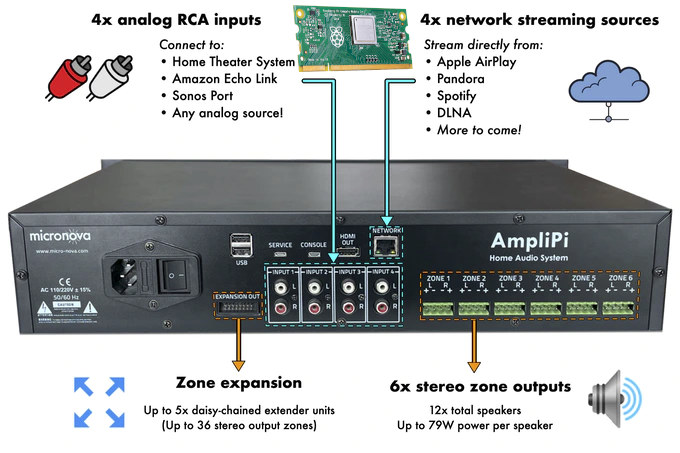
Micro Nova has put together an open-source, whole-house audio amplifier called AmpliPi based on Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3+. It is capable of streaming four independent sources to 6 stereo output zones, expandable to up to 36 stereo output zones through daisy-chained extender units.
AmpliPi specifically supports inputs from four networking streaming sources including AirPlay, Pandora, Spotify, and DLNA, as well as four analog RCA inputs for your media appliances.
AmpliPi key components and features:
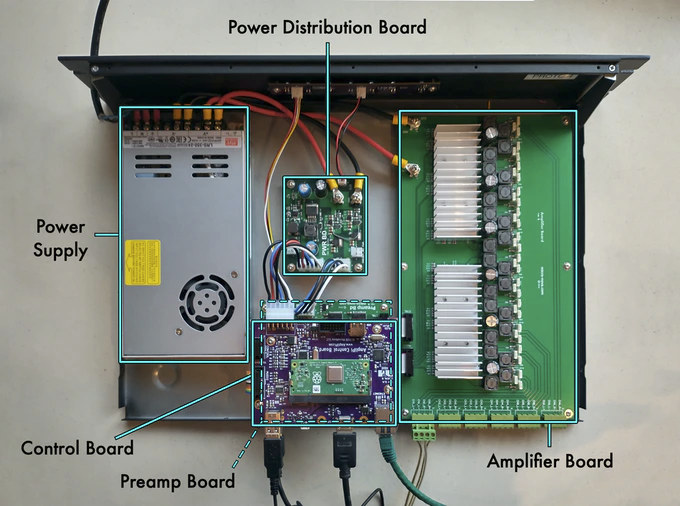
- Controller Board
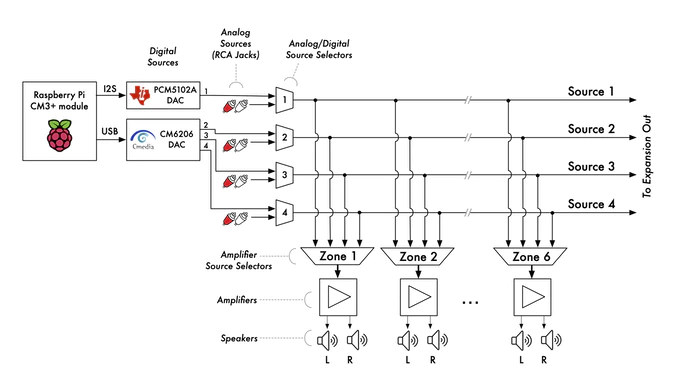
- Carrier board fitted with Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3+ and PCM5102A & CM6206 audio DACs. It also communicates over I2C with the STM32 MCU on the Preamp board (see below) to control the muxing and amplification systems.
- Interfaces
- 10/100M Ethernet port
- HDMI 1.4 output
- 2x USB 2.0 ports, plus one internal USB port
- Service and console ports for maintenance and/or debugging.
- Preamp Board
- Board equipped with a 6×4 audio matrix switching system and volume control network that is managed by an STM32F030 Arm microcontroller that also controls the mute and power settings for the amplifiers. The matrix switching system can also allow the user to mix multiple inputs on one or more outputs
- Connector
- 8x RCA inputs for 4x stereo sources
- Zone expansion connector
- Amplifier Board
- This board contains the 6 stereo class-D PWM amplifiers required by the 6 speakers. Class-D PWM amplifiers enable a more efficient system and reduce the need for cooling fans which are activated less often.
- 6x 4-pin speaker connectors
- Small display configured to show the IP address, system utilization, and volume levels by default.
- Mean Well switching power supply and power distribution board.
- Power Consumption – 6.7W in standby mode, up to 391W continuous, up to 782W peak
- Dimensions – 2U 19-inch rackmount system with 300mm depth
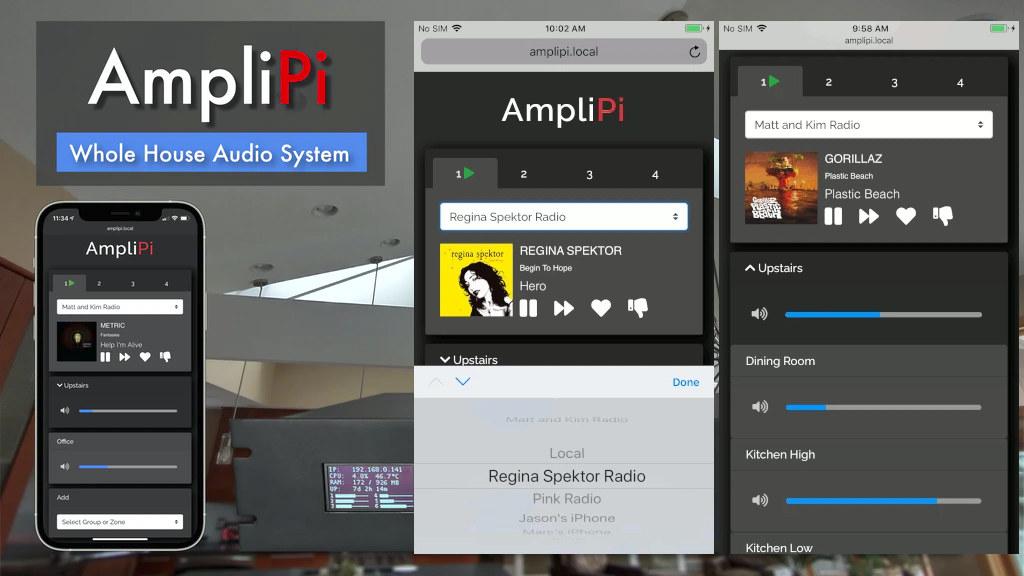
The Raspberry Pi module runs Raspberry Pi OS with Web App server, streaming music clients (Pandora, AirPlay, Spotify, etc), and custom software for the REST API interface.
The amplifier can be controlled from a mobile-friendly Web App written in Python running on the Raspberry Pi. The software, firmware, and PDF schematics are open-sourced under the GPL license and posted on GitHub, where you’ll also find documentation for the REST API.
AmpliPi Raspberry Pi-based audio amplifier has just launched on Kickstarter with a $10,000 funding target. Rewards start at $399 for the “developer special edition” that will ship early (April 2021) with beta software. If you prefer something that (hopefully) works out of the box, you’d have to pledge $499 for the “early bird special” scheduled to ship in May 2021. Shipping adds $35 to the US, $60 to Canada, and $100 to some European countries. The amplifier is not available in other countries. Additional information may also be found on the official website.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress