I’ve already written some posts with videos showing the many things you could do with your smartphone thanks to MHL Technology. Christian Qantrell (YouTube User) uploaded a video on YouTube where he connected his smartphone to a monitor with a MHL cable showing how it could be used as a desktop computer. I really like his setup with a Samsung Galaxy Nexus (Android 4.0) smartphone connected to a monitor with an MHL adapter (Micro-USB to HDMI) and Apple Bluetooth keyboard and (Magic) trackpad. He also mentioned external power, but this should not be needed if his monitor supported MHL. The Apple trackpad makes it very neat as it tracks the finger movements as it would if you used the smartphone touchscreen. He showed web browsing and music playback and said gmail works great. Thanks to the multi-touch trackpad, pinch and zoom also works. Overall, the user experience feels pretty good. […]
ARM Mali-200 and Mali-400 GPU Open Source Driver Released
There has been a lot of controversy around GPU drivers and open source, as GPU drivers usually come with a blob (a binary file). If you have been lurking in Raspberry Pi forums you’ll know what I mean. But this will change thanks to Lima. No, not the capital of Peru but the open source graphics driver for ARM Mali GPUs (Mali-200 and Mali-400) also called Lima whose goal is stated as follows: The aim of this driver is to finally bring all the advantages of open source software to ARM SoC graphics drivers. Currently, the sole availability of binary drivers is increasing development and maintenance overhead, while also reducing portability, compatibility and limiting choice. Anyone who has dealt with GPU support on ARM, be it for a Linux with a GNU stack, or for an Android, knows the pain of dealing with these binaries. Lima is going to solve […]
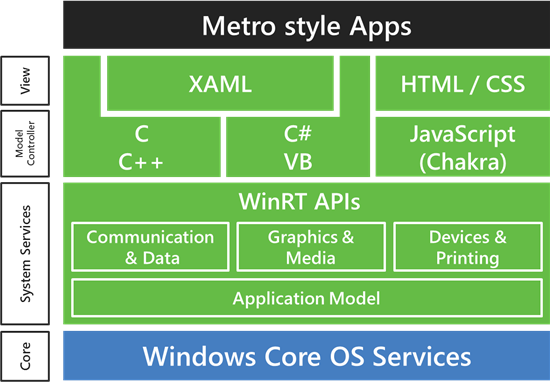
Microsoft Provides Windows 8 On ARM Technical Details
Steven Sinofsky, President of the Windows Division at Microsoft, has written a long blog post entitled “Building Windows for the ARM processor architecture” where he explains how Windows On ARM (WOA) will be deployed, the steps they took to develop it and what developers can do to program or port existing apps to Windows 8. Here are some keys and interesting points I noted: WOA and Windows 8 for x86/64 PCs will ship at the same time and the user experience should be the same for consumers on both platform. WOA PCs will be powered by Texas Instruments, Nvidia and Qualcomm processors. Microsoft will release an Unified OS Binary for WOA – That means one binary will run on all platforms (be it TI, Nvidia or Qualcomm). That seems impressive, and something Linux is not capable of, although much work is done on that and a unified linux kernel should […]
Android Kernel Source Released for HP TouchPad
The CyanogenMod team has been working on an Android port for the HP TouchPad for a while, and although good progress has been made, the firmware is still considered alpha due to issues with hardware and driver support. There are 2 versions: CM 7 (Alpha) with Android 2.3 and CM 9 (Alpha) with Android 4.0. The CM7 version is more complete and stable than CM9. The Android port might be sped-up as following pressure from the developer community, Hewlett Packard has released the Android kernel source and some other GPL packages modified for the HP TouchPad. Apparently, HP used those for factory testing. The source code is available on github at https://github.com/dalingrin/hp-kernel-tenderloin/tree/hp-topaz-android “green” user at rootzwiki built the kernel binary which is available at http://crimea.edu/~green/TP/oss-db910-QC1065-Kernel.tar.bz2 They also have the source code for: androidvncserver: http://crimea.edu/~green/TP/oss_db910_vnc.tar.bz2 i2c-tools: http://crimea.edu/~green/TP/oss_db910_i2c.tar.bz2 Apparently all components needed are available, except the wifi driver (Atheros AR6003), which HP […]
Yocto Project Quick Start Guide for Ubuntu
Yocto is an embedded Linux build system used to create a Linux distribution for a specific application/board combination. I’ll describe 2 methods to get started: Building and running a qemu image for x86 from scratch Using pre-built binaries to run the x86 image in qemu This is a shorter version of the longish Yocto Project’s Quick Start Guide. The official guide is more complete (explains all details) and give instructions for several distributions, whereas this guide simply lists each step and is focused on Ubuntu. So you could use this guide to start the build, and during the build (which will last a while), read the official guide to actually understand how it all works. Prerequisites First, you need to use bash instead of dash in Ubuntu:
|
1 |
sudo dpkg-reconfigure dash |
and select “No” to use bash. Then install the required packages with apt-get:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
sudo apt-get install sed wget cvs subversion git-core coreutils \ unzip texi2html texinfo libsdl1.2-dev docbook-utils gawk \ python-pysqlite2 diffstat help2man make gcc build-essential \ g++ desktop-file-utils chrpath libgl1-mesa-dev libglu1-mesa-dev \ mercurial autoconf automake groff libtool xterm |
Building and running a qemu image for […]
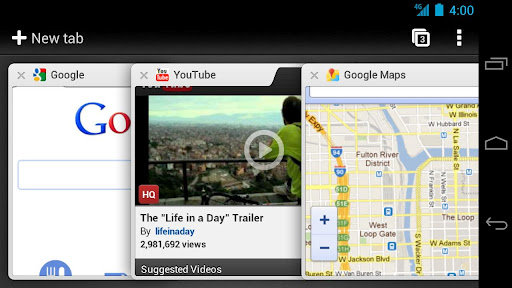
Google Releases Chrome for Android (Beta)
Google has introduced the beta version of Chrome for Android, bringing Chrome’s capabilities to smartphones and tablets running Android 4.0 (but not earlier versions). The key features of Chrome for Android: View open tabs: Access the tabs you left open on your computer (also signed into Chrome)—picking up exactly where you left off. Swipe on your mobile device to switch between tabs. Get smarter suggestions: If you visit a site often on your computer, you’ll also get an auto-complete suggestion for it on your mobile device, so you can spend less time typing. Sync bookmarks: Access your favorite sites no matter which device you are using. You can watch the teaser video below. On the technical side, Chrome for Android brings support for many of the latest HTML5 features to the Android platform including hardware-accelerated canvas, overflow scroll support, HTML5 video. Chrome for Android also brings new capabilities such as […]
Pengutronix uCLinux 3.2 for Energy Micro EFM32 Cortex-M3 Gecko MCUs
Energy Micro and Pengutronix announced that they will be demonstrating µClinux for Cortex-M3 on the EFM32 Gecko range (Leopard and Giant) of MCU during Embedded World Conference 2012 on 28 February – 1 March 2011 in Nuremberg, Germany. Pengutronix’s port of µClinux features the Linux 3.2 kernel, providing the cost and time-to-market benefits of Linux operating system, while maintaining low current consumption of just 1.6mA when in idle mode. The company explains that using µClinux reduces design cycles and accelerates time-to-market by giving the designer access to ready-made system functions such as IP connectivity, file systems, and multi-tasking. Users can also employ the broad range of free software and drivers available as open source, within a robust, portable open source framework. The teaser video (below) shows that the demo platform (Giant Gecko Development Kit?) uses 4 MB of RAM (755 KB used after boot-up) and the MCU delivers 9.07 Bogomips. […]
Trimble Yuma: A Military-Grade Rugged Ubuntu Tablet
SDG Systems announced an Ubuntu version of the Trimble Yuma, a rugged tablet for the industrial and military applications. The company also sells the product with Windows 7. This tablet enables the use of open source geospatial applications such as GRASS or Quantum GIS, as well as other Linux-based applications. The water- and dust-proof tablet meets the military MIL-STD-810F standard and run Ubuntu 10.04 LTS netbook edition, although the company said other Linux distributions are available on request with a minimum purchase agreement or engineering fee.. Here are the Yuma Trimble specifications: Processor: Intel Atom Z530 1.6 GHz processor Memory: 1 GB DDR2 Storage: 32 GB Solid State Hard Drive Expansion: SDIO memory slot ExpressCard 34mm slot Display: 7″ widescreen 1024×600 WSVGA 650 nit Standard Batteries: Dual hot-swappable Lithium-Ion batteries, 2600 mAmp each Extended Batteries: Dual hot-swappable Lithium-Ion batteries, 5100 mAmp each I/O: USB 2.0 port (x2), 9-pin serial port […]