Emcraft Systems has open sourced its ports of U-Boot and uClinux for Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4 which are available on github at https://github.com/EmcraftSystems. This release supports the following platforms: ST Micro STM32F2 NXP LPC17XX Actel SmartFusion Freescale Kinetis You can check the source code as follows: uCLinux: git clone git://github.com/EmcraftSystems/linux-emcraft.git U-boot: git clone git://github.com/EmcraftSystems/u-boot.git The company has also designed systems on module (SoM) with enough memory to run Linux with Cortex M3/M4 micro-controllers: Freescale Kinetis K70 SOM Actec SmartFusion SOM ST Micro STM32 SOM You might find more details on building/using u-boot or uClinux on EmCraft documentation page (especially linux-cortexm-um-1.4.1.pdf) and you may want to check EmCraft website for details on available hardware and BSP for Cortex M3/M4 solutions. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later […]
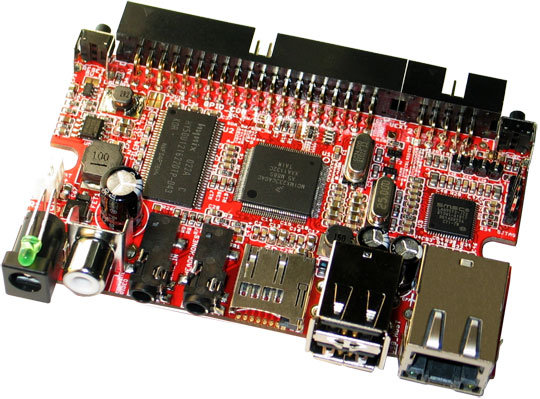
30 Euros Olimex iMX233-OLinuXino Linux Development Board
Olimex announced the first 10 prototypes of OLinuXino development board. Started in March of this year, OLinuXino is a development board based on Freescale i.MX233 aiming to provide a low cost (30 Euros) open source hardware and software single board computer to run Linux. Here are the specifications of OLinuXino single board computer: Freescale iMX233 454Mhz ARM9 processor 64MB of RAM Linux bootable image from SD-CARD TV-Video Output USB host for Keyboard, camera, WiFi, etc interfacing UEXT connector and GPIO connectors with the same style as DuinoMite so that developers can add external modules supporting Zigbee, Bluetooth, RFID readers, relays, switches, sensors, etc… The company also plans to provide 2 plug-in modules for this board: iMX-LCD – a 4.3″ TFT 24 bit color LCD with touchscreen (EUR 30) MX-HUB – A board adding 2 USB hosts and Ethernet (EUR 15) [Update: The company will actually make 2 versions of this […]
Ubuntu on AllWinner A10 based Mele A1000 Set-top Box
I’ve recently received and reviewed the 70 USD Mele A1000 STB powered by AllWinner A10, but haven’t been able to hack it yet since I’ve have not received the USB to Serial cable necessary for debugging the board. However, somebody else (Tom Cubie) had time to hack the box and run Ubuntu from a SD card (while still keeping Android in the flash) as you can see below. This port does not seem to include hardware accelerated GUI just yet, but this is definitely a step in the right direction. Tom said he just followed the instructions at http://rhombus-tech.net/allwinner_a10/hacking_the_mele_a1000/ and http://rhombus-tech.net/a10_mmc_boot/ to have Ubuntu working, but those do not appear to be that clear at the moment. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in […]
Second Release of Debian 6 for Raspberry Pi
As Raspberry Pi boards have started to ship this week, the Raspberry Pi foundation has also posted a new Debian 6.0 “squeeze” release to the downloads section of raspberrypi.org this week-end. This release contains several performance enhancements, including enabling the 128K system L2 cache for the first time, and first-cut ALSA drivers. Enabling the L2 cache will boost the ARM CPU performance, however, it may decrease the GPU performance. So this setup is ideal for headless server, but for other applications, for example a media player decoding 1080p30 videos, the performance might actually go down. This is still customizable, as the L2 cache can be enabled / disabled with enable_l2cache parameter in the config.txt file stored on the SD card. The ALSA drivers are here for audio support, so audio output might not have been supported in the first release (TBC), except if they used another type of audio drivers […]
Qt 5 for Raspberry Pi (QtonPi) 0.1 Release
Nokia Qt Labs has announced the very first release of Qt5 for Raspberry: QtonPi 0.1. QtonPi 0.1 includes a pre-alpha release of Qt 5, but Qt 5 alpha will be part of the next release. So bear in mind that it’s likely to be buggy and some features are missing. This release is includes: Base Layer Fedora RPM Packages plus some additional Raspberry Pi specific packages Linaro GCC 4.5.4 toolchain QtonPi image creator and sysroot tools Middleware Documentation on how to get toolchain + sysroot + Qt Creator working to Develop Apps Qt 5 running on full-screen EGFS mode The release can be downloaded via: BitTorrent – qtonpi-0.01.tar.bz2.torrent HTTP Download – qtonpi-0.01.tar.bz2 Alternatively if you are already running the Debian 6 image in the emulator or Raspberry Pi board, you can install the latest snapshot (e.g. nightly build) by adding deb http://archive.qmh-project.org/rpi/debian/ unstable main to /etc/apt/sources.list and run the following […]
ADLINK Technology SP-860 Smart Panel Computer Powered By TI Sitara AM3517
ADLINK Technology has recently unveiled the SP-860 Smart Panel, a panel computer combining an 8″ LCD and a TI Cortex A8 Sitara AM3517 processor with 256 MB RAM, 2GB flash, 2 Ethernet ports and WiFi/BT connectivity, targeted at industrial applications such as Point-of-Sales (POS), stationary displays, and outdoor/ruggedized operations. Here are ADLINK SP-860 Specifications: CPU – TI Sitara AM3517 Cortex-A8 processor @ 600 MHz with Power-VR SGX 3D graphics accelerator Main Memory- 256 MB DDR2 DRAM Storage – 2 GB NAND Flash (4GB Optional) + SD Card slot LCD – 8″ 4:3 panel, resolution: 800 x 3 (RGB) x 600 with LED backlight and an optional 4-wire resistive touch sensor. Ethernet – 1 internal LAN Port 10/100 Mbps MAC+PHY and 1 external 10/100 Mbps controller Wireless – Wi-Fi / Bluetooth IEEE 802.11b/g/n & BT 2.1 + EDR CAN BUS – Internal High-End CAN 2.0b Controller USB – 4x USB 2.0 […]
AMLogic Announces AML8726-MX Dual Core Cortex A9 Processor
Amlogic announced the availability of the AML8726-MX, a SoC based on a dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore processor clocked at 1.5 GHz with a Mali-400 MP GPU. It is the successor of the similarly named AML8726-M with a single core Cortex A9 @ 1 GHz. The company explains this SoC is particularly suitable for Over The Top (OTT) delivery, 3D Gaming and other Internet applications and targets the tablet, set-top-box and smart-TV markets. AMLogic AML8726-MX include 10/100/1000 Ethernet, 2x USB interfaces, 3-in-1 Card Reader support, Analog and digital video outputs, LVDS and T-CON (Timing Controller) with backlight control, digital video and camera interfaces. Wi-Fi is supported via external chipsets. Here are the highlights of the AML8726-MX family provided by AMLogic: A dual-core Cortex-A9 processor achieving over 7500 DMIPS of performance Direct to panel connection with advanced scaling, de-interlacing and picture quality enhancement Industry leading power management technology to extend battery life […]
Calixto Systems Announces TI AM335x VERSA SOM
Calixto Systems is a technology company based in Bangalore, India, providing System-on-Modules (SoM), evaluation boards (EVM) and consultancy services for Android, Linux and WinCE. The company has announced an update to its VERSA families of system-on-modules by including support for Texas Instruments Sitara AM335x processors. The previous version is based on TI OMAP-L138 C6-Integra DSP+ARM Processor. The AM335x SoM will provide higher performance than the previous module and targets industrial automation, smart grid, remote terminals, healthcare, handheld point-of-service (POS) terminals and weighing scales. Here are M335x VERSA SOM specifications: Texas Instruments AM335x (Cortex A8) processor @ 720 MHz with 3D Graphics Support (PowerVR) 256/512 MB of DDR3 SPI Flash Wireless LAN (b/g/n) (Optional) Bluetooth 4.0 (Optional) Two 10/100 Ethernet (One PHY on SOM) 24 bit LCD with Touch Screen interface 2x USB 2.0 OTG, 2x CAN, 4x UARTs McASP, PRU , SPI, I2C etc. 200 pin SODIMM connector Dimension: 34mm x […]