It is of fundamental importance across a broad range of electrical projects to ensure the right wire size is chosen for the given application.
Accordingly, then, there are few more critically needed skills among electricians and engineers than knowing how to convert from AWG to mm2.
Before we go any further, let’s quickly set out these two units of measurement:
- “AWG”, of course, refers to American Wire Gauge – a standardised wire gauge system that goes back to the mid-19th century. As its name indicates, AWG is predominantly used in North America.
- In Europe and elsewhere in the world, however, millimetres squared, or “mm2”, see widespread use for directly measuring a cable’s cross-sectional area, or CSA.
In some contexts, then, you might see AWG being used, while in others, references to wire size may be in mm2.
Being able to quickly convert between these two systems will help ensure both the safety and performance of your projects.
How Do Accurate Wire Sizing Conversions Help Ensure Safety?
The size of a wire dictates its ampacity, or “ampere capacity” – the maximum amount of electrical current that a wire or conductor is able to safely carry without overheating.
So, if you opt for too small a wire for a particular application, there could be a risk of insulation melting and a fire breaking out.
How Do Accurate Wire Sizing Conversions Help Ensure Performance?
Getting the wire size right can help minimise voltage drop – as can be a particular issue with long-distance wiring – and enhance the reliability of the system.
A thicker wire generally has lower resistance than a thinner wire, due to its larger CSA. This can mean more space for electrons to flow, reduced resistance, and therefore less voltage drop.
So, How Do You Convert from AWG To Millimetres Squared?
The mathematics involved in converting from AWG to mm2 are… messy, at least if someone is attempting to do the calculation manually.
Some of the confusion around this can be attributed to the fact that AWG is structured on a logarithmic scale. So, as the gauge number goes up, the corresponding wire diameter and CSA actually decrease.
You’ll notice this if you look at the various conversion tables available online for AWG to mm2:
- 22 AWG, for example, converts to 0.326 mm2, which is the kind of CSA used for low-level electronic signals or data transmission.
- At the other end of the scale, an AWG reading of 2 translates to a wire CSA of 33.6 mm2. This size of wire is typically used for applications necessitating high current capacity – such as for large appliances or certain industrial equipment.
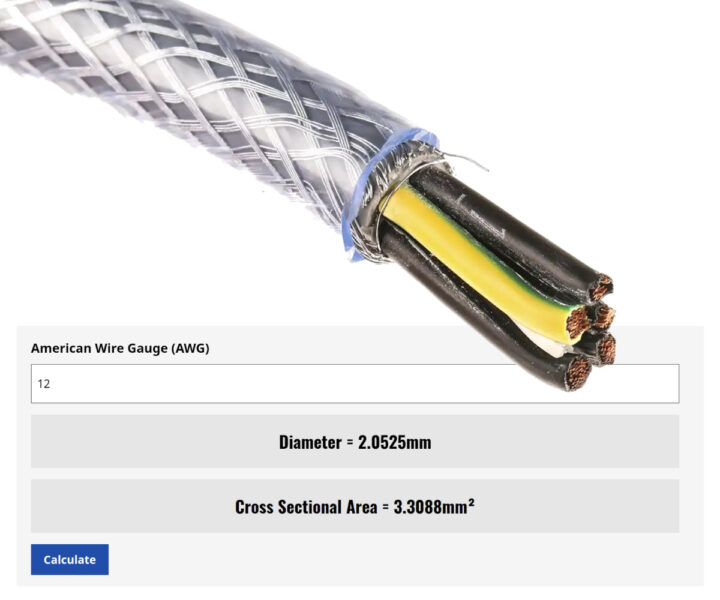
So, what about the middle of the spectrum? A 12-AWG wire is one with a 3.31 mm2 CSA. Wires of this size are customarily used for circuits designed to handle 20-amp loads, such as those found in kitchens, bathrooms, or garages. Wiring of 12 AWG is also often chosen for home theatres and audio systems such as speakers and amplifiers.
Ultimately, instead of fiddling around with complicated mathematics, you might favour seeking out one of the many free online tools out there.
The RS Online website, for example, offers a useful and accurate AWG conversion calculator for engineers and electricians, who simply need to input a particular AWG number to be presented with the corresponding diameter and cross-sectional area.
When it comes to the performance and safety priorities you have for your projects, you can’t afford to take any avoidable risks. Fortunately, with tools like these available, you don’t need to do so.

This account is for paid-for, sponsored posts. We do not collect any commission on sales, and content is usually provided by the advertisers themselves, although we sometimes write it for our clients.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress