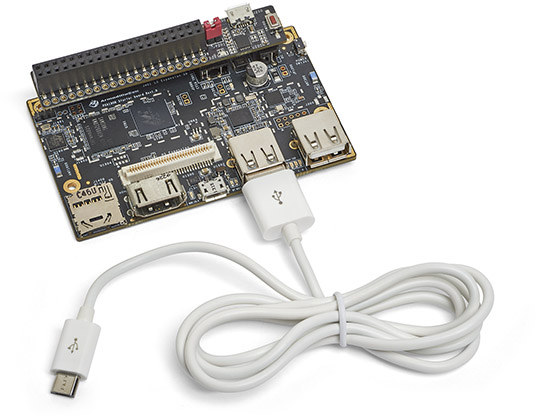
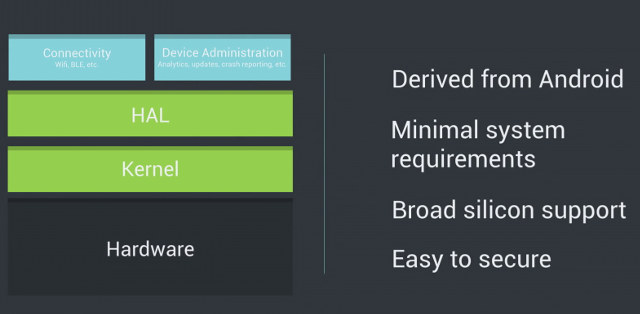
Karim Yaghmour – founder of Opersys, a company specializing in Embedded Linux and Android training and development – is currently at Android Devcon 2016 were he gave a full day Embedded Android Workshop on August 1st, as well as a separate 1+ hour talk about Brillo/Weave internals on August 2, and more talks scheduled on the next two days about Android memory management, debugging and development, and Project Ara. He has just released the presentation slides on Slideshare, with the first “Embedded Android Workshop with Marshmallow” presentation totaling 175 pages, and dealing with Linux and Android concepts, overall architecture, system startup, the Linux kernel, hardware support, native user-space, Java for Android, JMI, AOSP, and more… The second presentation is much shorter with 29 slides, and deals specifically with Brillo / Weave internals including Embedded Linux, Android, Binder, DBUS, HAL, the source tree architecture, and so on. While you’d probably learn […]
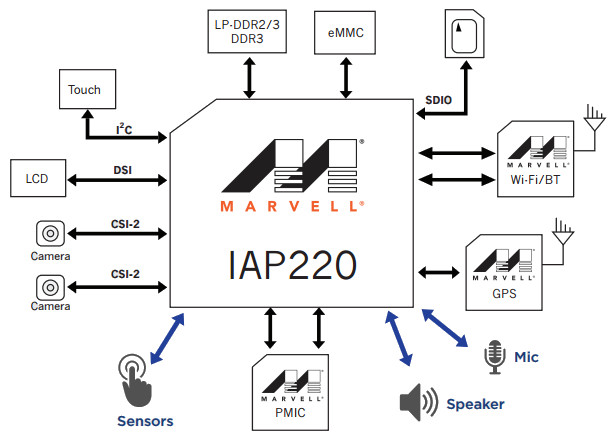
Marvell IAP220 “IoT” Processor Targets Low Power Touchscreen Enabled Appliances
After IAP140 quad core Cortex A53 processor found in Brillo compatible AndroMeda Box Edge, Marvell has recently introduced another IAP processor for the Internet of Things with IAP220 dual core Cortex A7 processor targeting “low power cost sensitive home automation, industrial, security, and wearable applications”. IAP220 SoC specifications: Processor – Dual ARM Cortex-A7 core up to 1.0 GHz GPU – 3D GPU with OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0 support MCU – ARM Cortex M4F Memory I/F – LP-DDR2/3, DDR3 Storage – eMMC and SDIO interfaces Display – MIPI video and command mode; LCD display Video – Full HD encode and decode with H.264, MPEG-4, H.263, MJPEG and more Camera – Digital video camera interface, 2x, 2-lane CSI Audio – I2S, TDM; support for multiple PDM (pulse-density modulation) microphones and speakers Sensor hub • Low power sensor processing Management I/O – SPI, GPIO, PWM? (the product brief says PWD instead), UART, 1-wire, I2C […]
Embedded Linux Conference 2016 and OpenIoT Summit 2016 Schedule
The Embedded Linux Conference 2016 and the OpenIoT summit 2016 will take place on April 4 – 6, 2016 in San Diego, California, and over 800 attended will meet including kernel & system developers, userspace developers, and product vendors. The Linux Foundation has recently published the schedule, so I’ve had a look at some of the talks, and designed my own virtual schedule to find out more the current development focus although I won’t attend. Monday April 4 10:40am – 11:30am – Linux Connectivity for IoT by Marcel Holtmann, Intel OTC There are many connectivity solutions that available for IoT. For example Bluetooth Low Energy, 802.15.4, Zigbee, OIC, Thread and others. This presentation will provide and overview of the existing technology and upcoming standard and how they tie into the Linux kernel and its ecosystem. 11:40 – 12:30 – BoF: kernelci.org: A Million Kernel Boots and Counting by Kevin Hilman, […]
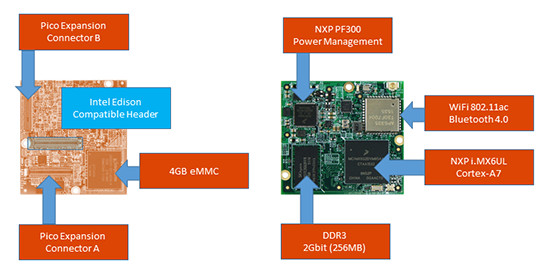
Wandboard Introduces $69 Hobbitboard Made for Brillo Powered by NXP i.MX6 UltraLite Processor
Wandboard was one of the first to launch boards based on Freescale i.MX6 Solo, Dual and Quad in early 2013. The boards are comprise of an EDM system-on-module and a carrierboard, that makes it not only suitable as a single board computer, but you could also use the boards to start developing software, while making your own carrierboard to match your application. Wandboard.org community sent me an email last night to let me know about their latest board called Hobbitboard, or in full “Hobbitboard Made for Brillo”, powered by NXP i.MX6 UltraLite Cortex A7 processor, which follows the same principle, and includes Hobbit Compute Module and Hobbit I/O Carrierboard. Hobbit Compute Module specifications: SoC – NXP i.MX6 UltraLite Cortex A7 processor @ 528 MHz System Memory – 256MB DDR3 Storage – 4GB eMMC flash Connectivity – 802.11ac WiFi and Bluetooth 4.0 (Ampak AP6335) Board Connectors – Two Pico Expansion header […]
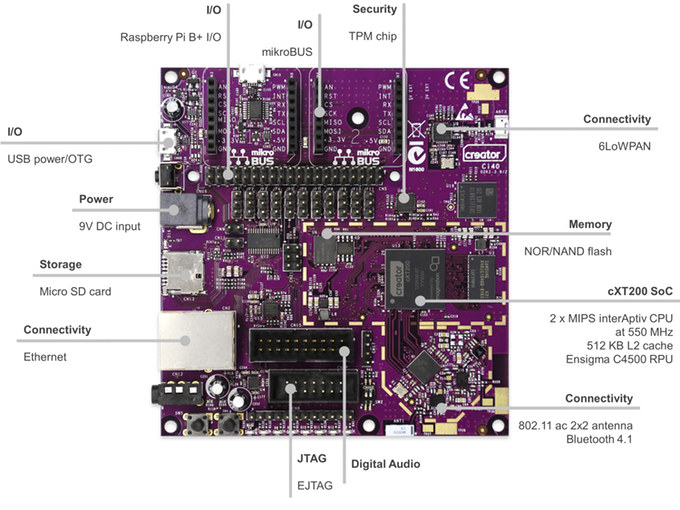
MIPS Creator Ci40 Development Board Powered by cXT200 SoC Launched for $53 on Kickstarter
Last year, Imagination Technologies launched their first community development board with MIPS Creator CI20 powered by Ingenic JZ4780 dual core MIPS processor running both Android and Linux, and now supported by various projects. The company has been teasing about its MIPS Creatort Ci40 for a few weeks, and was already announced as the MIPS platform of choice for Google Brillo operating system, but the board has now officially been launched via a Kickstarter campaign where you can get the board for $53, as well as some add-on boards. But instead of using a processor from one of their partner, Imagination just designed their own MIPS interAptiv SoC for the board. Creator Ci40 board specifications: SoC – Imagination Technologies Creator cXT200 with 2x MIPS interAptiv core @ 550MHz, 512KB L2 cache, and an Ensigma C4500 RPU (for 802.11ac/ BT 4.1 LE) System Memory – 256 MB DDR3 Storage – 512 MB […]
How to Build Brillo Operating System from Source Code and Run Brillo Emulator
Google formally launched Brillo operating system a few weeks ago. The new operating system is a stripped down version of Android that targets Internet of Things (IoT) applications, and more recently the company pushed the source code to their servers. So I’ve given it a try by checking out the code, building Brillo emulator for Intel/AMD, and running it in Ubuntu 14.04 64-bit. First you’ll need to retrieve the source code:
|
1 2 3 4 |
mkdir brillo-master cd brillo-master repo init -u https://android.googlesource.com/brillo/manifest -b master repo sync -j8 |
It took a few hours here with some errors the first time, so I tried again and I finally got the code a few hours later. Once this is done, set the build environment and configuration:
|
1 |
source build/envsetup.sh && lunch |
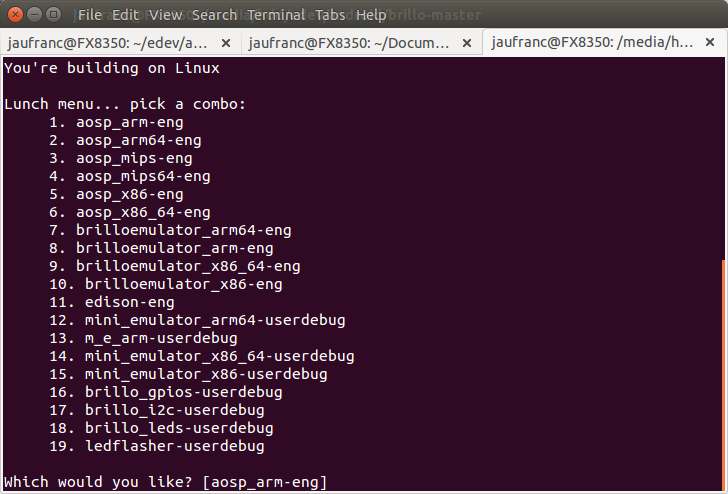
Lunch will bring a list of possible builds:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
You're building on Linux Lunch menu... pick a combo: 1. aosp_arm-eng 2. aosp_arm64-eng 3. aosp_mips-eng 4. aosp_mips64-eng 5. aosp_x86-eng 6. aosp_x86_64-eng 7. brilloemulator_arm64-eng 8. brilloemulator_arm-eng 9. brilloemulator_x86_64-eng 10. brilloemulator_x86-eng 11. edison-eng 12. mini_emulator_arm64-userdebug 13. m_e_arm-userdebug 14. mini_emulator_x86_64-userdebug 15. mini_emulator_x86-userdebug 16. brillo_gpios-userdebug 17. brillo_i2c-userdebug 18. brillo_leds-userdebug 19. ledflasher-userdebug Which would you like? [aosp_arm-eng] 9 |
You could also run the “Brillo emulator” on ARM, and edison-eng must be the build for Intel Edison board. Now you can start the build:
|
1 |
make -j8 |
It has to complete 21491 different tasks, […]
AndroMeda Box Edge Brillo Starter Board Features Marvell IAP140 Processor, 96Boards Form Factor
Google announced Brillo, a new operating system based on Android and targeting the Internet of things, at the end of October. The company also disclosed that ARM, MIPS and x86 architectures were supported via respectively TechNexion Pico-i.MX6UL system-on-module and PICO-DWARF baseboard, MIPS Creator CI-40 board, and Intel Edison development board. A few days later, Marvell announced Andromeda Box, an IoT platform supporting Brillo and Weave, based on IAP140, a quad-core ARM Cortex A53 application processor for the “Edge” version, and ARMADA 385 dual core Cortex A9 processor for the “Connect” version, but without the full details. AndroidMeda Box Edge is now listed on Solid Run and Arrow websites, where it is sold for $74.99. If the board looks familiar, it’s because it clearly follows 96Boards form factor, but instead of officially being supported by Linaro, it has been designed specifically as a Google’s Brillo development platform with the following specifications: […]
Brillo Android based OS for IoT Projects Supports ARM, Intel and MIPS Platforms
You’d think there are already enough lightweight operating systems that could provide a good enough platform for IoT and embedded projects, but Google decided to make their own Brillo operating system for IoT, based on Android, most probably to leverage the existing Android tools, and make it easier for app developers to move to the Internet of Things space. Brillo ‘s hardware requirements are pretty low as the operating system can run on devices with 32MB of RAM, and 128MB of storage. Google will provide a complete ecosystem with an embedded OS, core services, and a developer kit with tools to build, test, and debug. Just like in Android, three architectures will be be officially supports, starting with the following hardware platforms: ARM – TechNexion Pico-i.MX6UL system-on-module based on Freescale i.MX6 UltraLite and Broadcom BCM4339 802.11ac + Bluetooth 4.0 wireless module, combined with PICO-DWARF baseboard. MIPS – Upcoming MIPS Creator […]