Atollic has just announced that Atollic TrueSTUDIO for ARM 3.0 – a C/C++ development tool for embedded developers – will be released on the 28th of February 2012, at Embedded World 2012, Nuremberg, Germany. Atollic TrueSTUDIO v3.0 will bring the following improvements: Redesigned user interface that is more intuitive to C/C++ developers New support for NXP LPC1000 Cortex-M0 and Cortex-M3 devices New support for Infineon XMC4000 Cortex-M4 devices New support for Energy Micro EFM32 (Cortex-M3) Upgraded support for STMicroelectronics STM32 devices Improved real-time interrupt tracing with ARM Serial Wire Viewer (SWV) interface. Execution time profiling now present information using bar charts Upgraded ECLIPSE platform to the latest “Indigo” release (3.7.1) Major upgrade of the GNU command line tools Upgraded TrueINSPECTOR, TrueANALYZER and TrueVERIFIER add-on products Supports over 800 ARM devices Hundreds of minor improvements Since the product has not been released, that’s currently all information there is. Further information will certainly […]
Raspberry Pi OpenGL and OpenMAX IL “Hello World!” Applications
As you may already know, Raspberry Pi has released their first SD card image with Debian. This morning, I explained how to use that image in qemu. I’ve been waiting for samples to take advantage of the power Videocore GPU inside Broadcom BCM2835 SoC used in the Raspberry Pi board and the goods news is that they added Hello World code samples in C to make use of those capabilities. The sample are located in /opt/vc/src/hello_pi directory: hello_audio – Audio output demo using OpenMAX IL through the ilcient helper library hello_triangle – A rotating cube rendered with OpenGL ES with 3 images used as textures on the cube faces. hello_video – Video decode demo using OpenMAX IL through the ilcient helper library You can either compile those samples in the board or cross-compile them in your host machine. Since you need the GPU, you will obviously not be able to […]
Debian is Worth a Lot (Yet it’s Free) and C/C++ Language Still Rules
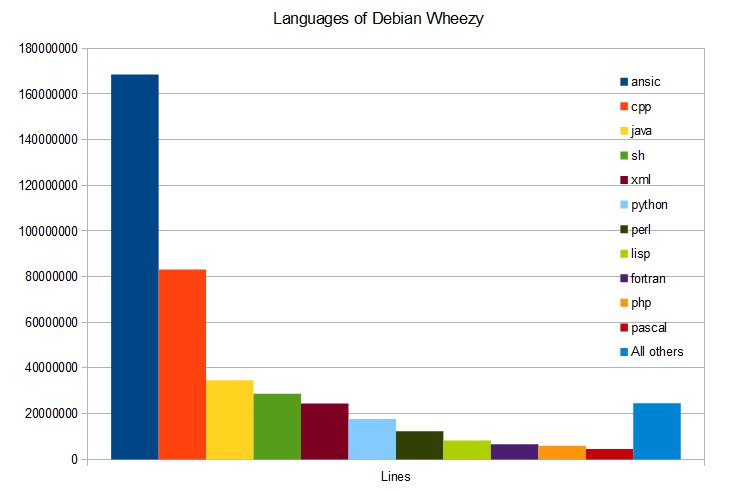
James E. Bromberger (JEB) , a contributor to Perl CPAN and Debian, has estimated the cost of developing Debian Wheezy (7.0) from scratch based on the the number of lines of code (LOC) counted with SLOCCount tool, the Constructive Cost Model (COCOMO) and the average wage of a developer of 72,533 USD (using median estimates from Salary.com and PayScale.com for 2011). He found 419,776,604 lines of code in 31 programming languages giving an estimated cost of producing Debian Wheezy in February 2012 of 19 billion US dollar (14.4 Billion Euros), making each package source code (out of the 17,141 packages) worth an average of 1,112,547.56 USD to produce. He also estimated the cost of Linux 3.1.8 Kernel with almost 10 millions lines of source code would be worth 540 million USD at standard complexity, or 1.877 billions USD when rated as ‘complex’. I don’t know which tool he used for […]
Microsoft Provides Windows 8 On ARM Technical Details
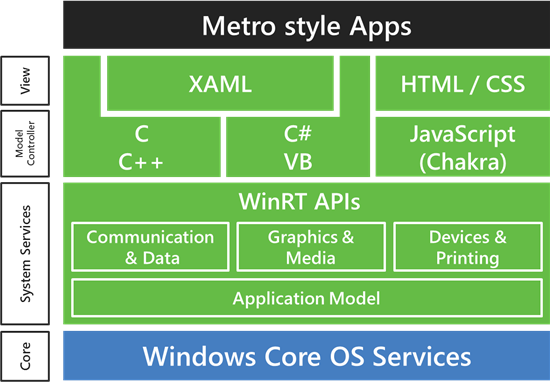
Steven Sinofsky, President of the Windows Division at Microsoft, has written a long blog post entitled “Building Windows for the ARM processor architecture” where he explains how Windows On ARM (WOA) will be deployed, the steps they took to develop it and what developers can do to program or port existing apps to Windows 8. Here are some keys and interesting points I noted: WOA and Windows 8 for x86/64 PCs will ship at the same time and the user experience should be the same for consumers on both platform. WOA PCs will be powered by Texas Instruments, Nvidia and Qualcomm processors. Microsoft will release an Unified OS Binary for WOA – That means one binary will run on all platforms (be it TI, Nvidia or Qualcomm). That seems impressive, and something Linux is not capable of, although much work is done on that and a unified linux kernel should […]
Yocto Project Quick Start Guide for Ubuntu
Yocto is an embedded Linux build system used to create a Linux distribution for a specific application/board combination. I’ll describe 2 methods to get started: Building and running a qemu image for x86 from scratch Using pre-built binaries to run the x86 image in qemu This is a shorter version of the longish Yocto Project’s Quick Start Guide. The official guide is more complete (explains all details) and give instructions for several distributions, whereas this guide simply lists each step and is focused on Ubuntu. So you could use this guide to start the build, and during the build (which will last a while), read the official guide to actually understand how it all works. Prerequisites First, you need to use bash instead of dash in Ubuntu:
|
1 |
sudo dpkg-reconfigure dash |
and select “No” to use bash. Then install the required packages with apt-get:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
sudo apt-get install sed wget cvs subversion git-core coreutils \ unzip texi2html texinfo libsdl1.2-dev docbook-utils gawk \ python-pysqlite2 diffstat help2man make gcc build-essential \ g++ desktop-file-utils chrpath libgl1-mesa-dev libglu1-mesa-dev \ mercurial autoconf automake groff libtool xterm |
Building and running a qemu image for […]
Opersys Releases Their Android and Linux Training Materials
Opersys has decided to release their courseware under a Creative Common license (CC-BY-SA 3.0). The materials are available in PDF and ODP format for the following classes: Embedded Android – 5-days hands-on class covering Android (AOSP) for Embedded Systems (not only smartphones and tablets) Presentation Slides: PDF | ODP Exercises: PDF | ODT Android App Development – 5-day class to learn how to build your own Android Apps using Google’s SDK Presentation Slides: PDF | Tarball with Beamer files Exercises: PDF | ODT Embedded Linux– 4-days hands-On class learning about cross development, the kernel, the rootFS and the bootloader Presentation Slides: PDF | ODP Exercises: PDF | ODT Linux Device Drivers– 3-days hands-on class about modules, locking, interrupts and memory management, as well as char, block, network and USB drivers training. Presentation Slides:PDF | ODP Exercises: PDF | ODT You can freely use this material to learn more about Android and […]
App Inventor for Android is Now Open Source
Android App Inventor has been phased out by Google some weeks ago. But it is not dead yet, as Google made it open source and it is hosted at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The developers of App Inventor said they won’t be accepting contributions to the source code for now, but they plan to accept other developers contribution once the project is “complete and deployed to a large-scale public server”. App Inventor is a tool that allows non-programmer to design applications for Android via a web-based interface for designing Android apps without the need to get into Java programming with the Android software development kit. The projct is being transfered between Google and MIT, and you won’t be able to use App Inventor at the moment. MIT anticipates the public instance of App Inventor will be available for the general public to access some time in the first […]
Linux Debugging: Listing Shared Libraries at Runtime
I had a library (a python plugin) that crashed and outputted the “very useful”: illegal instruction I tried pdb (the Python Debugger) to find the issue without success. So I tried to add some printf to this library but none were outputted at runtime. So I guessed the illegal instructions was generated by the shared libraries. Let’s see how many libraries we’ve got: ldd libbrowsernode.so | wc -l 125 Oh dear!… 125 libraries.. This is where panic sets in. Luckily, there is a simple way to list the dynamic libraries as they are loaded (and some more useful info). Simply set: export LD_DEBUG=files before running your program. This is extremely verbose, so I recommend you redirect the output to a file. This method allowed me to find undefined symbols during dynamic libraries load time with errors such as: opening file=/usr/lib/gtk-2.0/2.10.0/loaders/libpixbufloader-png.so [0]; direct_opencount=1 14121: 14121: /usr/lib/gtk-2.0/2.10.0/loaders/libpixbufloader-png.so: error: symbol lookup error: undefined […]