Based in March, I wrote about Xilinx Zynq-7000 Extensible Processing Platform (EPP), a SoC comprises of a Dual Cortex A9 and an FPGA, as well as the corresponding development boards and kits: Xilinx Zynq-7000 EPP ZC702 Evaluation Kit based on Zynq-7020 with all the basic components (595 USD). Xilinx Zynq-7000 EPP Video Kit based on Zynq-7020 with all necessary hardware, software and IP components for the development of custom video applications (1195 USD). Zynq-7000 EPP ZedBoard, a low cost development board for the developers community. At the time, the first 2 (expensive) boards were available, but there was little information about the Zedboard. But yesterday evening, I noticed Zedboard website had a lot more information and we now know details about the board and it is even possible to purchase it. Here are the Zedboard specifications: Processor – Xilinx Zynq-7020 Dual ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore @ 677 MHz Memory 512 MB […]
Linaro 12.05 Release with Kernel 3.4 and Android 4.0.4
Linaro has just released version 12.05 based on Linux Kernel 3.4 and Android 4.0.4. This release provides lots of improvement for Origen (Samsung Exynos 4) on Android, further work has been done on big.LITTLE processing and ARMv8 work appears to have started for Ubuntu and Debian. armel vs armhf benchmarks show a massive improvement (up to 15x) when using armhf for povray (3D rendering),. but for most other tests, there is little improvement, and in some rare cases armhf is slightly slower than armel. Here are the highlights of the release: Android Created a stable Google hangout build for Origen Updated DS-5 and gator daemon to 5.10 Stress tests from big.LITTLE testing have been integrated into LAVA Completed big.LITTLE Android tasks Monkeyrunner tests for automating common Android usage have been integrated into LAVA Ordered a new power measurement device from National Instruments Updated and Origen 3.4 rc7 Completed Android HAL […]
Samsung Releases Galaxy S3 Source Code
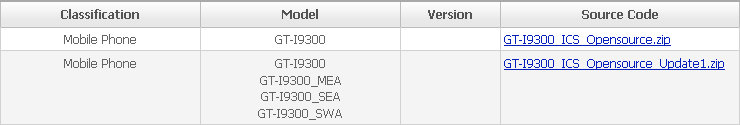
Samsung Galaxy S III has just hit the shelves in several countries and Samsung has decided it was a good time to release the source code for the device (codenamed GT-I9300). Two files are available: the original release (GT-I9300_ICS_Opensource.zip – 189 MB) and a new update (GT-I9300_ICS_Opensource_Update1.zip – 190 MB) which can both be downloaded here after accepting some legalese. Alternatively, you can also clone the kernel code from github @ https://github.com/sgs3/GT-I9300_Kernel which is just an import of the file(s) above. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
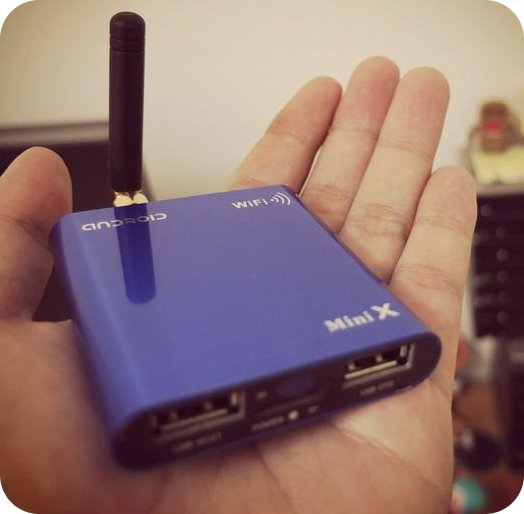
MINI X Android 2.3 Network Media Player Based on AllWinner A10
Here’s another tiny device based on AllWinner A10 processor. The MINI X is an Android 2.3.4 set-top box with 512MB RAM and 4GB NAND Flash that costs 77.50 USD including worldwide shipping. Here are the device specifications: CPU – AllWinner A10 (Cortex A8) with Mali-400 GPU Memory – 512MB DDR3 RAM Storage – 4GB NAND Flash, microSD slot Video Output – HDMI 1.3 USB – 2x USB 2.0 host Connectivity – WiFi 802.11 b/g/n Video Formats – MKV, TS, TP, M2TS, RM/RMVB, BD-ISO, AVI, MPG, VOB, DAT, ASF, TRP, FLV etc Video Codecs – MPEG1/2/4, H.264, VC-1, Divx, Xvid, RM8/9/10, VP6 Subtitle – SRT, SUB, IDX, SSA, SMI Audio Formats – MP3, ACC, OGG, WMA, WAV, M4A, APE Image format – JPG, BMP,GIF, TIF, PNG IR Remote Control Dimension: 72 x 61 x 13mm Weight: 51g This device is half-way between the MK802 HDMI stick and the Mele A1000 STB. […]
Toshiba Unveils TMPM061 Cortex-M0 MCU for Smart Meters
Toshiba America Electronic Components (TAEC) has announced the TMPM061, a new 32-bit ARM Cortex-M0 MCU specifically designed for smart metering applications. This new micro-controller provides a single chip solution for smart meters, eliminating the need for the two-chip approach with an analog front end (AFE) and a MCU, delivering a smaller footprint and lower costs. In order to simplify smart meter power measurement, the TMPM061 features an onboard power calculation engine that can calculate active energy, reactive energy and power factor as well as monitoring voltage and frequency fluctuation. In addition, the TMPM061 features up to 128KB on-chip Flash ROM and 8KB on-chip RAM, as well as on-board peripherals including: 3-channel 24-bit Delta-Sigma analog-to-digital converter (ADC) supporting sampling up to 6 kHz 10-bit ADC Temperature-compensated real-time clock (RTC). 9-channel 16-bit timer LCD display controller Temperature sensor Voltage detection circuit Watchdog timer 5-channel general-purpose serial interface Serial bus interface (I2C bus mode or […]
Zero Devices Z900 Android 4.0 HDMI Stick
A reader (Thanks Javier!) tipped me about the Zero Devices Z900, an upcoming Android 4.0 mini PC, by one of the companies providing the MK802 / Z802 mini PC. Here are the unofficial specifications: ARM Processor @ 1Ghz with Mali-400 GPU (AllWinner A10 ?, Wrong guess. It’s Telechips TCC8925) 512 MB RAM 4 GB Flash and microSD slot HDMI video output Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n 1x USB 2.0 port and 1x mini USB port (power) OS – Android 4.0 Dimensions – 89 x 32 x 18 mm Weight – 38 grams This little device also support 3D video playback. Availability and pricing are not available yet, but we can expect it to be in the same price range of his little brother (MK802 / Z802) that is around 70 to 80 USD including shipping. Since it has an HDMI male connector, it can be more convenient than the MK802 as you […]
Dell Announces Copper ARM Servers Based on Marvell ARMADA XP SoC
It looks like 2012 will be the year of ARM servers. After previous announcements of ARM servers based on Calxeda and Applied Micro SoC, Dell has just announced its own “Copper” ARM servers powered by Marvell ARMADA XP SoC (MV78460) that allegedly runs Ubuntu Server with a LAMP stack. Dell “Copper” ARM server is composed of 12 sleds with 4 SoC each slotted into a 3U C5000 Chassis. Here are the specs: Form factor 3U chassis 48 independent servers Architecture 1S 1.6GHz, quadcore Marvell Armada XP system on a chip (SoC) 4 discrete server nodes per sled 12 sleds per 3U chassis Memory 1 DIMM slot DDR3 UDIMM VLP, 1333MHz up to 8GB per node Drive bays 1 x 2.5″ SATA per node Hard disk drives 2.5″ SATA (7.2K rpm) Networking 1GB Marvell Ethernet uplink per node (QSGMII) connected to Marvell Integrated L2 Switch (98DX4122) Dell believes that ARM based […]
Open Source Mali 200/400 Drivers (LIMA) Demo on Android Tablet
Luc Verhaegen, the lead developer of LIMA open source project, provided an update at LinuxTag 2012 last week-end. This open-source MALI GPU driver isn’t ready for consumers yet, but the LIMA team has made some progress and showcased an OpenGL ES demos running on a Chinese tablet running Android. Luc said the tablet used for the demo is the same hardware as the Spark KDE/Vivaldi tablet, so the video demo below must be running on an AMLogic 8726-M processor with a Mali 400 GPU. The drivers already (partially) work on both Mali-200 and Mali-400 GPUs. The fragment shader instructions set is fully known and they have disassembler and assembler fully implement, but they still need to work on the compiler. The vertex shader instruction set is 80% known, they have a simple shader disassembler and are working on the assembler. You can also watch the 40 minute presentation at LinuxTag […]