Last week at Design West 2012, Green Hills Software announced it had achieved the highest compiler performance scores ever certified by EEMBC CoreMark and that it outperformed the nearest competing compilers by 35.5% using its MULTI 6.0 – Compiler 2012. Benchmarks were completed on 3 ARM Cortex-M4 microcontrollers: Freescale Kinetis K60 MCU @ 100 Mhz – 35.5% improvement over nearest competitor. Freescale Kinetis K70 MCU @ 120 Mhz – 29.6% improvement over nearest competitor. STMicroelectronics STM32F417IGt6 @ 168 MHz – 34.7% improvement over nearest competitor. Since apparently it’s bad marketing to name competitors in press releases, I went directly to the source (EEMBC Coremark benchmark results) to check out the results and competitors (IAR and Keil) for Kinetis K60 MCU. The first thing you may notice is that there are 2 tests per compiler / MCU combination. That’s because there 2 test configurations: Code in internal Flash – Data in internal […]
Vim Touch: Vim Editor for Android
Many Linux developers or admins use vi or vim in Linux to edit source or/and configuration files and some may want to use it in the go in their smartphone or tablets. Some hacks are available to install vim on Android via ADB on a rooted device, but now, it has all become nice and easy, as a touch enabled version of vim called VimTouch is also available on Android. VimTouch supports full vim syntax and finger touch gestures to help VIM much more usable on touch screens. This vim editor for Android includes the following features: Touch to scroll Fling to scroll Long press to zoom-in Two-fingers to delete lines (“dd”) or new lines (“p”) Single tap to send “ESC” Read email attachments Single instance to open files in vim window Real VIM runtime You would think it is rather cumbersome to use vi/vim on a mobile device, but reviews […]
ARM Releases Ne10: An Open Source Library with NEON Optimized Functions
The Advanced SIMD extension (aka NEON or “MPE” Media Processing Engine) is a combined 64- and 128-bit single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instruction set that provides standardized acceleration for media and signal processing applications for ARM Cortex-A (ARMv7) processors and the goal of these instructions is similar to MMX, SSE, and 3DNow! extensions for x86 processors. Starting early 2011, ARM has been working internally on a project codenamed Snappy to develop common functions accelerated by NEON. They have now released the first version of Snappy, now called the Ne10 library, which is available on GitHub at https://github.com/projectNe10/Ne10 . The code has been developed in C and Assembler and tested on Ubuntu on ARM (Linaro). A Makefile is also included to build it for Android (AOSP). The current functions include vector and matrix operations accelerated by NEON instructions. Since the library is open source, ARM hopes developers will make use of the Ne10 […]
Android SDK Tools and ADT Revision 17 with VM Acceleration for x86 Emulator
Google has released revision 17 of the SDK Tools and the Eclipse plugin. This release brings new features and bug fixes in for Lint static checker, the build system, and the emulator among other things. Here’s what’s new for Lint in r17: Lint API Check – Added check for Android API calls that require a version of Android higher than the minimum supported version. You can use the @TargetApi annotation to specify local overrides for conditionally loaded code. New Lint Rules – Added over 40 new Lint rules for a total of over 80, including checks for performance, XML layouts, manifest and file handling. Ignoring Lint Warnings – Added ability to suppress Lint warnings in Java code with the new @SuppressLint annotation, and in XML files with the new tools: namespace prefix and ignore attribute. New Eclipse Lint UI – Improved HTML and XML reporting and Eclipse integration. Improvements to […]
Designing An Android Sensor Subsystem: Pitfalls and Considerations – Android Builder Summit 2012
Jen Costillo of Lab 126 discusses the Android sensor subsystem at the Android Builder Summit in February 2012. Abstract: This lecture will arm Android device architects with the tactical knowledge they need to navigate the Android Sensor subsystem and make knowledgeable design choices to improve user experience and improve battery performance. The talk will address: Hardware architecture and trade-offs including latency, power, and software architecture implications: Wake up events and power considerations Gesture Detection Algorithm processing location and considerations Testing methodologies (Creating tools to aid develop and collect data. This talk targets the kernel/firmware developer responsible for the sensor architecture. They should be familiar with kernel drivers, embedded systems, hardware bring up, Android services, and the C language. You can also download the presentation slides on linuxfoundation.org website. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and […]
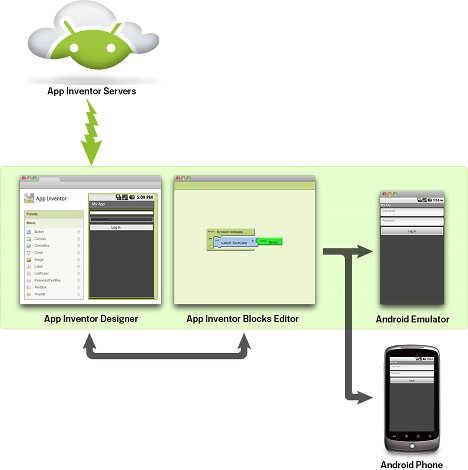
MIT Announces App Inventor Open Beta Preview
At the end of 2010, Google Introduced App Inventor, a web based tool allowing non-programmers to easily design Android applications, before phasing it out at the end of 2011. Google eventually made App Inventor open source and it is now handled by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) which planned to make a beta version of App Inventor available to the general public in Q1 2012. This happened yesterday, as the MIT App Inventor service is now open to everyone and all you will need is a Google ID for log-in such as a gmail account. There is no need to install any software as was the case with the original version of App Inventor and everything is handled in the web browser. Since this is the first release, MIT explains that there may be issues due to the load from a large number of users and there may be […]
Free Electrons Releases Embedded Linux Training Materials
Free Electrons, a technology company offering embedded Linux consulting services as well as embedded Linux training, has released their training materials for Linux and system development for embedded systems including their Lab sessions. The training materials are available in their git repository in LaTeX format. If you want the latest documentation in PDF, you’ll need to build it by following those steps: Install the required packages:
|
1 |
sudo apt-get install git dia inkscape texlive-full python-pygments |
Get the embedded Linux slides source:
|
1 |
git clone <a href="git://git.free-electrons.com/training-materials.git">git://git.free-electrons.com/training-materials.git</a> |
Build the training materials:
|
1 2 3 4 |
cd training-materials make full-sysdev-labs.pdf make full-kernel-labs.pdf make full-sysdev-slides.pdf |
The last three commands will generate the PDF files respectively: full-sysdev-labs.pdf – Embedded Linux Training Lab Book (58 pages) with instructions for the IGEPv2 board based on on TI DM3730 or OMAP3530. full-kernel-labs.pdf – Linux kernel and driver development training Lab Book (37 pages) full-sysdev-slides.pdf – Embedded Linux system development presentation slides (506 pages) Free Electrons also have slightly older version of full-kernel-labs.pdf and full-sysdev-slides.pdf available for download as PDF so […]
Android Builder Summit and Embedded Linux Conference 2012 Videos
The Android Builders Summit and the Embedded Linux Conference took place on February 13-17 2012, in San Francisco. The Linux Foundation has now posted videos of the talks as well as presentation slides on their website. Android Builder Summit 2012 Buildbot and Gerrit Integration, Improved CI Automation Using Android Outside the Mobile Phone Space The Android Ecosystem Case Study of Android Ice Cream Sandwich Rapid Bringup Towards a Standard Audio HAL for Android Topics in Designing An Android Sensor Subsystem: Pitfalls and Considerations A Novel Approach to In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI) Based on Android Android Services Black Magic The Case For Security Enhanced (SE) Android Hardware and Android App Testing & Tuning Exposing the Android Camera Stack Usable Hardware Security for Android on ARM devices Using OpenOCD JTAG in Android Kernel Debugging The AllJoyn Open Source Project ADB: (Android Debug Bridge) : How It Works Android OTA Software Updates USB Device […]