Free Electrons recorded some videos from the Embedded Linux Conference Europe, in Cambrigde, United Kingdom on October 2010 by Chris Simmonds, the founder of 2net Limited, a UK company providing training, consultancy and custom software for Linux and other embedded platforms. The videos can either be downloaded in webm HD format at http://free-electrons.com/blog/elce-2010-tutorial-videos/ or you can watch them in HD format below. The PDF slides for the three parts and the lab notes are available at http://elinux.org/images/c/cc/Linux-quick-start.tar.gz The first video (53 minutes) deals with the following key points: Genesis of a Linux project The four elements: Tool chain; boot loader; kernel; user space Element 1: Tool chain Element 2: Boot loader The second video (1h19m) focuses on: Third element: Kernel Fourth element: User space The last video (1h07m) is more practical as it shows how to use embedded Linux on an NXP LPC3250 Stick (ARM9): Description of the hardware Installing […]
MIPS Launches New Android and Linux Developer Community
MIPS Technologies announced the launch of its new Developer Community at developer.mips.com. The new site is specifically tailored to the needs of software developers working with the Android™ platform, Linux operating system and other applications for MIPS-Based™ hardware. All information and resources on the site are openly accessible. “This new community demonstrates our ongoing commitment to the vibrant open source effort around the MIPS cores and architecture, as well as around our customers’ and their customers’ hardware platforms,” said Art Swift, vice president of marketing and business development, MIPS Technologies. “As the MIPS architecture continues to expand into new high-volume markets such as mobile handsets and tablets, we see an increasing need for these resources among the growing MIPS developer community.” Software engineers can find development resources and tools on the site including: Android on MIPS source code, porting instructions, a native development kit (NDK) for Android applications development on […]
Boot Linux in 300 milliseconds
MakeLinux.com managed to boot Linux from the bootloader to console within 300ms using a customized (and minimal) version of Linux running on Beagleboard based on TI OMAP 3530 (Cortex A8) as per their Super Fast Boot project. Here’s the analysis of the boot sequence and timings: Logging starts at 70 ms from reset. Boot time from reset is 300 + 70 = 370 ms. Logging starts at 330 ms from power on. Cold boot time is 330 + 300 = 630 ms. Loading of 1.5 MiB Linux image from NAND takes 237 ms with throughput 6 MiB/s. Code execution takes 60 ms or 43M CPU cycles. (For other CPU frequency execution time is different, but the number of processor cycles is the same) The most time-consuming operation is coping firmware from NAND flash. They used a Linux 2.6.32 kernel from DVSDK 3.01, in a minimal configuration (900KB footprint), the boot […]
Video commemorating the 20th Anniversary of Linux
Linux is born in April 1991, with Linus Torvalds making it public with the following post on minix newsgroups: Hello everybody out there using minix – I’m doing a (free) operating system (just a hobby, won’t be big and professional like gnu) for 386(486) AT clones. … PS. Yes – it’s free of any minix code, and it has a multi-threaded fs. It is NOT protable (uses 386 task switching etc), and it probably never will support anything other than AT-harddisks, as that’s all I have :-(. Today, Linux is powering all kind of devices from supercomputer, stock exchange servers to smartphones, smart tv, cars and anything you can think of. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
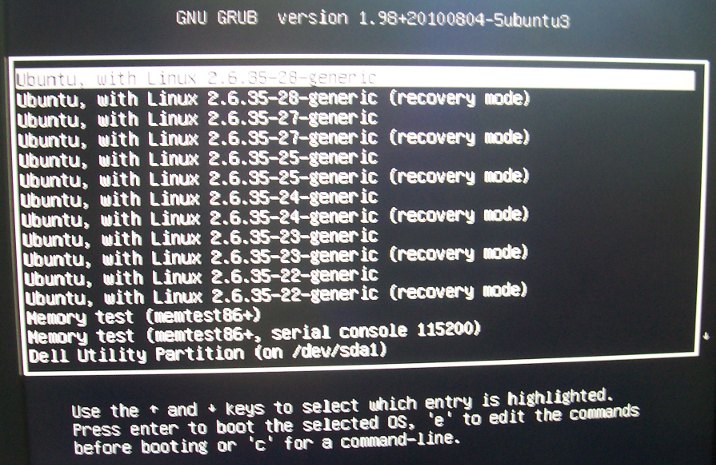
Removing Old Kernels in Ubuntu with Synaptic
If you have used Ubuntu for a while and performed upgrades, you may have quite a few kernels in GNU GRUB as shown below: Those kernels are usually not necessary, they take space on your hard disk and make you scroll down in GRUB to access your other OS (if any). I’ll show how to only keep the last 2 kernels (for safety) in GRUB with Synaptic. First, start synaptic as a superuser: sudo synaptic Select “System Administration“, in type “linux-image” in the Quick search field and show the installed kernel (green tick box). Then select the kernels you want to remove (keep the last 2 versions), right-click and select “Mark for Removal”. Synaptic Package Manager window should look like the screenshot below: After that, simply click on Apply and within a short time (one minute in my case), the selected kernel are removed. Removing 4 kernels, freed 429 MB […]
Phytec Texas Instruments OMAP4430 Computer Module
Phytec announced the first system on module based on Texas Instruments OMAP4430. The phyCORE-OMAP4430 features up to 1GB LPDDR2 DRAM, 1GB NAND Flash, one USB Host, one USB OTG port, Ethernet, I2C Interface, DSI and HDMI video output and consumes a maximum of 3 Watts only. Here are the full specifications of the phyCORE-OMAP4430 computer module: Texas Instruments OMAP4430 @ 1GHz PowerVR SGX540 GPU 56 KB On-chip SRAM and 512 MB (default) or 1 GB LPDDR2 DRAM 128, 256, 512 MB (default) or 1 GB NAND Flash 4 (default) or 32 KB EEPROM 2 SD/SDIO/MMC Expansion slot 4 UARTs, 1 RS232, 3 I2C, 1 I2S and 2 SPI/SSP serial connections. 1 USB Host and 1 USB OTG ports. 10/100 MBit Ethernet 2 x DSI, 1 x HDMI video output ports up to 1080p encode/decode and Touch screen support DVI/HDMI, PWM, Camera, Keypad, JTAG and RTC Dimensions: 41 x 51 mm […]
C Code to get MAC Address and IP Address
Function in C to return the MAC Address:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
/* Returns the MAC Address Params: int iNetType - 0: ethernet, 1: Wifi char chMAC[6] - MAC Address in binary format Returns: 0: success -1: Failure */ int getMACAddress(int iNetType, char chMAC[6]) { struct ifreq ifr; int sock; char *ifname=NULL; if (!iNetType) { ifname="eth0"; /* Ethernet */ } else { ifname="wlan0"; /* Wifi */ } sock=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM,0); strcpy( ifr.ifr_name, ifname ); ifr.ifr_addr.sa_family = AF_INET; if (ioctl( sock, SIOCGIFHWADDR, &ifr ) < 0) { return -1; } memcpy(chMAC, ifr.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data, 6) close(sock); return 0; } |
Function in C to return the IP Address:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
/* Returns the interface IP Address Params: int iNetType - 0: ethernet, 1: Wifi char *chIP - IP Address string Return: 0: success / -1: Failure */ int getIpAddress(int iNetType, char chIP[16]) { struct ifreq ifr; int sock = 0; sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); if(iNetType == 0) { strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, "eth0"); } else { strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, "wlan0"); } if (ioctl(sock, SIOCGIFADDR, &ifr) < 0) { strcpy(chIP, "0.0.0.0"); return -1; } sprintf(chIP, "%s", inet_ntoa(((struct sockaddr_in *) &(ifr.ifr_addr))->sin_addr)); close(sock); return 0; } |
Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
Setting Up an NFS Server in Ubuntu
You may need to setup an NFS server on Ubuntu to run and debug your program on your target platform or simply to share media files on the network composed of Linux clients. If you are using Windows clients, you would usually use SAMBA/CIFS, although it is possible to setup an NFS server in Windows as well using Windows Services for UNIX 3.5. Quick Guide to to setup an NFS server in Ubuntu without authentication. Install the required packages: # sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server nfs-common portmap Reconfigure and restart portmap: # sudo dpkg-reconfigure portmap # sudo /etc/init.d/portmap restart Edit /etc/exports: # sudo vi /etc/exports Add the directories to share with NFS and save the file, for example: /nfs 192.168.1.0/24(rw,no_root_squash,async) will give full read/write permissions to the nfs directory for computer in 192.168.1.0 subnet. Restart the NFS server: # sudo /etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server restart and reload the configuration: # sudo exportfs -a The […]