To support embedded design, there are several options when it comes to choosing an operating system (OS). Some of the traditional approaches to building custom Linux systems is to use built systems such as Yocto/OpenEmbedded or Buildroot. The options available for system integration include building everything manually, binary distributions (Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, etc.), and build systems (Buildroot, Yocto, PTXdist, etc.). The major drawback of build systems is that they are not as easy as a binary distribution and also the build time is more.
Why was ELBE born?
In the early days, the embedded devices had 4MiB flash and 16MiB of RAM. With these specifications, people started to hack a root file system for their devices. But in some cases, they had to start with building a cross-toolchain first. For this, tools like OpenEmbedded, Buildroot are good as long as they are well maintained. For this, a lot of libraries are used for the development of a system. Now, depending on the build environment that is used, it is difficult to add a package. Reproducibility, maintenance, and cross-compilation have always been challenging for low-level development. In such a case, Debian could be reused in a way that would fulfill our needs. Here comes the ELBE (Embedded Linux Build Environment) which is a Debian based system to generate root-filesystems for embedded devices.
ELBE alternative to Yocto/OpenEmbedded

So, the main advantage in this is to build your own package from the source which was more or less difficult in traditional approaches, and not feasible with Debos a similar solution to build custom Debian images. You can also manage your license and it supports several architectures. The open-source community has contributed to Ubuntu’s support for ELBE. Recently, ELBE was used to build Ubuntu systems for an ARM32 i.MX6 platform and an ARM64 Rockchip RK3399 platform.
ELBE process
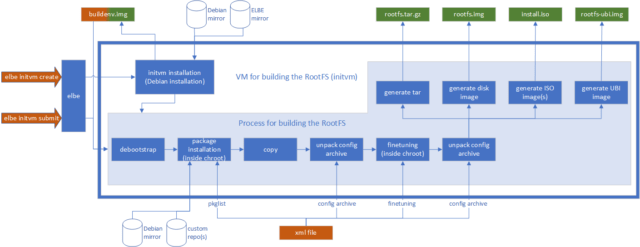
When you run ELBE, it will create a VM for building root-filesystems, this VM is called “initvm”. In the process of building the root-filesystems, it should be supplied with an XML file. The ELBE XML file can contain an archive, which can contain configuration files, and additional software. It uses pre-built software in the form of Debian packages (.deb). It is possible to use custom repositories to get special packages into the root-filesystem which is generally difficult in other build systems. Through Debian’s tools like APT (advanced package tool), the resulting root file systems (customized Debian installations) are maintained. This is the biggest difference between ELBE and other build systems like the Yocto Project and Buildroot.
Besides all this, ELBE can also create software development kits to build the root filesystem. This SDK is very similar to Yocto’s Standard-SDK.
How to get started?
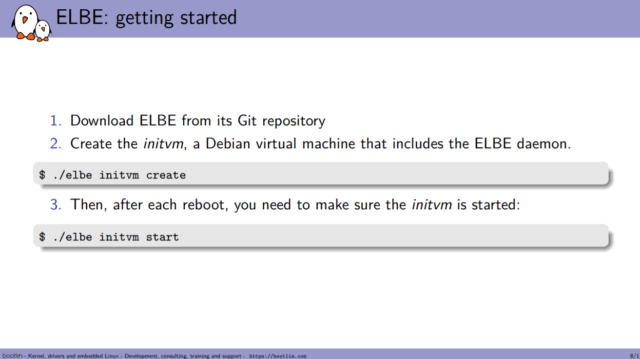
Steps 1,2,3 only need to be performed once.
- Install Debian 10 (Buster) on your host computer or virtual machine
- install ELBE and dependencies with apt on you Debian host
- Generate the
initvmrunning the build environment:
1elbe initvm create - Then build a root-filesystem inside the initvm, for example for Beaglebone Black:
1elbe initvm submit examples/armhf-ti-beaglebone-black.xml
The complete guide for creating initvm, and submitting an XML file can be found here. In the end, it’s up to the software developer to judge whether ELBE is a viable alternative to Yocto/OpenEmbedded or Buildroot for his/her own project(s) depending on the level of flexibility needed and resources on the target system(s).
Source: All the images were taken from Bootlin’s Embedded Linux and Kernel Engineer, Köry Maincent’s presentation slides from the Open Source Summit 2020 and Wiki.

Abhishek Jadhav is an engineering student, RISC-V Ambassador, freelance tech writer, and leader of the Open Hardware Developer Community.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress




