People got really interested in low cost small factor Intel devices at the end of the year, and one of my article about MeegoPad T01, an HDMI TV Stick powered by an Intel Atom Z3735F processor, even made it to the top 10 posts of 2014 on this blog. But instead of simply relying on partners, Intel had decided to enter the fray with Intel Compute Stick that will run Windows or Ubuntu on an Atom Bay Trail processor. There will actually be two versions of the hardware one for Windows 8.1 with Bing with 2GB RAM, and 32GB storage, and one for Linux with 1GB RAM, and 8G Storage. Intel Compute Stick preliminary specifications: SoC – Unnamed Intel Atom “Bay Trail” processor System Memory – 2 GB RAM (Windows) or 1 GB RAM (Linux) Storage – 32 GB eMMC (Windows) or 8 GB eMMC (Linux) + micro SD slot […]
ECS LIVA X Bay Trail Mini PCs Support Up to 4GB RAM, Windows and Linux OS
ECS LIVA was on of the first Bay Trail mini PC available on the market, and included both memory and storage. Elitegroup Computer System (ECS) has now officially announced an upgrade at CES 2015 with ECS LIVA X, another Bay Trail-M/I mini PC with up to 4GB, and 64GB storage. LIVA X specifications: SoC – Intel Bay Trail-M / I SoC up to 2.25 GHz. The M version is most probably featuring a dual core Celeron N2808 processor. System Memory – 2 or 4GB DDR3L Storage – 32 or 64GB eMMC + mSATA for SSD. 64Mb SPI Flash ROM with AMI BIOS. Video Output – 1x HDMI, 1x VGA. Dual independent displays supported. Audio – 1x audio combo jack (LIne In and Mic IN); Realtek ALC283 HD codec Connectivity 1x Gigabit Ethernet (Realtek RTL8111G) 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 4.0 USB – 1x USB 3.0, 2 x USB 2.0 […]
How to Take Screenshots and Record Videos in Android mini PCs without Root Access
I’ve started to test BFS 4KH Android TB box featuring HiSilicon HI3798M processor. I’m also the first things I normally do is to check for built-in screenshot support, and if not, I simply install a screenshot app like Screenshot Ultimate. This normally works pretty well, but the firmware is not rooted, and the usual root method for HiSilicon devices does not work, as it fails at the adb root stage with the message: “aabd cannot run as root in production builds”. So I was out of luck, and people who sent the sample for review do not seem to check / answer their email in a timely manner. ScreenShot Ultimate provides “No Capture Method Help“, but I found the instructions long, and it required me to install download and install something extra. So instead I check if I could do something with adb instead. adb can connect via USB or […]
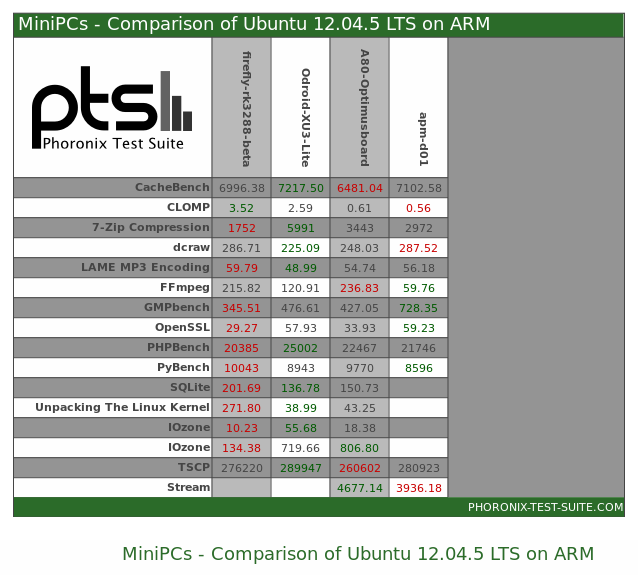
Linux Benchmarks – Rockchip RK3288 vs Exynos 5422 vs AllWinner A80 vs Intel Atom Z3735F
With all these Intel Atom Z3735F been released right now at a price similar to ARM based mini PCs, many people, including myself, are wondering about the performance of the low cost Intel processor against their ARM competitors. Ian Morrison just published some results from Phoronix Test Suite comparing the performance of Firefly-RK3288 (Rockchip RK3288), ODROID-XU3 Lite (Samsung Exynos 5422 BIN2), and A80 OptimusBoard (Allwinner A80) in Linux (Ununtu 12.04.5), against the performance of MeegoPad T01 (Intel Atom Z3735F) running Linux from a Live CD on a USB drive. Some of the benchmarks failed because Phoronix Test Suite got apparently confused with the file systems located on a USB drive, but at least we’ve got a comparison point, and the results are a bit confusing, as they’re no clear winner. In some tests like FFmpeg, the Intel SoC really crushed the ARM competition being at least twice as fast as […]
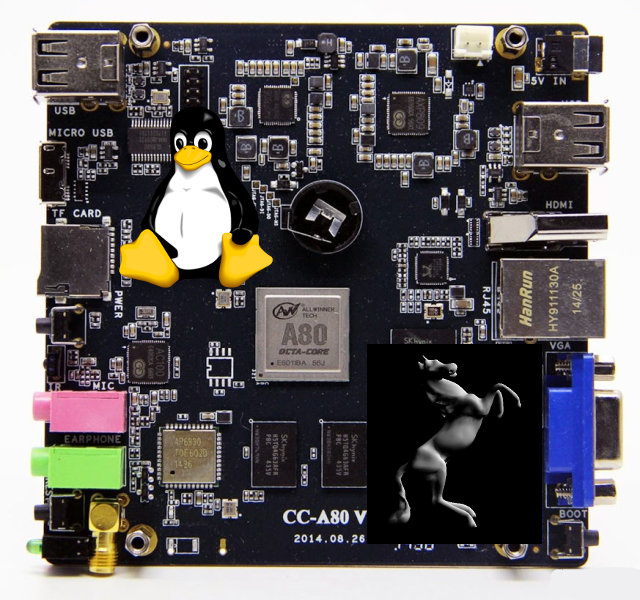
3D Graphics Acceleration in Linux on Allwinner A80 based Cubieboard4
Allwinner A80 is a powerful octa-core processor found in development boards and TV boxes such as Cubieboard4 or Tronsmart Draco AW80. Some early Ubuntu images and instructions had already been released for A80 Optimusboard and Draco AW80, but none of these featured GPU drivers for 3D acceleration, which to be honest, has limited advantages in Linux desktop distributions since desktop environments and most apps require full OpenGL support, i.e. not only OpenGL ES, and the only ARM SoC that can provide OpenGL support without external graphics card is Nvidia Tegra K1 SoC. Having said that GPU drivers would pave the way for smooth OpenELEC / Kodi user interface support in Allwinner A80 Linux distributions. That’s only one part of the puzzle, since the GPU normally handles the user interface, while the VPU takes care of video decoding. The good news is that CubieTech release updates images for their Cubieboard4 (CC-A80) […]
Iliad’s Online Labs Offers Quad Core ARMv7 Dedicated Servers
Iliad (Free) is a French company known to bring the price of technology down for the masses. Several years ago, they disrupted the Internet broadband market, by bringing low cost triple play broadband services to market, and more recently they entered the mobile market with 2 Euros 3G/4G monthly subscriptions. The company also owns Online.net providing hosting services, and which has recently launched a public preview for Online Labs cloud platform. Most hosted solutions nowadays relies on x86 servers and virtualization, but Online Labs instead features dedicated physical ARM servers connected to SSDs. The company call their custom-made credit-card size server modules C1 boards, completely unrelated to ODROID-C1 boards, as those are powered by a quad core ARMv7 Marvell processor with 2GB RAM, and a 1Gb/s network interfaces. These are then assembled into racks as shown below. And finally 16 racks are inserted into a chassis with a control board, […]
How to Install Ubuntu ARM64 on Nexus 9 Tablet
HTC Nexus 9 is one of the first 64-bit ARM platform with powerful ARMv8 cores (e.g. not Cortex A53) that both commercially available, and relatively affordable at $399 to $599, at least significantly cheaper than the server boards such as Applied Micro X-C1. The tablet comes with Android 5.0 Lollipop, but for those of you who wish to have an ARM64 platform running Ubuntu or other 64-bit Linux operating systems, Ubuntu installation instructions provided by Ryan Houdek, Dolphin emulator developer, might come handy, especially it won’t affect your Android installation provided you have already unlocked your bootloader. The instructions are fairly long so I won’t reproduce them all here, so I recommend you check the detailed instructions on XDA, but the short summary below may give an idea of the amount of work needed: Install dependencies such as Aarch64 toolchain:
|
1 |
sudo apt-get install gcc g++ git gcc-4.9-aarch64-linux-gnu g++-4.9-aarch64-linux-gnu |
Build a initramfs with buildroot. You’ll need to enable […]
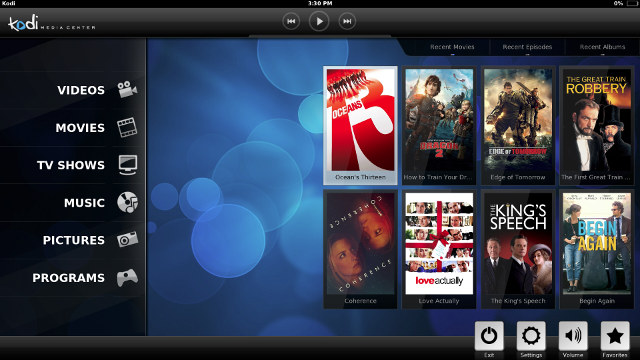
Kodi 14.0 Helix Release
XBMC (name) is definitely dead, as developers of the popular open source “entertainment center” project have announced the first stable Kodi release – the new name of XBMC – with XBMC 14.0 Helix. Key changes and new features include: Update to FFmpeg 2.4.4 – Adds H.265 / HEVC and VP9 video codecs support. Software decode only. Library Improvements – Scanning speed greatly improved, better UPnP support including with PlanOn and MediaBrowser servers. New Configuration features – Add-on update controls, choice of virtual keyboard layouts for tablets and remote control users in order to support multiple languages. Android, iOS and Embedded – 4K support for Amlogic S802, more ARM SoCs are now supported in Android, fast forward/rewind improvements. Airplay support fixed, except for Android. Freescale i.MX6 support for Kodi Linux. Windows, OSX, and Linux – Audio playback improvements. DXVA video playback has been improved for Windows too. A critical Kodi Linux […]