LinuxCon (North America) 2012 will take place on August 29 – 31, 2012 at Sheraton Hotel & Marina, in San Diego, California. The event will be co-located with the Linux Kernel Summit, the Linux Plumbers Conference, and CloudOpen 2012. LinuxCon consists of 3 days of keynotes, business and developers related sessions as well as tutorials. There will be over 80 sessions and keynotes during those 3 days. I’ll highlight a few sessions that I find particularly interesting and related to embedded Linux, software development and ARM. August 29 10:45 – 11:30 – Life After BerkeleyDB: OpenLDAP’s Memory-Mapped Database by Howard Chu, Symas Abstract: OpenLDAP’s new MDB library is a highly optimized B+tree implementation that is orders of magnitude faster and more efficient than everything else in the software world. Reads scale perfectly linearly across arbitrarily many CPUs with no bottlenecks, and data is returned with zero memcpy’s. Writes are on […]
Stella Mira Pocket Console AllWinner A10 mini PC with Built-in Bluetooth and Up to 128 GB Flash
Stella Mira, a new technology startup, has come up with a new Android mini-PC based on AllWinner A10 (how original!) called the Pocket Console (aka MiraPC). What makes it stand apart is that it comes with built-in Bluetooth, has several versions based on the NAND flash size: 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, 64 GB and even 128 GB, and the company plans to release a 3G version in September. The company also provides a dock, the Stella Mira Pocket Dock, that comes pre-loaded with one of supported Linux distributions, without the requiring the knowledge and time to configure microSD card for Linux. The company will provide 4 Linux distributions: Ubuntu 12.04 (Custom build – Ready) Lubuntu 12.04 (Custom build – Ready) Xubuntu 12.04 (Custom build – Final stage of development) Fedora 17 XFCE (Not officially supported, but backed by a large development community) Beside running Linux, the Pocket Console can also “run […]
VIA Announces VIA VAB-800 Pico-ITX Board Based on Freescale i.MX537 Processor
VIA Technologies has announced the VIA VAB-800 Pico-ITX board powered by a Freescale i.MX537 (ARM Cortex A8) processor clocked at 800MHz or 1GHz depending on the requirements, with 1GB DDR3-800 SDRAM and support for eMMC Flash with a capacity of up to 64 GB. The VIA VAB-800 is an industrial board that can operate in a wide temperature range and targets high-end industrial and in-vehicle embedded applications. Here are the specs of the board: Processor – Freescale Cortex-A8 single core iMX537 @800MHz System Memory – 1GB DDR3-800 SDRAM, using 128M x16 memory devices Flash – eMMC Flash, up to 64GB Graphics – Supports two independent, integrated graphics processing units: an OpenGL® ES 2.0, 3D graphics accelerator and an OpenVG™ 1.1 2D graphics accelerator Ethernet – SMSC LAN8720A 10/100 PHY transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX support Audio – Freescale SGTL5000 low power stereo codec with headphone amp HDMI – Silicon image SiI9024A […]
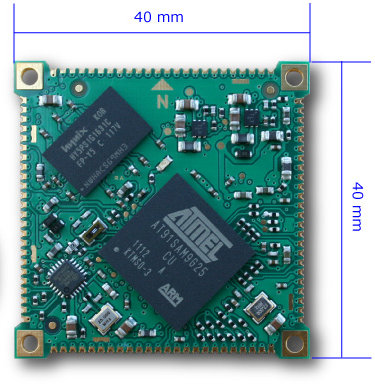
24 Euros Aria G25 Atmel SAM9 (ARM9) Linux Embedded Module
ACME System, an Italian company specializing in low-cost microprocessor boards, has designed the Aria G25, a tiny system-on-module (SoM) based on Atmel SAM9G25 for Linux embedded devices, that will be available in August and sell for 24 Euros (128 MB RAM version) and 29 Euros (256 MB RAM). Here are Aria G25 specifications: CPU – Atmel AT91SAM9G25 (ARM9) @ 400Mhz CPU System Memory – 128MB (G25-128) or 256MB (G25-256) DDR2 RAM Connectivity – 10/100 Mbit Ethernet interface USB – Up to 3 USB 2.0 host ports (2 Hi-Speed, 1 Full-Speed) Interfaces: Up to 6 serial lines 2x I2C buses 2x SPI buses 60 GPIO lines 4x A/D lines @ 10 bit Dimensions – 40 x 40 mm Operative temperature range – 0-70 °C (but they also plan to release an industrial temperature range SoM) Power – 3.3V | Consumption: 0.3 Watt The company will provide a Debian Linux distribution with […]
Linux 3.5 Release
Linus Torvalds has announced the release of Linux Kernel 3.5: Subject: Linux 3.5 released Ok, not a lot happened since -rc7. There’s a number of MIPS commits (for some reason MIPS has had a horrible track record with the -rc time schedule, I suspect I should just stop pulling late in the game), but most of the rest is pretty small. A couple of dm/md fixes, some gma500 work, make kgdb ‘dmesg’ command work again, some networking fixes, some xfs and cifs noise, yadda yadda. About 50% of the patch is actually the SPEAr clock name renaming that is just some search-and-replace. … Linux 3.4 brought updates to Btrfs file system, some new Intel, AMD and NVidia GPU drivers, X32 ABI, perf tool improvements and support for Yama security module and QNX6 file system. Linux 3.5 brings the following key changes: ext4 metadata checksums: Ext4 has added the ability to […]
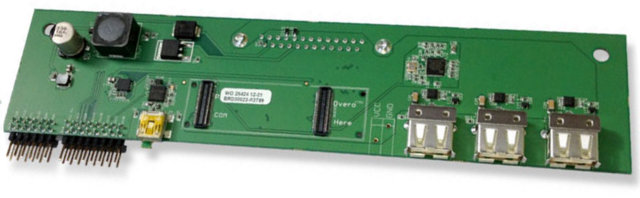
Gumstix TurtleCore Expansion Board for iRobot Create
Last month, Gumstix announced the TurtleCore expansion board for iRobot Create Programmable Robot, featuring 3 USB ports, several male-header pins with GPIO access, as well as standoffs and screws to support the TurtleCore in the Create cargo bay.. The TurtleCore is a baseboard for TI OMAP3 and Sitara based Overo COMs or Overo STORM series of COMs that replaces the Command Module on iRobot Create to provide a more flexible and powerful solution. Overo COMs have very good Linux support (OpenEmbedded) with source code, tools and documentation available, including support for the Robot Operating System (GumROS) for high level programming. They released the hardware early so that the community could work on the software, and there have been some good progress as you can see from the video below. You can already download the schematics and PCB layout file, but the software and instructions do not appear to be available […]
Nightly Builds for AllWinner A10 U-boot, Linux Kernel and Hardware Packs
Kent of SCUZ Technologies has graciously provided a build machine (Intel Xeon E5645) for Rhombus Tech (and possibly other) open source projects, and I’ve setup nightly build scripts for AllWinner A10 kernel, bootloader (u-boot) and hardware packs for Mele A1000 (HDMI), Mele A1000 (VGA), A10 mini PCs (using MK802 script.bin) as well as a server build for Mele A1000. The nightlies are built using a10-hwpack-bld.sh script which is available in github, and can be downloaded from http://dl.linux-sunxi.org/nightly/ The resulting files are copied to a dropbox folder, until a better solution is found. For each build, you’ll find the following files : u-boot.bin – U-boot sun4i-spl.bin – U-boot SPL uImage – Kernel image product_YYYY.MM.DD.log (e.g. mele-a1000_2012.07.20.log) – The build logs whether the build succeeds of fails. One per hardware pack. product_hwpack_YYY.MM.DD.log ( e.g. mele-a1000_hwpack_2012.07.20.7z) – The hardware pack with the kernel, u-boot which can be used with a1x-media-create.sh script to create […]
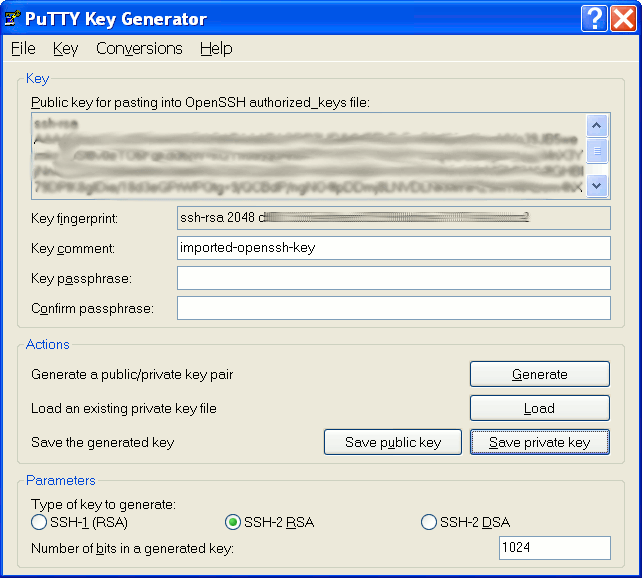
How To Use Putty with an SSH Private Key Generated by OpenSSH
I have access to a remote server where I am only allowed to login via SSH with a key, and I can’t add an extra key by myself, as described in “No Password SSH” post. The private key (RSA) has been generated with ssh-keygen in Linux, and I can login from Linux without issue. This morning, I wanted to do the same with Putty in Windows XP, so I just copied the private key to Windows and loaded it in Putty, but it failed:
|
1 |
Unable to use key file "F:\Downloads\cnxsoft\a1000\id_rsa" (OpenSSH SSH-2 private key) |
After a few minutes of research, I found my answer on UbuntuForums, and the reason it fails is because Putty does not support openssh keys, but uses its own format. Here’s what I had to do: Convert OpenSSH private key to Putty private key with Putty Key Generator (puttygen) Start puttygen, and click on Conversions->Import key, then click Browse and select the private key generated with […]