The 19th China Content Broadcasting Network Exhibition (CCBN 2011) took place on March 23 – 25 2011 at the China International Exhibition Center in Beijing. During this event, numerous Android STB were showcased with processors from several vendors. Trident Microsystems PNX8400 Trident Microsystems demonstrated their Cortex-A9 Apollo/Shiner SoC family, the PNX8400, which included all the major building blocks needed to develop Next Generation Broadcasting (NGB) solutions. NGB is a government initiative for smart tv in China. On 24th of March 2011, Trident Microsystems also announced that its STB SOCs were selected for the first trial deployments of NGB in China. LG (LG Smart Box) and Cycle Century demonstrated their Android based cable STB using Trident Microsystems NXP8400. This stb supports DVB, Conditional Access, 1080p video streaming, a browser with an Apps store, 3D gaming and VoIP. To see more about Trident Microsystems Android STB have a look at the video […]
Compile with ARM Thumb2 to Reduce Memory Footprint and Improve Performance
ARM claims that Thumb-2 instructions (for ARM Cortex cores and all ARMv7 processors) provides performance improvements and code size optimization: Thumb-2 technology is the instruction set underlying the ARM Cortex architecture which provides enhanced levels of performance, energy efficiency, and code density for a wide range of embedded applications. For performance optimized code Thumb-2 technology uses 31 percent less memory to reduce system cost, while providing up to 38 percent higher performance than existing high density code, which can be used to prolong battery-life or to enrich the product feature set. Thumb-2 technology is featured in the processor, and in all ARMv7 architecture-based processors. Dave Martin (Linaro) has recently posted a message entitled “ARM/Thumb-2 kernel size comparison” on Linaro mailing list:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
The question of the size impact of building the kernel in Thumb-2 came up to day, so I extracted some quick numbers: $ size vmlinux-* text data bss dec hex filename 8420507 463356 826928 9710791 942cc7 vmlinux-arm 6715539 463260 826928 8005727 7a285f vmlinux-thumb2 This is for a recent mainline kernel built with the linaro omap config. In this case we save about 20% for code and read-only data (i.e., text) and 17.5% overall -- which accounts for a little under 2MB saved in this example. This doesn't take loadable modules into account; we can probably expect to see a similar size ratio there. |
The results provided by Linaro at not as high as those claimed by ARM, but a 20% code size reduction is still impressive. If you want to use Thumb2 to compile […]
Is it IPv6 Time ? IPv6 Basics on Linux
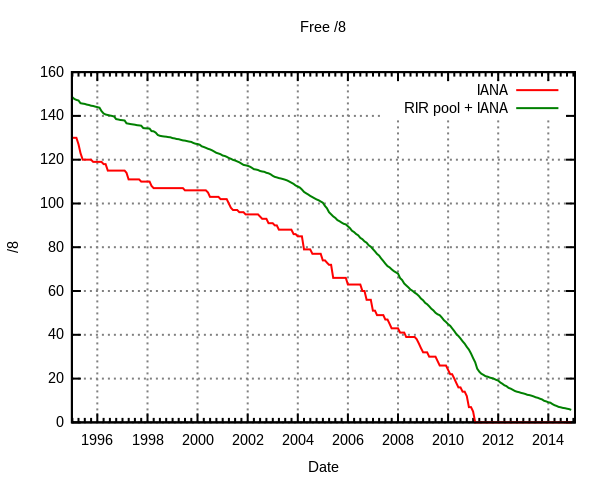
The first time I worked on IPv6 was in 2000 in my master’s degree thesis where I started an implementation of Mobile IP based on IPv6 in Linux Redhat. Over a decade later, IPv6 has not really taken off, even though we hear stories about the IPv4 address space running out and I have yet to see an embedded device using anything else than IPv4. APNIC Ran out of IPv4 However, this may be about the change as on the 15th of April 2011, Japan Network Information Center (JPNIC) announced that APNIC (Asia Pacific Network Information Centre) ran out of IPv4 addresses. They will still try to make it last longer by reusing previously allocated IPv4 and an “IPv4 address transfer system” whose details will be made available later. You can also see a chart based on IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) data that shows this is a problem right […]
Embedded Linux Quick Start / Tutorial Videos
Free Electrons recorded some videos from the Embedded Linux Conference Europe, in Cambrigde, United Kingdom on October 2010 by Chris Simmonds, the founder of 2net Limited, a UK company providing training, consultancy and custom software for Linux and other embedded platforms. The videos can either be downloaded in webm HD format at http://free-electrons.com/blog/elce-2010-tutorial-videos/ or you can watch them in HD format below. The PDF slides for the three parts and the lab notes are available at http://elinux.org/images/c/cc/Linux-quick-start.tar.gz The first video (53 minutes) deals with the following key points: Genesis of a Linux project The four elements: Tool chain; boot loader; kernel; user space Element 1: Tool chain Element 2: Boot loader The second video (1h19m) focuses on: Third element: Kernel Fourth element: User space The last video (1h07m) is more practical as it shows how to use embedded Linux on an NXP LPC3250 Stick (ARM9): Description of the hardware Installing […]
Rockchip RK2918 based Set-Top Box and Laptop
Rockchip RK2919 is apparently being implemented in many tablets such as Arnova 10, but they are also used in STB / media players and Laptops. Rockchip showcased their set-top box reference design at Hong Kong Electronics Fair 2010. Their board features 100MB Ethernet, one USB host port, one HDMI video output and one SD Card connector. The BOM cost is around 50 USD. The reference designs runs Android 2.3 (gingerbread). They also exhibited a laptop based on RK2918 supposedly manufactured by one of their customers running Android 2.3. There are no details specs nor price information available yet. But with an ARM Cortex A8 running at 1.2Ghz it should offer decent performance compared to existing ARM based laptops although I’d rather have Ubuntu preloaded (now optimized by Linaro) than Android on this kind of device. Here’s a video by Charbax (armdevices.net) of this laptop. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software […]
MIPS Launches New Android and Linux Developer Community
MIPS Technologies announced the launch of its new Developer Community at developer.mips.com. The new site is specifically tailored to the needs of software developers working with the Android™ platform, Linux operating system and other applications for MIPS-Based™ hardware. All information and resources on the site are openly accessible. “This new community demonstrates our ongoing commitment to the vibrant open source effort around the MIPS cores and architecture, as well as around our customers’ and their customers’ hardware platforms,” said Art Swift, vice president of marketing and business development, MIPS Technologies. “As the MIPS architecture continues to expand into new high-volume markets such as mobile handsets and tablets, we see an increasing need for these resources among the growing MIPS developer community.” Software engineers can find development resources and tools on the site including: Android on MIPS source code, porting instructions, a native development kit (NDK) for Android applications development on […]
RK2918 based Arnova 10 Tablet with Capacitive Touchscreen
Arnova, a subsidiary of Archos in Hong Kong, has already released the resistive touchscreen version of Arnova 10 based on Android 2.1 and powered by Rockchip RK2918 in March 2011. In May, they will start to sell the latest version of Arnova 10 with capacitive touchscreen and Android 2.3 (Gingerbread). The price should only be slightly higher then the first Arnova 10 with a retail price of 229 USD / 229 Euro. This device is very similar to Archos 101 except it has a more powerful processor (Rockchip RK2918 vs. OMAP 3) but it does not have kickstand and surprisingly no HDMI output. Watch the hands-on video by Charbax below. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
Android 2.3.3 Firmware for HTC, Motorola, ZTE, Samsung smartphones
CyanogenMod is an aftermarket firmware for a number of cell phones and tablets based on the open-source Android operating system. It offers features not found in the official Android based firmwares of vendors of these cell phones. People often use it because the official firmware of their phone may not get an update or because they do not like the custom Android UI of the manufacturer. The latest version is CyanogenMod 7 (11th of April 2011) with the following: Android version: 2.3.3 Kernel 2.6.37.4 with CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) Root access BusyBox tools Apps2SD Reboot menu – options to perform a reboot, reboot into recovery, or reboot into bootloader Input settings – Haptic feedback adjustments, trackball wake, menu unlock, music controls on lock screen Performance settings – surface dithering, JIT, VM heap size, and lock messaging in memory CyanogenMod 7 also offers user interface improvement, some pre-install apps, networking support (OpenVPN, tethering, etc..), audio […]