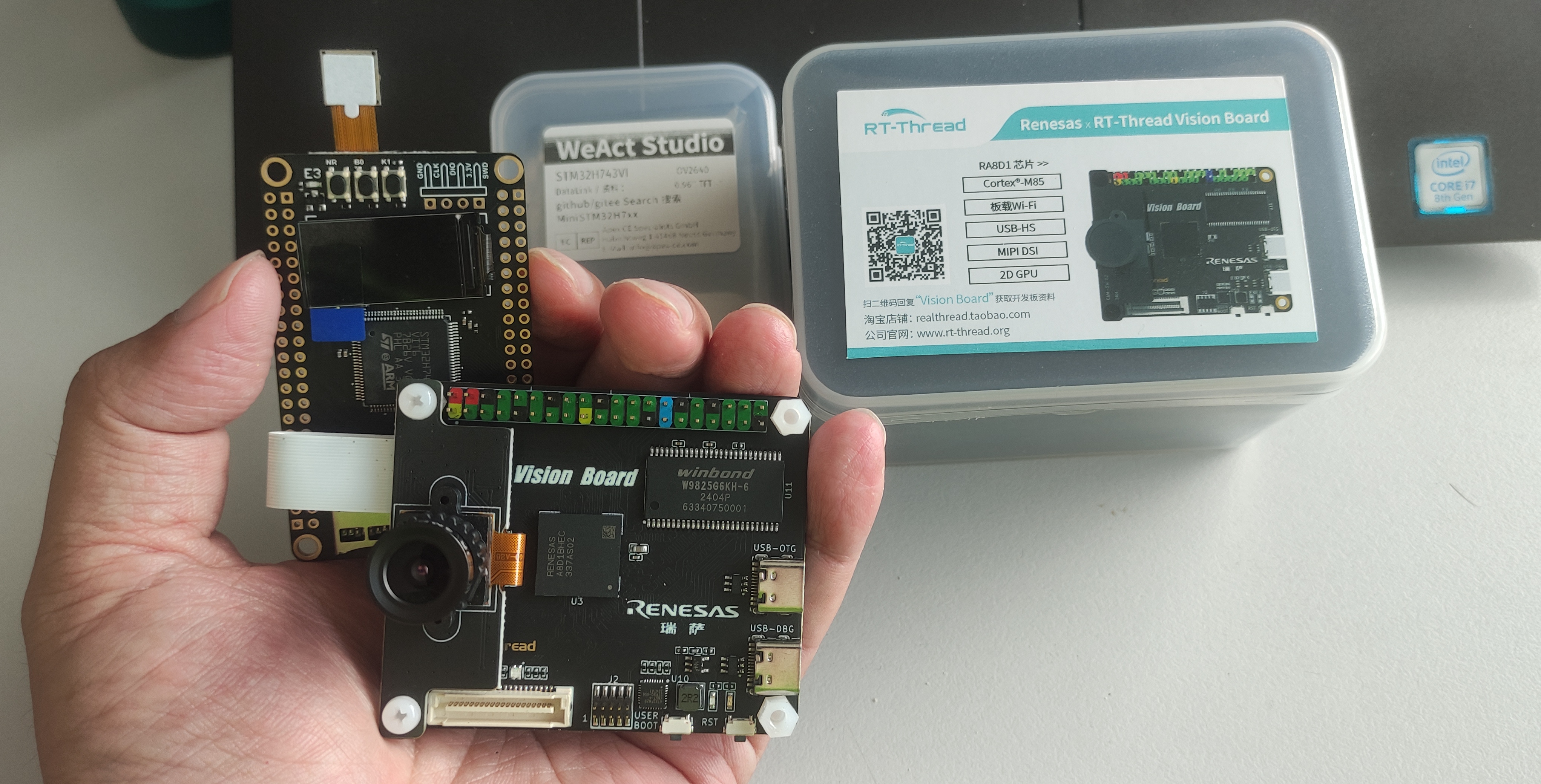
RT-Thread Vision board review – Part 1: OpenMV on Renesas RA8D1 Cortex-M85 microcontroller
I am always interested in real-time operating systems (RTOS) for microcontrollers (MCUs) with my past backgrounds in µC/OS-II, mbed, and FreeRTOS. When the opportunity arose to get my hands on the RT-Thread Vision Board, thanks to the RT-Thread team and CNX Software, I was excited to check it out. This board, a collaboration between RT-Thread and Renesas, packs a powerful Renesas RA8D1 Cortex-M85 MCU and comes pre-loaded with OpenMV firmware. OpenMV’s MicroPython engine lets you jump right into embedded vision development, perfect for experimenting with computer vision tasks. But the real power lies in RT-Thread’s ability to handle tasks very quickly, which we’ll explore with C/C++ development in part two. This first part will focus on getting you familiar with the hardware using the OpenMV firmware, making it a smooth entry point for beginners. Plus, I have a collection of other Renesas evaluation boards, so you can bet I’ll be […]