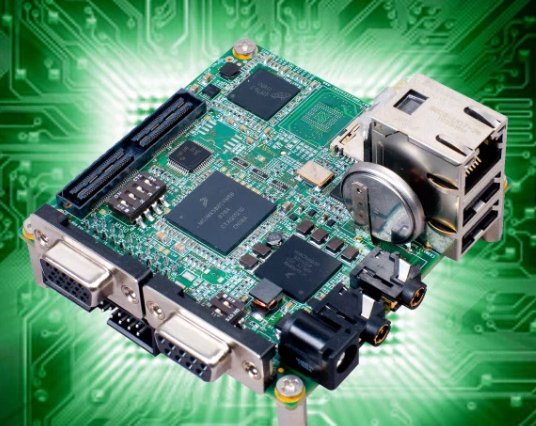
iWave Systems has just uploaded a new video of its new Freescale .i.MX508 low cost development board RainboW-G13S Quick Start Board, an alternative to the original Freescale i.MX53 QSB. This board targets the development of eReaders, industrial kiosks, home/industrial/office automation, portable medical devices and appliance control applications. Here are the specifications of this development board: CPU – Freescale i.MX508 processor (Cortex A8) @ 800MHz System Memory – 256MB LPDDR2 Storage – 2/4 GB micro SD card loaded with boot code and Linux, 4MB SPI Flash (optional) and 8 GB eMMC (optional) Connectivity – 10/100Mbps Ethernet USB – Micro USB 2.0 Device port, 2x USB 2.0 Host Type A port Standard SD port for SDIO expansions Video Output – VGA Audio – Audio IN & OUT port Debug Ports – DB9 Debug Serial port & JTAG connector Expansion connector port for EPD & LCD expansion. The company provides Board Support Packages […]
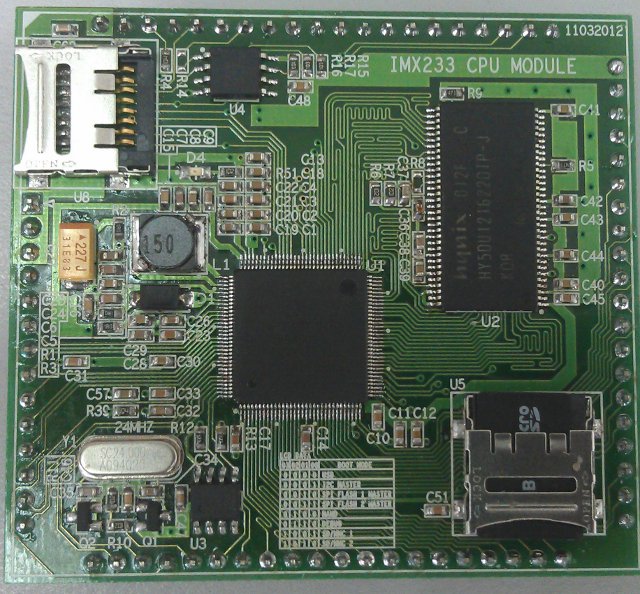
Locux: 15 USD Freescale i.MX233 System On Module
These days, low cost boards seem to pop-up a bit everywhere… Featuring the same processor as Olimex OLinuXino, the Locux board will be powered by a Freescale i.MX233 with 64 MB and boot from a microSD card (no NAND on the board). This project is quite different from other low cost board projects, since it is a system on module (SoM) and will require a carrier board to access peripherals such as Ethernet, USB Host and video output, although the developers managed to boot it with a simple breadboard. The developers also explain that this board stands apart as it does not feature any BGA parts and can be hand soldered, which could be an advantage when sourcing the boards and some hobbyist may also like to do the soldering themselves. The Raspberry Pi is still hard to get and the some other low cost boards such as the Beaglebone […]
How-to Make a Process Continue to Run After Closing an SSH client
If you are connected to a remote server via SSH, you may want to start a time-consuming task or a background task in the server and right after starting it, close your SSH client, because you need to turn off your computer to “save the earth”, reduce your electricity bill, or simply because you need to bring your laptop with you. The problem is that if you close your SSH client, the terminal session will be terminated together all processes launched from this terminal. There are 2 tools to solve this issue: GNU screen and nohup. GNU screen screen may not be installed in your Linux distribution. In Debian/Ubuntu you can install it with apt-get: sudo apt-get install screen In your SSH terminal, start GNU screen: screen Press enter to discard the text, run your command and press Ctrl+a+d (and not Ctrl+Alt+d) to detach the screen. That’s it. You can […]
Raspberry Pi Releases 19-04-2012 Debian and Arch Linux Images
Within less than a week, a new image for Raspberry Pi Debian has been released as well as an Arch Linux image. Debian 6 can be downloaded via: BitTorrent – debian6-19-04-2012.zip.torrent Direct HTTP download – debian6-19-04-2012.zip Username/Password: root/raspberrypi Arch Linux can be downloaded via: BitTorrent – archlinuxarm-19-04-2012.zip.torrent Direct HTTP download – archlinuxarm-19-04-2012.zip Username/Password: root/root The following Changelog is provided for Debian 6 release: Overscan adjustments ALSA driver Re-enable 1600×1200 output (regression in 13-04-2012 release) Boot file tidyup – and remove test cmdline file vcgencmd provides a version number Fixes for EDID parsing Drive DMT modes in DVI modes by default, even if HDMI is reported as supported Some initial packages that might make setting up Wi-Fi possible Includes the non-free software source (nothing from it though) – useful for Wi-Fi firmware Qt5 snapshot A small package that will allow Raspberry Pi to be used as for Qt5 development out of […]
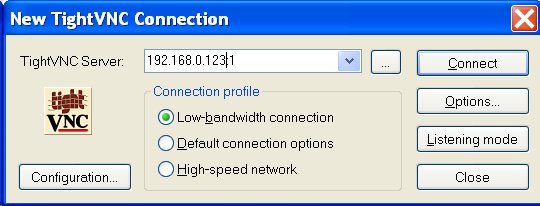
How-to Setup a VNC Remote Connection to a Raspberry Pi
I don’t have a Raspberry Pi board, yet I’m using one right now remotely thanks to the VNC (Virtual Network Computing) protocol. The Raspberry Pi I use runs the latest Debian-13-04-2012 image. Here’s how to do to access the Raspberry Pi desktop in Windows XP. These instructions could also be followed to connect to any remote networked Linux device with minor modifications. Connect to the Raspberry Pi via SSH Install a VNC server (e.g. tightvncserver): # sudo apt-get install tightvncserver Run startx in the background # startx & Start the VNC server (it will ask a password of your choice): # tightvncserver New ‘X’ desktop is raspberrypi:1 Starting applications specified in /home/cnxsoft/.vnc/xstartup Log file is /home/cnxsoft/.vnc/raspberrypi:1.log Back to your computer. Install a VNC client such as TightVNC for Windows. You only need to select “TightVNC Viewer” during installation. Start TightVNC Viewer (In Windows XP, Start->All Programs->TightVNC->TightVNC Viewer) Enter the Raspberry […]
Emcraft Open Sources uCLinux and U-boot for Cortex M3 and M4 MCUs
Emcraft Systems has open sourced its ports of U-Boot and uClinux for Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4 which are available on github at https://github.com/EmcraftSystems. This release supports the following platforms: ST Micro STM32F2 NXP LPC17XX Actel SmartFusion Freescale Kinetis You can check the source code as follows: uCLinux: git clone git://github.com/EmcraftSystems/linux-emcraft.git U-boot: git clone git://github.com/EmcraftSystems/u-boot.git The company has also designed systems on module (SoM) with enough memory to run Linux with Cortex M3/M4 micro-controllers: Freescale Kinetis K70 SOM Actec SmartFusion SOM ST Micro STM32 SOM You might find more details on building/using u-boot or uClinux on EmCraft documentation page (especially linux-cortexm-um-1.4.1.pdf) and you may want to check EmCraft website for details on available hardware and BSP for Cortex M3/M4 solutions. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later […]
Building Chromium OS for Raspberry Pi (ARMv6)
I had previously written the instructions to build an older version of Chromium (via Berkelium) for ARM using Beagleboard/Overo rootfs in order to use it with Xibo digital signage. Recently I’ve been contacted by hexxeh, who maintains Chromium OS vanilla builds for x86 and MacOS computer, as he intends to provide Chromium OS for the Raspberry Pi, and you should be able to get a SD card image once everything is working from the site above. Today, I’ll post the steps followed to build Chromium OS LKGR (“the latest revision to pass only unit tests”) optimized for ARMv6 processor with soft-float support, which is the type of processor (Broadcom BCM2835) used in the Raspberry Pi. Please note that although it can build, it still does not run properly and a few more changes are needed. First, you’ll need a fast machine to build Chromium OS in a reasonable amount of […]
30 Euros Olimex iMX233-OLinuXino Linux Development Board
Olimex announced the first 10 prototypes of OLinuXino development board. Started in March of this year, OLinuXino is a development board based on Freescale i.MX233 aiming to provide a low cost (30 Euros) open source hardware and software single board computer to run Linux. Here are the specifications of OLinuXino single board computer: Freescale iMX233 454Mhz ARM9 processor 64MB of RAM Linux bootable image from SD-CARD TV-Video Output USB host for Keyboard, camera, WiFi, etc interfacing UEXT connector and GPIO connectors with the same style as DuinoMite so that developers can add external modules supporting Zigbee, Bluetooth, RFID readers, relays, switches, sensors, etc… The company also plans to provide 2 plug-in modules for this board: iMX-LCD – a 4.3″ TFT 24 bit color LCD with touchscreen (EUR 30) MX-HUB – A board adding 2 USB hosts and Ethernet (EUR 15) [Update: The company will actually make 2 versions of this […]