The Advanced SIMD extension (aka NEON or “MPE” Media Processing Engine) is a combined 64- and 128-bit single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instruction set that provides standardized acceleration for media and signal processing applications for ARM Cortex-A (ARMv7) processors and the goal of these instructions is similar to MMX, SSE, and 3DNow! extensions for x86 processors. Starting early 2011, ARM has been working internally on a project codenamed Snappy to develop common functions accelerated by NEON. They have now released the first version of Snappy, now called the Ne10 library, which is available on GitHub at https://github.com/projectNe10/Ne10 . The code has been developed in C and Assembler and tested on Ubuntu on ARM (Linaro). A Makefile is also included to build it for Android (AOSP). The current functions include vector and matrix operations accelerated by NEON instructions. Since the library is open source, ARM hopes developers will make use of the Ne10 […]
Virtual Hardware Platforms: Test & Debug Software Before the Silicon is Ready
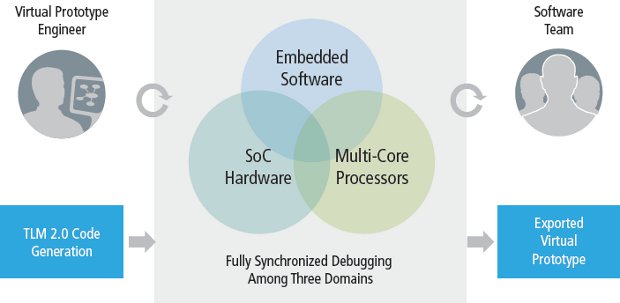
Historically software could only be tested and debugged when the first silicon sample was ready, and the software team could not participate in the design process. But thanks to Virtual Hardware Platforms, software can be executed at speeds close to real time on an abstract model of the hardware, available long before a design has been completed. The virtual platform is designed to simplify the creation and support of virtual prototypes and allow design teams to begin developing software weeks to months before a hardware prototype is available, and software teams can use it as their application development platform. For example, Freescale is using a Virtual Hardware Platform for their new Vybrid Controllers to emulate both Cortex A5 and Cortex M4 cores, as well as peripherals and run OS such as Linux or MQX before the Controllers are ready (Q2 2012). One Virtual Hardware Platform has just won the ACE […]
Cross-compiling the ARM Linux Kernel in Ubuntu 12.04 LTS
Yesterday I installed Ubuntu 12.04 ‘Precise’ Beta 1 in Virtual Box to give it a try (I could not manage to have HUD working btw), and today, I’ve noticed an article entitled “Ubuntu 12.04 ‘precise’ and cross compilation of ARM kernels” explaining how to build Linaro ARM kernel in Ubuntu 12.04. So I’ve decided to give it a try, especially it seems straightforward. I followed the instructions in the aforementioned link, it basically worked except I had to install dpkg-dev package that also installed the build essentials (gcc, g++, etc…) and use sudo for some commands. You’ll notice the name change for the ARM gcc toolchain as it now uses hard-float by default which seems to provide quite a boost in performance for the Pandaboard. Here are the steps I followed: Install the ARM GCC cross compiler and the development package of dpkg:
|
1 |
sudo apt-get install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf dpkg-dev |
Retrieve the kernel source:
|
1 |
apt-get source linux-source-3.2.0 |
Install […]
Freescale Vybrid Controllers: Cortex A5 + Cortex M4 Solutions
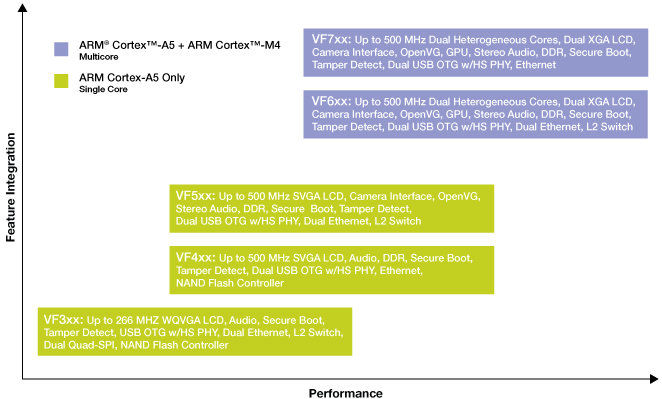
Freescale announced the new Vybrid platform based on Cortex A5 application processor and Cortex-M4 MCU (VF6xx and VF7xx family only) which targets building/home automation and control, industrial automation, point-of-sale systems, medical devices, smart energy equipment, and appliances. There are 5 families of Vybrid Controllers which support the following common features: Video/Camera Interface Unit + optional OpenVG GPU (except VF3xx) Up to 800 MHz data rate DDR3 and LPDDR2 support (except VF3xx) USB 2.0 OTF with Integrated PHY (1 or 2 depending on model) Ethernet 10/100 MAC (1 or 2 depending on model) Display controller (WQVGA to XGA resolutions) High-assurance boot with Crypto Acceleration Up to 1.5 MB on chip SRAM NAND Flash controller and Dual Quad-SPI with eXecute-In-Place(XIP) Dual 12-bit ADC and DAC Here are the 5 families of Vybrid platforms and key differentiating features: VF3xx: ARM Cortex-A5 up to 266 MHz, 1x USB 2.0 OTG, 2x Ethernet, display up […]
Glark, an alternative to Grep
grep is a very useful tool to search or filter strings in order to look for files, parse useful info in log files and more. glark is an alternative to grep, it has few features that grep does not such as complex expressions, Perl-compatible regular expressions, and excluding binary files. It also has a more fancy way of display results. It is described as follows in the manpage: Similar to “grep”, “glark” offers: Perl-compatible regular expressions, color highlighting of matches, context around matches, complex expressions (“and” and “or”), grep output emulation, and automatic exclusion of non-text files. Its regular expressions should be familiar to persons experienced in Perl, Python, or Ruby. File may also be a list of files in the form of a path. glark is not installed by default. To install it in Debian/Ubuntu/Mint: sudo apt-get install glark It does not appear to be available in Fedora and […]
iWave Systems Rainbow-G15M-Q7: Qseven SOMs Based on Freescale i.MX 6 Series
iWave Systems, an embedded systems company based in Bangalore, India, has launched Qseven Modules powered by Freescale i.MX 6Quad (quad-core Cortex A9 processor), i.MX 6Duo (dual -core) and i.MX6 Solo. The Rainbow-G15M-Q7 modules are compliant with Qseven specification R1.20 and target the Industrial, Automotive and Medical markets. Here are the modules specifications: CPU: Freescale i.MX6 Cortex A9 Q/D/S core @ 1 GHz Memory: 1GB DDR3 SDRAM– Expandable to 4GB Optional 8GB eMMC Flash On-Board Micro SD slot Qseven Edge Connector : PCIe v2.0 HDMI 1.4 SATA 3.0 Gigabit Ethernet Dual LVDS LCD Support 4 x USB 2.0 Host | 1x USB 2.0 device AC97 Audio 8-Bit SD/MMC CAN1, SPI & I2C ports Debug Port Expansion Connector: 2x Camera CSI MIPI CSI & DSI 24 Bit RGB LCD IF Triple UART 4×4 Key Matrix ESAI (Embedded Software Application Interface) , SPDIF MLB (Media Local Bus), CAN2 I2C, PWM, GPIO, Memory bus Form […]
ARCHOS G9 Tablets Firmware 4.0.5 Released
Two weeks ago, Archos released the first firmware for Archos 80 G9 / 101 G9 and A70B supporting Android 4.0.3 (ICS), so it was likely a new one would soon follow to fix a few bugs. Here’s the ChangeLog: Version 4.0.5 – March 22nd, 2012 Wi-Fi: fix slow throughput and disconnections happening on some access points HDMI: solve no sound or no video output issue on some TVs Bluetooth: make sure Bluetooth does not prevent device suspend VPN: fix VPN connection failing Touchscreen: avoid loss of first finger touch while tapping with second finger The update should be done automatically OTA, but alternatively the firmware can be downloaded at http://update.archos.com/9/gen9/gen9_4.0.5/firmware_archos_it4.aos Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
Android SDK Tools and ADT Revision 17 with VM Acceleration for x86 Emulator
Google has released revision 17 of the SDK Tools and the Eclipse plugin. This release brings new features and bug fixes in for Lint static checker, the build system, and the emulator among other things. Here’s what’s new for Lint in r17: Lint API Check – Added check for Android API calls that require a version of Android higher than the minimum supported version. You can use the @TargetApi annotation to specify local overrides for conditionally loaded code. New Lint Rules – Added over 40 new Lint rules for a total of over 80, including checks for performance, XML layouts, manifest and file handling. Ignoring Lint Warnings – Added ability to suppress Lint warnings in Java code with the new @SuppressLint annotation, and in XML files with the new tools: namespace prefix and ignore attribute. New Eclipse Lint UI – Improved HTML and XML reporting and Eclipse integration. Improvements to […]