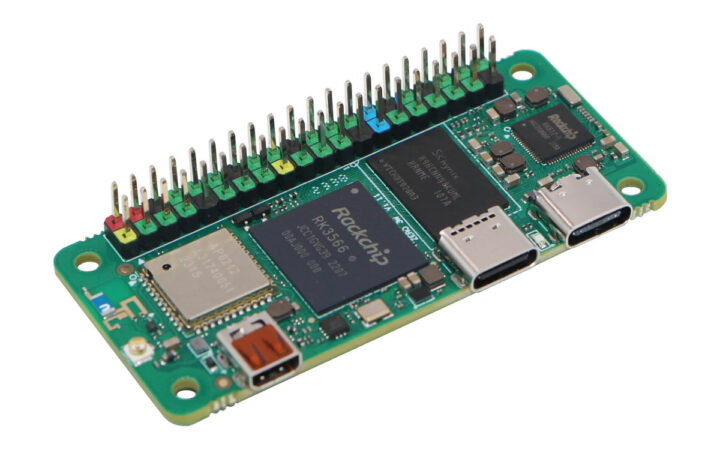
More Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W lookalikes are coming to market, as after the Allwinner H618-based Orange Pi Zero 2W, the Radxa Zero 3W has now been introduced with a 1.6 GHz Rockchip RK3566 processor and up to 8GB RAM, plus WiFi 6 and Bluetooth 5.4 connectivity, which makes it one of the most powerful Arm Linux SBCs in the compact Raspberry Pi Zero form factor.
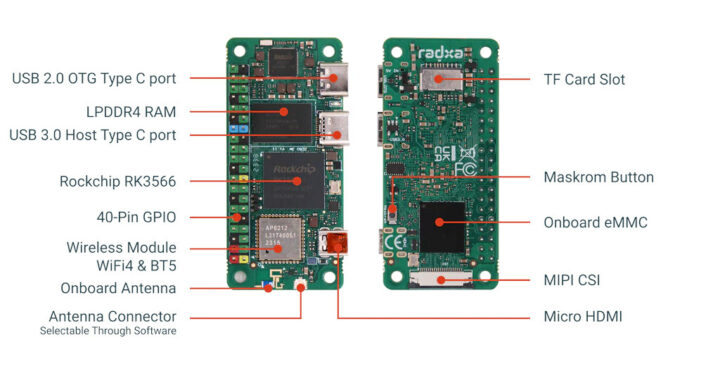
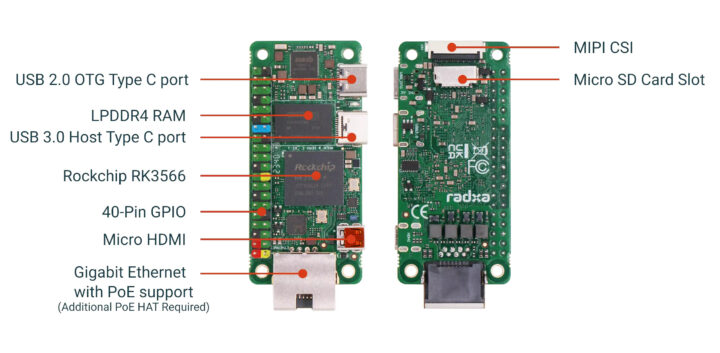
The board also comes with an optional eMMC flash with up to 64GB capacity, a microSD card, a micro HDMI port, two USB Type-C ports, a MIPI CSI camera connector, and of course, the usual 40-pin Raspberry Pi GPIO header.
Radxa Zero 3W specifications:
- SoC – Rockchip RK3566
- CPU – Quad-core Arm Cortex-A55 processor @ 1.6 GHz (Note the RK3566 is usually clocked at up to 1.8 GHz but may have been underclocked here due to heat issues at the higher frequency as the tiny PCB makes it hard to cool the CPU).
- GPU – Arm Mali G52-2EE GPU with support for OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0/3.2, Vulkan 1.1, OpenCL 2.0
- NPU – 0.8 TOPS AI accelerator
- VPU – 4Kp60 H.265/H.264/VP9 video decoding, 1080p100f H.265/H.264 video encoding
- System Memory – 1GB, 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB LPDDR4
- Storage
- Optional 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, or 64GB eMMC 5.1 flash
- MicroSD card slot (SDR104 capable)
- Video Output – Micro HDMI port up to 1080p60 (Not sure why 4Kp60 is not listed since the processor supports it)
- Camera – MIPI CSI connector with support for Raspberry Pi Camera V1.3 (OV5647) and Raspberry Pi Camera V2 (IMX219). It’s unclear whether more recent Raspberry Pi camera modules can also work.
- Wireless – WiFi 6 (802.11 b/g/n/ac/ax) and Bluetooth 5.4 with onboard antenna and uFL connector (antenna option configured by software) via “Radxa Wireless Module D8”.
- USB – 1x USB 3.0 Type-C host port, 1x USB 2.0 Type-C OTG port
- Expansion – Optional 40-pin color-coded GPIO header with up to 28x GPIO, 5x UART, 1x SPI, 2x I2C, PCM/I2S, 6x PWM, 5V, 3.3V, and GND
- Misc – MaskROM button
- Power Supply – 5V/2A (recommended) via USB-C OTG port
- Dimensions – 65 x 30mm
The company provides Debian and Ubuntu OS images (XFCE or Server variants) as well as hardware access/control library for Linux. You’ll find instructions to get started on the documentation website. Note that you’ll also need a 5V power supply (5V/2A recommended) and a microSD card, and unless you’re going for a headless system, you’ll also want an HDMI monitor or TV, a micro HDMI to HDMI cable, a USB keyboard and mouse (connected via a USB Type-C dock or hub), and potentially a USB to serial debug board and a MIPI CSI camera.
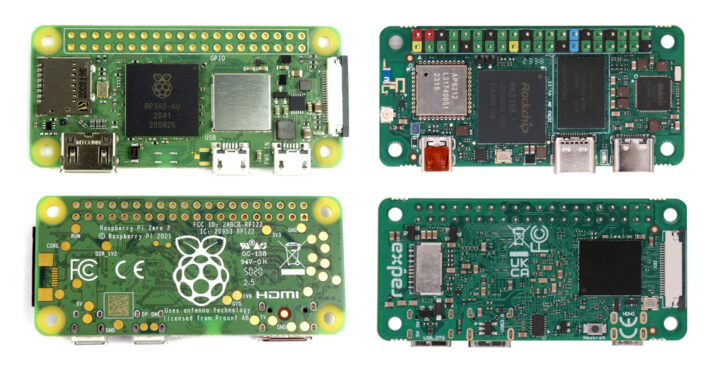
While the Radxa Zero 3W has a form factor similar to the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W, some of the connectors are different, for instance, micro HDMI vs mini HDMI, and the placement of the MIPI CSI connector and microSD card slot is different as can be seen in the photo below.
Performance-wise, while we don’t have benchmarks for the Radxa Zero 3W SBC per se, the Rockchip RK3566 and RK3568 processors have now been around for several years and we have plenty of benchmark results in Android and Linux, and for instance, it is should be close to 50 around 33 percent faster than the Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W in 7-zip multi-core benchmark. [Update: Now we do have sbc-bench.sh results.]
The Radxa Zero 3W is now available for as low as $14.90 with 1GB RAM, WiFi 6, no eMMC flash, and no GPIO headers on Arace (in stock) or AllNet China (no stock for now) and the price goes up to $66 with 8GB RAM, 64GB eMMC flash, and female GPIO headers soldered to the board.
As a side note, Radxa is also working on the Radxa Zero 3E replacing WiFi 6 with a Gigabit Ethernet port, and a slightly wider Zero 2 Pro board with a 2.2 GHz Amlogic A311D hexa-core Cortex-A73/A53 processor that will deliver even more performance and require a proper cooling solution with a heatsink covering the board and a small fan. We’ll write about those in more detail once they become available.
Thanks to Bing for the tip.
Updated: This post was initially published on October 30, 2023, and updated following the launch of the Radxa Zero 3W and the upgrade to WiFi 6 from WiFi 4.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress