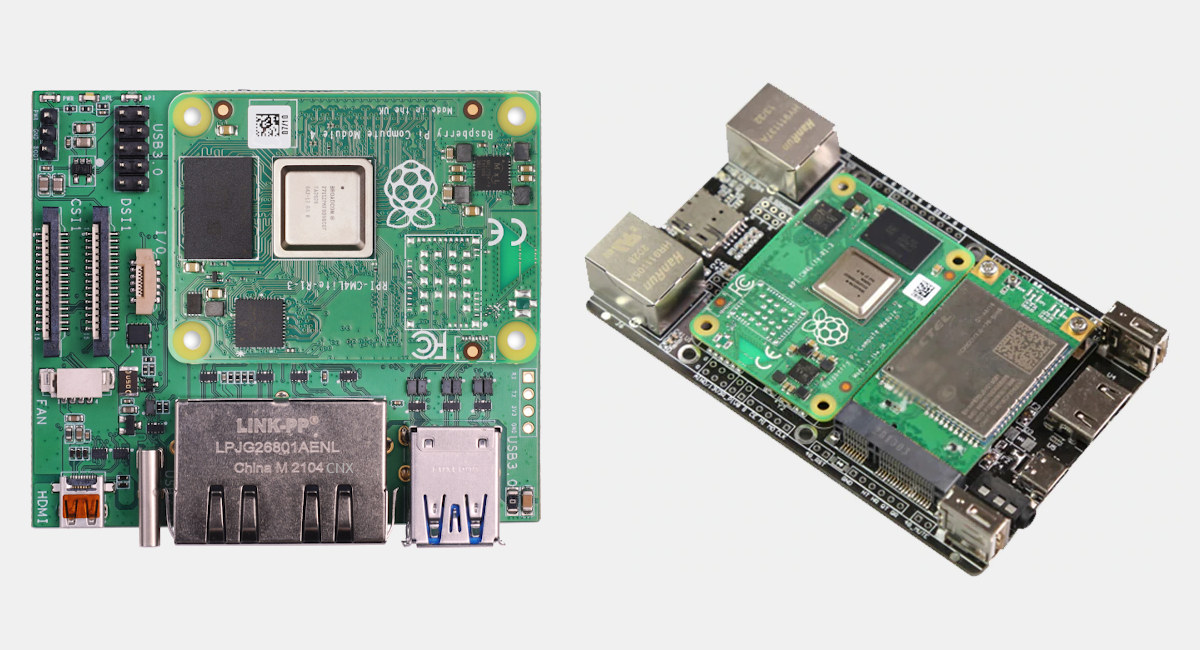
Since the launch of Raspberry Pi CM4 and CM4Lite systems-on-module last October, we’ve seen carrier boards bring their own set of features including industrial communication interfaces, a stereoscopic camera, four SATA ports to build a NAS, a DIN-rail based industrial controller, and more. But so far, I have not seen a Raspberry Pi CM4 carrier board with dual Ethernet ports. Seeed Studio’s “Dual Gigabit Ethernet Carrier Board for Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4” was brought to our attention this morning, but there’s another one with 4G LTE connectivity, Fast+Gigabit Ethernet ports, and extra I/Os courtesy of MCUZone’s CM4-4G IO board. Let’s have a look at both of them. Dual Gigabit Ethernet Carrier Board for Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 Specifications: Supported SoMs – Raspberry Pi CM4 and CM4Lite with up to 8GB RAM, 32GB eMMC flash, optional WiFi & Bluetooth Storage – MicroSD card slot to load OS on CM4Lite […]
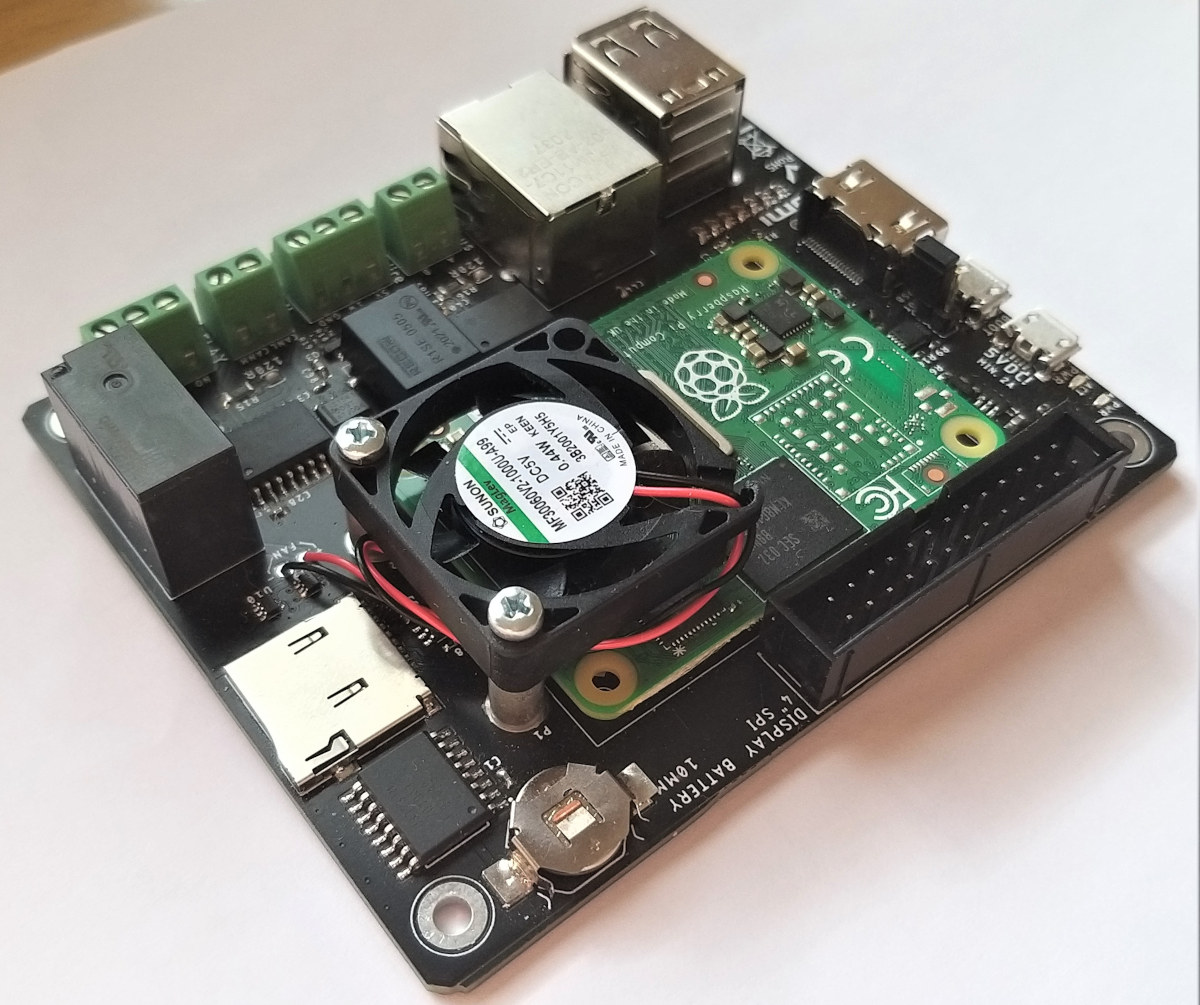
Raspberry Pi CM4 Carrier Board comes with RS485/Modbus, CAN, 1-wire interfaces (Crowdfunding)
Another day, another Raspberry Pi CM4 carrier board. Just like the TOFU carrier board, CM Hunter carrier board for Raspberry Pi CM4 targets industrial applications, but in a different way, as it focuses on industrial communication protocols with Galvanically-Isolated RS485/Modbus, 1-Wire, CAN 2.0B, and together with more common interfaces like Ethernet, HDMI, USB, etc… CM Hunter specifications: Supported systems-on-module – Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 / 4 Lite Industrial communication Interfaces Isolated RS485/Modbus (Profibus compatible) based on Texas Instruments ISO1410 controller Isolated CAN 2.0B based on Microchip MCP2515 controller and MAX14879 CAN transceiver Isolated 1-Wire via Maxim DS2482 I2C bridge Storage – MicroSD card slot Video Output – HDMI 2.0, optional 3.5-inch or 4-inch 480×320 LCD display with resistive touch connected over SPI Networking – Gigabit Ethernet RJ45 port and optional 802.11b/g/n/ac WiFi 5 plus Bluetooth 5.0 LE USB – 2x USB 2.0 ports, 1x micro USB 2.0 OTG port […]
Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 industrial carrier board supports M.2 NVMe SSD, 4G LTE modem
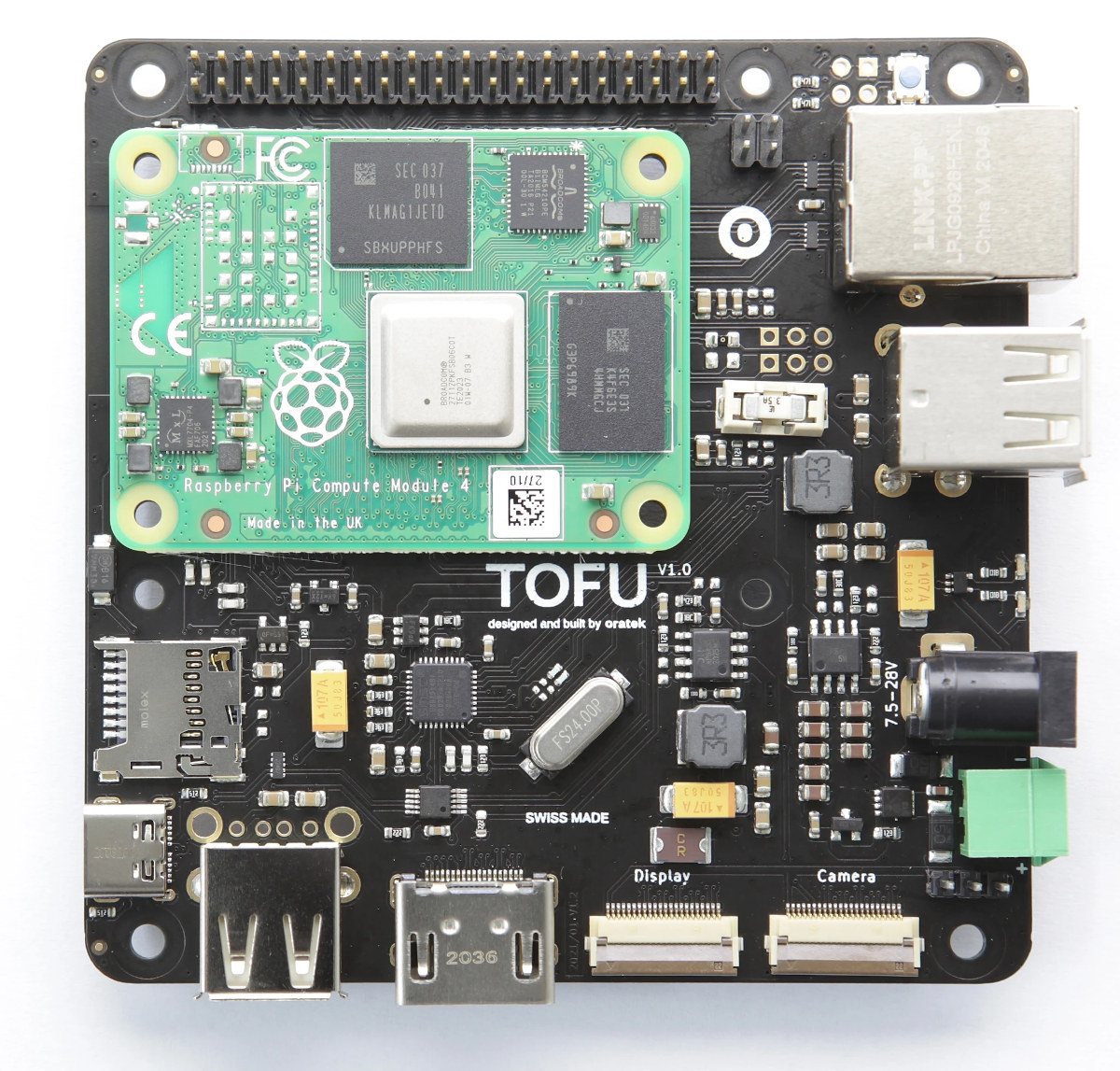
Since the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 launch last fall, we’ve seen several interesting carrier boards for the system-on-module including Wiretrustee to build a NAS with up to four SATA drives, the compact, Arduino-sized Piunora board that also include an M.2 socket, or Over:Board mini-ITX carrier board. Oratek brings another one specially designed for industrial use cases with TOFU Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 carrier board offering wide DC input, Gigabit Ethernet with PoE, M.2 NVMe SSD or 4G LTE modem support, among many other features. Specifications: Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 socket Storage NVMe SSD via M.2 2242 Key B socket (See Expansion section) MicroSD card slot Video Output HDMI 2.0 port up to 4Kp60 MIPI DSI connector for Raspberry Pi LCD display Camera – 1x MIPI CSI connector for Raspberry Pi camera Connectivity Gigabit Ethernet port with PoE Optional WiFI 5 and Bluetooth 5.0 on Raspberry Pi CM4 […]
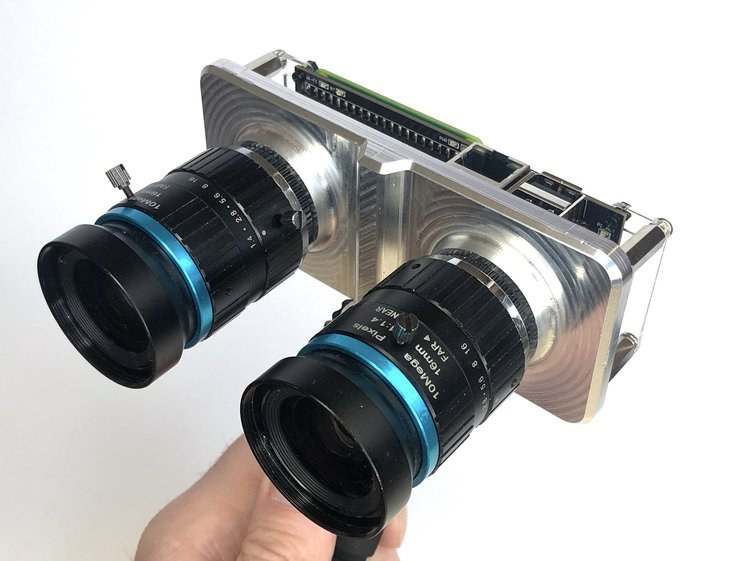
StereoPi v2 stereoscopic camera is powered by Raspberry Pi CM4 (Crowdfunding)
StereoPi stereoscopic camera based on Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3 was introduced in late 2019 on Crowd Supply. The camera can record 3D video, create 3D depth maps with OpenCV, and benefits from the Raspberry Pi software ecosystem. The developers are now back with an upgraded model. StereoPi v2 comes with many of the same features, but as it is based on Raspberry Pi CM4 (Compute Module 4) it offers better performance, Gigabit Ethernet, Wifi & Bluetooth connectivity out of the box, while other features like PoE, TFT screen, shot button, etc.. are optional. StereoPi v2 specifications: Supported SoM – Raspberry Pi CM4 or CM4Lite modules Storage – MicroSD card socket Video Output – Micro HDMI port Camera I/F – 2x MIPI CSI camera connector plus “hackable camera lines” Networking – Gigabit Ethernet RJ45 port, plus optional WiFi 5 and Bluetooth 5.0 on Raspberry Pi CM4 module USB – 2x […]
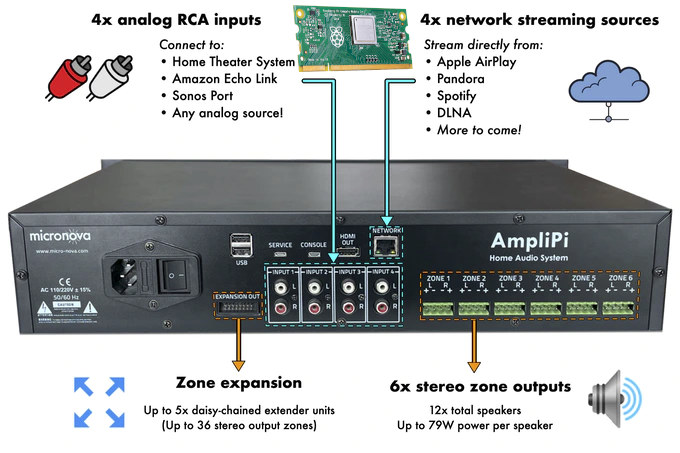
AmpliPi – A Raspberry Pi-based whole house audio amplifier (Crowdfunding)
Micro Nova has put together an open-source, whole-house audio amplifier called AmpliPi based on Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3+. It is capable of streaming four independent sources to 6 stereo output zones, expandable to up to 36 stereo output zones through daisy-chained extender units. AmpliPi specifically supports inputs from four networking streaming sources including AirPlay, Pandora, Spotify, and DLNA, as well as four analog RCA inputs for your media appliances. AmpliPi key components and features: Controller Board Carrier board fitted with Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3+ and PCM5102A & CM6206 audio DACs. It also communicates over I2C with the STM32 MCU on the Preamp board (see below) to control the muxing and amplification systems. Interfaces 10/100M Ethernet port HDMI 1.4 output 2x USB 2.0 ports, plus one internal USB port Service and console ports for maintenance and/or debugging. Preamp Board Board equipped with a 6×4 audio matrix switching system and […]
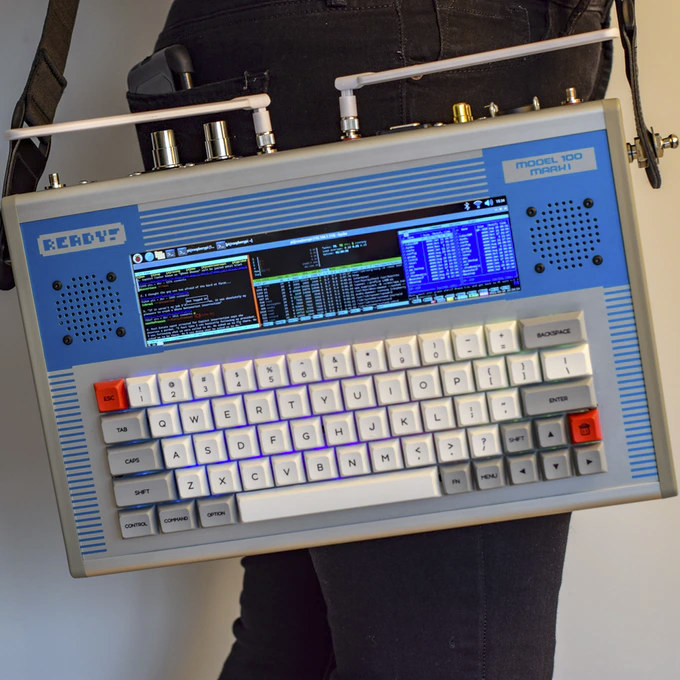
Ready! Model 100 is a retro computer shell for Raspberry Pi, SBCs, Nano/Pico-ITX boards (Crowdfunding)
We recently wrote about Devterm, a modular, retro-looking portable computer that looks like a typewriter with an extra-wide display, and takes Raspberry Pi CM3-series modules, or other compatible modules made by Clockwork based on Rockchip RK3399 or Allwinner H6. If you’re into this kind of device, but would like to use your own Raspberry Pi, another SBC, an Intel NUC motherboard, a Nano/Pico-ITX board, or even your smartphone, Ready! Model 100 single board computer expansion system may be worth looking into. Ready! Model 100 key features and specifications: Compatibility – Accommodates any hardware using 5V or 12V power input including smartphones, or arm or x86 SBCs such as Raspberry Pi 4, and compact motherboard following NUC, 4×4, 5×5, or Nano/Pico ITX form factors. Storage – Space for SSD Display – 8.8-inch 1920×480 “3xVGA” HDMI Touchscreen Video Output – HDMI (if dual HDMI supported on SBC) Audio – 10W stereo speaker […]
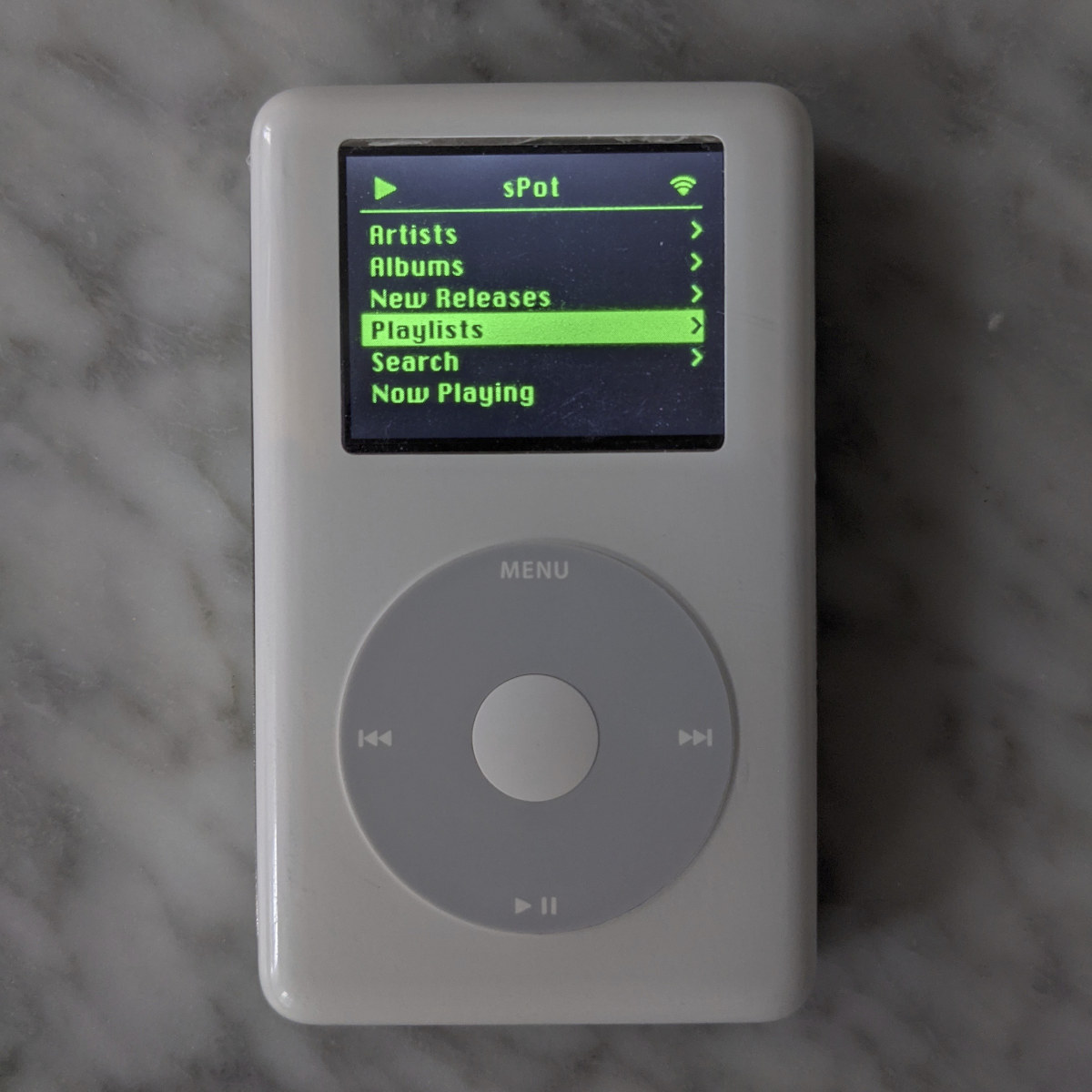
iPod Classic given new life with Raspberry Pi Zero W & Spotify
Guy Dupont got a bunch of 2004, fourth-generation iPod Classic MP3 players from his mother-in-law, and instead of playing MP3 files on the media players, he decided to repurpose one with a Raspberry Pi Zero W to be able to stream music from Spotify over WiFi. The resulting project is called sPot (ess-pot), and looks just like an original iPod, but it’s a Linux device that can stream/search via Spotify with a UI written in Python and based on the original iPod experience. But apart from the enclosure, and the original “click wheel” there’s not much left from the original design. Besides the Raspberry Pi Zero W SBC and iPod enclosure, the sPod includesAdafruit Mini LiPoly/LiIon USB Charger and PowerBoost 1000 Basic boards for charging and power management, a 1,000mah,3.7V rechargeable li-ion battery, vibration motor discs For haptic feedback, a 2-inch Adafruit TFT display, and a few other components, wires, […]
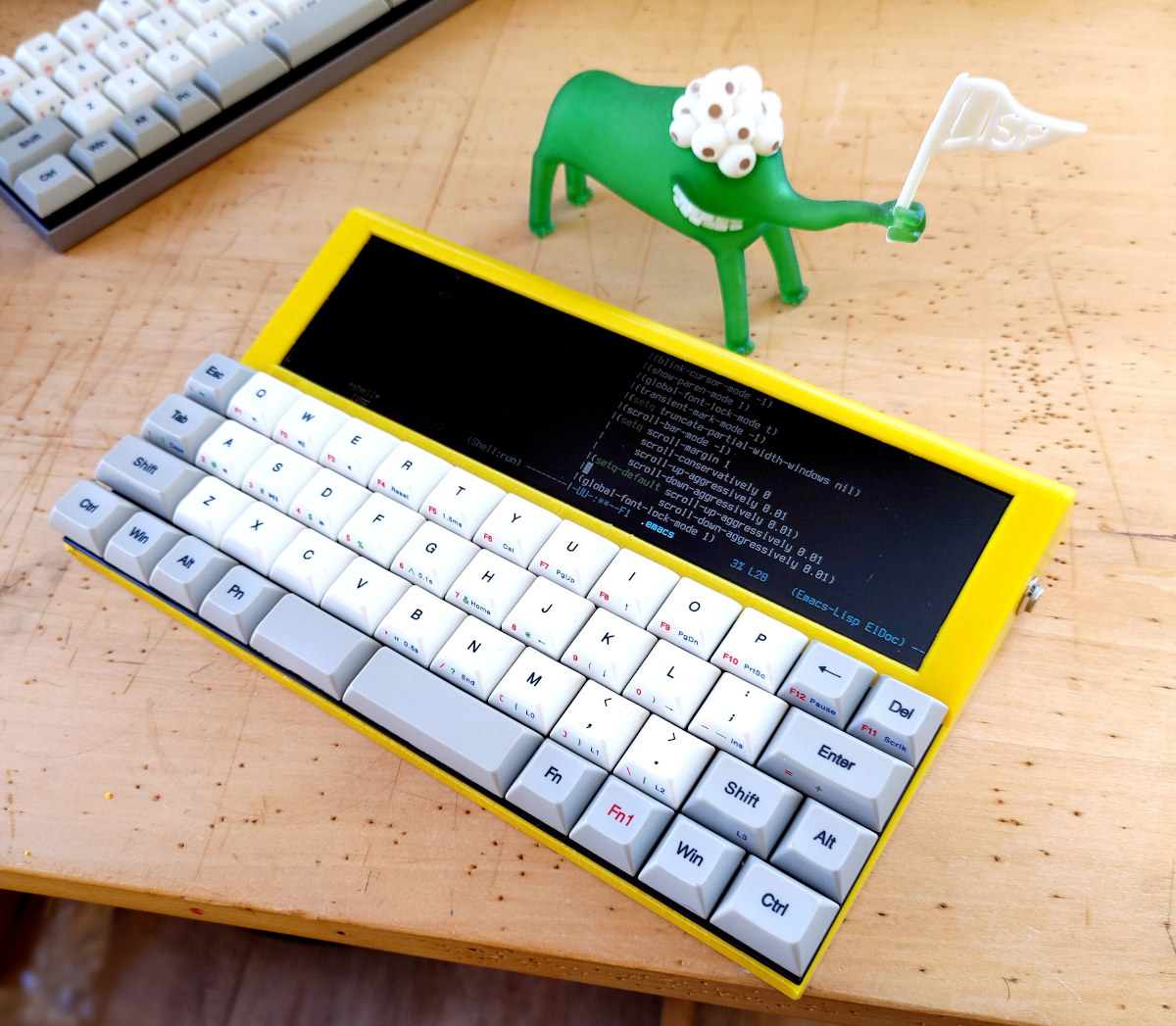
Lisperati1000 Lisp portable programming workstation features Raspberry Pi Zero W, ultra-wide display
Conrad Barski (Lisperati) wanted a portable “workstation” to write in Lisp and see all those parentheses. Since there aren’t many devices with an ultra-wide display, he decided to build his own “Lisperati1000” ultra-compact Lisp programming workstation powered by a Raspberry Pi Zero W, and equipped with an ultra-wide 1920×480 8.8-inch display, a compact keyboard made of Cherry Brown switches, and a 4,400mAh dual battery all housed in a 3D printed enclosure. When Conrad first showcased his little handheld computer on Twitter, he first claimed only 3 will ever be built, but think quickly got out of control with the project being featured on Hacker News, and he changed his mind after seeing the popularity of the DIY computer. UPDATE: Due to high demand, I have decided to fund a project to release this as a kit. If you are an electrical engineer and/or know about machining Aluminum, please get in […]