Earlier this week, the Linux Foundation announced yet another new Linux-based open source operating system for mobile and consumer devices based on Web standards called Tizen. This project is backed by Intel and Samsung who have already been involved with Linux based operating systems before, respectively with MeeGo and Bada. Both companies will be part of the technical steering team. It looks like Tizen will replace Meego overtime. Meego developers blasted the move and posted angry comments especially in relation to Qt support and the fact that all the previous work put into the project has probably gone to waste. My take is that using HTML5 is probably not such a bad ideas as many applications are currently developed in HTML5/Javascript for Chrome Webstore for example, and it could make porting those to Tizen straightforward. Tizen will support multiple device categories including: Smartphones Tablets Smart TVs Netbooks In-vehicle infotainment devices […]
How to Transfer files between Host and Qemu
I previously posted instructions to install and run nano and ARM Linux Internet Platform (ALIP) distribution images for Overo and Beagleboard on QEMU, If the image support networking, you could use ssh (install dropbear server in qemu) or nfs to transfer files between the host computer and qemu, or even run your program from the NFS share. This should be possible to do that on the Overo emulator since it support Ethernet. However, although I can access Internet, I cannot access the host via ssh as the host is in a private subnetwork (192.168.0.0) and qemu in another (10.0.2.0). We would probably have to enable bridge networking for that but the tun driver is apparently not compiled in ALIP kernel. I’ll look into that later on. [Update: Finally, we don’t need tun/tap to make this work, please read http://www.cnx-software.com/2011/10/02/how-to-transfer-files-between-host-and-qemu-via-ssh-and-nfs/ for details.] Today, I’ll just show how to mount a Qemu […]
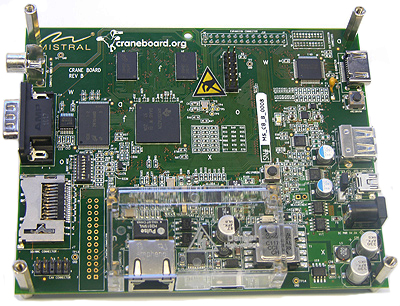
CraneBoard: Low Cost Development Board based on TI AM3517
The CraneBoard is a low-cost, open-source hardware development platform based on the AM3517 Sitara ARM Cortex-A8 microprocessor. The CraneBoard was announced in December 2010, can be purchased for 199 USD and can be an alternative to the Beagleboard-xM. AM3517 is especially suited to industrial applications and would be a preferable platform if your project needs CAN or PoE support. The board has less RAM (256 MB vs. 512MB) and no camera port. Here are the features and specifications of the board (I highlighted the differences with Beagleboard-xM in green): AM3517 Sitara ARM Cortex-A8 – 600MHz Integrated 3D Graphics Accelerator RAM: 256 MB NAND Flash: 256MB Support for on-chip peripherals: 10/100 EMAC USB OTG utilizing on-processor PHY 3.3V I/O CAN Bus DDR2 Power over Ethernet and other power options including USB and DC MMC/SD Card Support Fully open-source four-layer PCB Fully Open Source Linux Board Support package (2.6.32) Based on existing […]
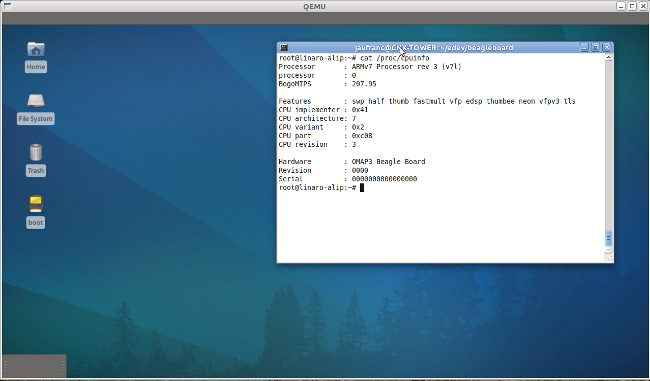
Beagleboard Emulator in Ubuntu with Qemu
If you just want to try a program on Beagleboard, but do not want (or have the means) to purchase a board, you may be able to use qemu to emulate the Beagleboard or BeableBoard-xM. I’ll details the instructions to run the Nano build (minimal kernel) and the ARM Linux Internet Platform (ALIP) distribution for Beagleboard on qemu. Please read the full post before starting the installation before there are currently some issues such as no Ethernet support. First, install or update linaro-media-create: sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linaro-maintainers/tools sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install linaro-image-tools Then download the nano image and omap3 hardware pack: wget http://releases.linaro.org/platform/linaro-n/nano/11.08/nano-n-tar-20110823-1.tar.gz wget http://releases.linaro.org/platform/linaro-n/nano/11.08/hwpack_linaro-omap3_20110823-0_armel_supported.tar.gz Generate the image for qemu: sudo linaro-media-create –image_file beagle_sd.img –dev beagle –binary nano-n-tar-20110823-1.tar.gz –hwpack hwpack_linaro-omap3_20110823-0_armel_supported.tar.gz If you don’t have it already, get the latest qemu-linaro package from Linaro Maintainers PPA: sudo apt-get install qemu-system Check the version is correct: qemu-system-arm -version QEMU emulator version […]
UEFI Secure Boot – Windows 8 vs Linux
Last week, Microsoft showcased Windows 8 PCs with super fast boot thanks to the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). The latest UEFI standard, released on April 8, includes a secure boot protocol which will be required for Windows 8 clients. Secure UEFI is intended to thwart rootkit infections by requiring keys before allowing executables or drivers to be loaded onto the device. Problem is, such keys can also be used to keep the PC’s owner from wiping out the current OS and installing another option such as Linux. It all started with slide 11 in one Powerpoint presentation entitled “Delivering a secure and fast boot experience with UEFI” presented by Arie van der Hoeven, Principal Lead Program Manager Microsoft Corporation during Build conference: Secure boot Current issues with boot Growing class of malware targets the boot path Often the only fix is to reinstall the operating system UEFI and secure […]
Open a File Directly at the Requested Line with Vi
When you compile a program and an error occur, the compiler will report the file name and line number with the error. Usually, I use vi to access the file, then type “:line_num”, for example if I want to jump to line 123, I would type :123 after opening the file. But there is a way to do that directly with vi by using +line_num. For example: vi +123 code.c To go to the last line, I would normally use the capital letter G when vi is started, but this can be done while opening the file as follows: vi +$ code.c One last tip: To go back at the top of the file in vi, simply use :0 or the capital letter H. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily […]
99 USD OMAP3 Based Overo Computer On Module by Gumstix
Gumstix has manufactured its Overo COMS based on OMAP3503 and OMAP3530 since 2008. They have now announced a new low cost version named Overa Sand that sells for 115 USD per unit or less than 99 USD per unit for orders of 1,000 units or more. Overo Sand COM is Gumstix’s most basic computer-on-module with 256MB RAM and no on-board NAND. Here are the board specifications and features: Processor: Texas Instruments OMAP 3503 Applications Processor: – ARM Cortex-A8 CPU @ 600 Mhz Memory: 256MB RAM NO On-Board NAND Included Features: microSD card slot TPS65950 Power Management Expandability: via one 140-pin expansion board of Gumstix Overo series or custom, 140-pin expansion board via 27-pin camera board Connections: – (2) 70-pin connectors with 140 signals for: – I2C, PWM lines (6), A/D (6), 1-wire – UART, SPI, Extra MMC lines – Headset, Microphone – Backup battery – High Speed USB Host and […]
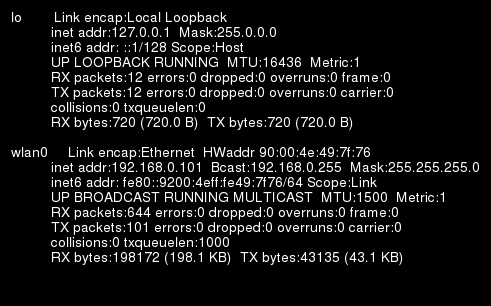
How-to Convert a Command Line Result into an Image in Linux
Here’s a technique to convert a command line result into an image in Linux using ImageMagick. You could also do a screenshot (with PrtSrc key) and use Gimp to trim the image, but this method is faster and does not require a graphical interface. The simplest command to convert the result of ifconfig into an image: ifconfig | convert label:@- cmd.png This will give an image with a white background and black text, but If you want to have a black background with white text you can use the following: ifconfig | convert -background black -fill white \ label:@- cmd.png If you want to change the font and the font size: ifconfig | convert -background black -fill white \ -font Helvetica -pointsize 14 \ label:@- cmd.png You can retrieve the list of fonts with this command: convert -list font | grep Font: Finally, use this command to add an extra […]