I previously wrote about different options available to run Linux on Cortex M3 & M4 Microcontrollers, and more recently Vladimir Khusainov, co-founder and Director of Engineering at Emcraft Systems,wrote a longish article entitled “Practical Advice on Running uClinux on Cortex-M3/M4” on electronicdesign.com, where he explains how SoM are usually selected, the costs of running uClinux on Cortex M3/M4 MCUs such as Freescale K70 or STmicroelectronics STM32F2/F4, as well as performance and power consumption considerations. First, Vladimir addresses one comment that says there’s basically no use for uClinux on Cortex M3/M4 MCU, since external memory is needed and an ARM7/ARM9 modules (with MMU) can be purchased for almost the same price. There are 2 counter arguments to this point of view: In practice, customers usually select an hardware platform first, then think what OS can be used on the platform. For example, if a company decided to use an hardware based […]
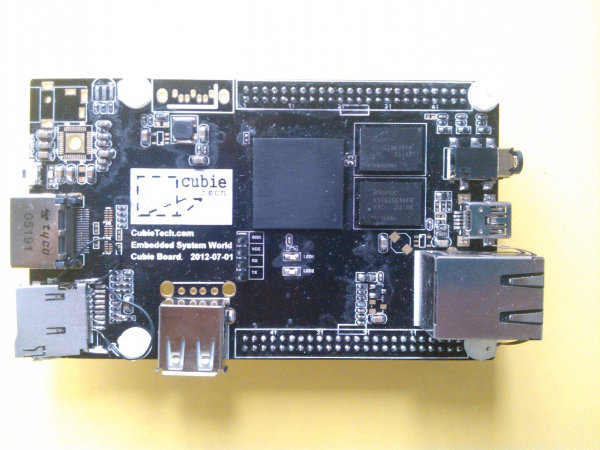
$49 Cubieboard: AllWinner A10 Open Hardware Development Board
The Cubieboard is a development board for the AllWinner A10 Cortex A8 processor. Contrary to some other AllWinner A10 “development board” that are simply based on a tablet or mini PC PCB, the cubieboard has been designed specifically as a development platform and provides access to I/O pins. Here are the specs of this development board: SoC – AllWinner A10 1GHz ARM cortex-A8 processor with Mali400 GPU System RAM – 1GB DDR3 @400MHz Storage – 2 MMC slot Video Output – HDMI 1080p Connectivity – 10/100M Ethernet USB – 2 USB Host, 1 USB OTG 1 IR sensor 96 expansion pins including i2c, spi, lvds, sata… Wi-Fi and Bluetooth can be supported via external USB dongle(s). The prototype above is the first revision of the hardware, and final hardware may look different. Some connectors (e.g. SATA) are not soldered in the picture above. The cubieboard is expected to be an […]
Linaro 12.08 Release with Kernel 3.6 and Android 4.1.1 Jelly Bean
Linaro release 12.08 includes Linux Kernel 3.6-rc2 and is the very first release with Android Jelly Bean (4.1.1-R4). The Android platform team has managed to port Android Jelly Bean to all their main development platforms: Versatile Express, Versatile Express RTSM, Samsung Origen, TI PandaBoard, ST Ericsson Snowball, as well as Samsung Galaxy Nexus smartphone. They’ve also added TINY_ANDROID, a minimal Android build that can be used for kernel development, toolchain work and other development where users only need a console. It’s possible to get the source code, build it and access the shell within 10 minutes. U-boot-Linaro has been updated and is now based on the latest upstream release v2012.07. Next month, we might be able to see a preliminary port of Android on 64-bit platform (ARMv8). Here are the highlights of the release: Android Automated Methanol (http://gitorious.org/methanol) browser benchmarking in Linaro Android. Automated over 100 Jelly Bean AOSP tests. […]
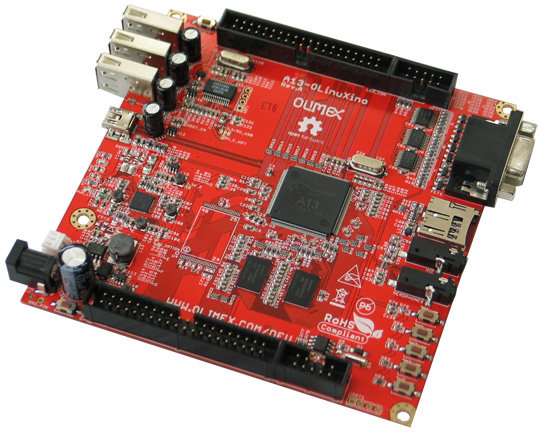
Olimex A13-OLinuXino-WIFI Developer Edition is Now Available
Olimex has announced that they started shipping A13-OLinuXino-WIFI-DEV, an AllWinner A13 development board with 512 MB, 4GB and a Realtek RTL8188CU Wi-Fi module that costs 55.00 Euros with free shipping by courier for a limited time. They announced the start of this project late April, so it took them just 3 months to bring this board to to market. The board has the following specs: SoC – AllWinner A13 Cortex A8 processor at 1GHz, 3D Mali400 GPU Memory – 512 MB RAM Storage – 4GB NAND flash + SD Card slot Power – 6-16VDC input power supply, noise immune design USB – 3 + 1 USB Host, 3 available for users and 1 for Wi-Fi module + 1 USB OTG port Wi-Fi – WIFI RTL8188CU 802.11n 150Mbit module on board Video output – VGA video output + LCD signals available on connector. Audio Output / Input RTC – PCF8536 on […]
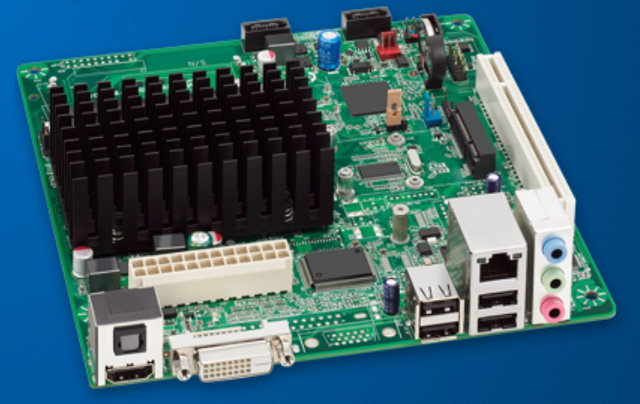
Intel to Give Away 5 Atom D2700 Development Kits to Selected Engineers
As part of its “Eureka! Design Challenges“, Intel is asking hardware engineers to submit ideas about what they’ll do with an Intel Atom D2700 development kit with 2Gb RAM, a 40 GB SSD drive & lots of ports and expansions, and will give one to the 5 candidates with the best project ideas. Here are the key features of this development kit: Development board with the Intel Atom Processor D2700, and IntelNM10 Express Chipset Board Support package from the Linux Foundation’s Yocto Project 2GB DDR21066 MT/s non-ECC memory 40GB SSD, installed, with SATA extension cable Power supply The Intel Software Development Tool Suite (GNU tool compatible) Documentation and software Comes in a mini-ITX chassis with dual independent display capabilities. I’m not sure why Intel is focusing on hardware engineer for this type of project, and I suppose if you have some embedded systems development ideas that interface with external hardware, […]
More AMLogic AML8726-MX Source Code Released by Ainol
Last week, I found out that AMLogic released the kernel source code for AML8726-MX, its dual core Cortex A9 processor, but this code is only for the “common” platform, and some source code specific to tablets or media players is missing (e.g. some drivers). But today, Ainol released the source code for the Ainol Novo 7 Elf II and Aurora II tablet, both of which are based on on AML8726-M6 dual core processor: Ainol Novo 7 Elf II Source Code (2 GB) – http://dl.vmall.com/c0yqzpadah Ainol Novo 7 Aurora II source code (2 GB) – http://dl.vmall.com/c0imlixp7d The files are pretty big, and the download very slow on my side (“1 day, 16 hours remaining”), so I’ll probably have to give up. I assume “fards” will import the source code into a new repo in his github account. Anyway, this potentially makes AMLogic AML8726-MX a very interesting development platform, although we’ll have to […]
QuickEmbed UPuter Pi – $69 AllWinner A10 Development Board
I’ve been informed of a new AllWinner A10 development board which is marketed as some sort of Raspberry Pi “clone”, although the hardware is different. The UPuter Pi is a small board designed by QuickEmbed Technology, a Shanghai based company, that features AllWinner A10 processor @ 1.5 GHz, 512 to 1 GB RAM, and 4 to 8 GB Flash. Here are the specs as mentioned on the company website: CPU 1.5GHz ARM Cortex-A8 multi-core Mali400 graphic engine Memory 512M/1GB DDR3 Flash 4G/8G DC 5V USB power working temperature -10 to 70C storage temperature -20 to 80C Android 4.0 WIFI/RJ45 network USB/Wireless keyboard/mouse 3G usb card TF card, U-disk, usb harddisk 720P/1080P/2160P I must have gone blind because I don’t see any RJ45 connector (for Ethernet). The board will support Android 4.0 and all the usual Linux distros supported by Allwinner A10 processor. QuickEmbed may have pushed the clone concept a […]
MPEG2 and VC-1 Codecs, H.264 Encode and HDMI CEC Are Now Available for the Raspberry Pi
Many people appear to have bought the Raspberry Pi in order to use it as a cheap media player by installing distributions such as Raspbmc or OpenElec. The only problem is that this low cost board was primarily designed as an educational platform, so the Raspberry Pi foundation only paid for H.264 licensing, which means you could only playback H.264 videos, and all other video codecs could not be played (by hardware) making it a rather poor media player. But things have improved, as the good people at the Raspberry Pi foundation have worked out a deal with the licensing organizations and now offer support for 2 new codecs: MPEG2 license key – 2.4 GBP (~3.8 USD) VC-1 license key – 1.2 GBP (~1.9 USD) Once those 2 codecs are enabled you should be able to play your DVD rips and most HD wmv files smoothly. The way it work […]