RAK Wireless launched its first Mini PCIe LoRaWAN concentrator module in 2018 with RAK833 mPCIe card featuring Semtech SX1301 LoRa baseband chip. It was soon followed by RAK2247 mPCIe with a very similar design but some tweaks to increase its maximum transmission power and range, and improve thermals and stability with the addition of a heatsink.
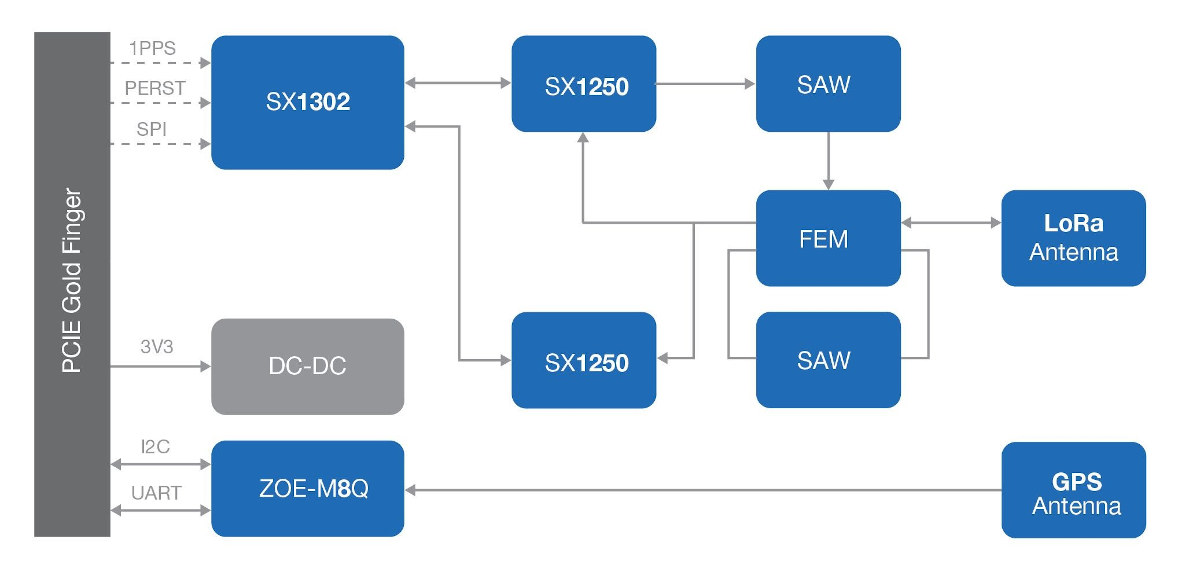
The company has now introduced a new version with RAK2287 Mini PCie LoRaWAN concentrator module being mostly inspired by RAK2247 module but replacing Semtech SX1301 by Semtech SX1302 LoRa transceiver that’s suppose to reduce current consumption (and heat), lower the BoM cost, and able to handle a higher amount of traffic. The new mini PCIe card also adds u-blox ZOE-M8Q GPS system-in-package to provide GNSS functionality.

- LoRa Connectivity
- Semtech SX1302 LoRa Transceiver with 2x SX1250 Tx/Rx front-end
- Tx power – up to 27dBm
- Rx sensitivity – down to -139dBm @ SF12, BW 125 kHz
- LoRaWAN® 1.0.2 compatible.
- LoRa band coverage – RU864, IN865, EU868, AU915, US915, KR920, AS923
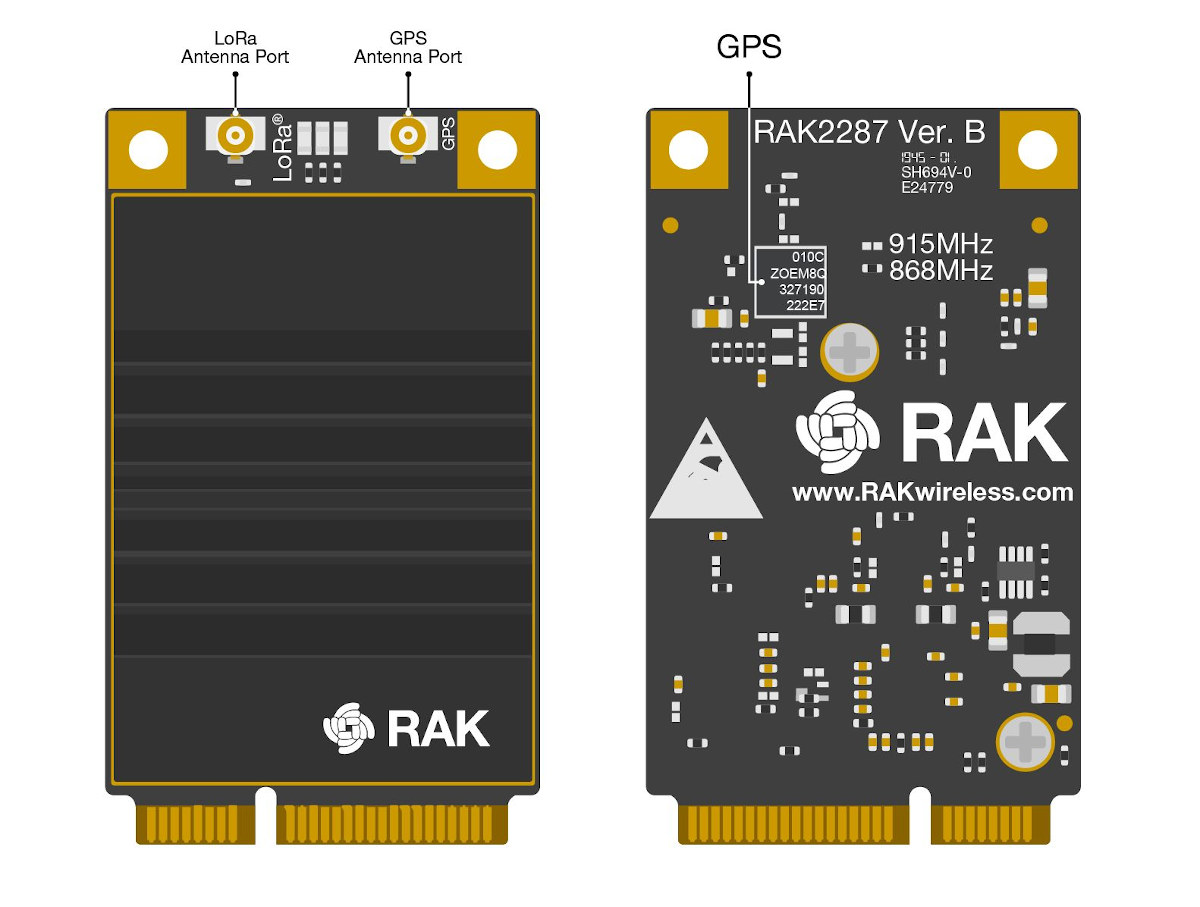
- 1x iPEX antenna connector for LoRa
- GNSS – GPS / QZSS, BeiDou, Galileo, and GLONASS via U-blox ZOE-M8Q GPS SiP; 1x iPEX antenna connect for GPS
- Host Interface – 3.3V SPI interface on mPCIe edge connector
- Dimensions – 50.95 x 30.0 x 10.5 mm (mini-PCIe form factor)
- Weight – 16.3 grams
Thanks to SX1302 chip, the company explains the module can handle Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications that require node density of up to 500 nodes per km² in an environment with moderate interference. If you wonder why a usually fixed gateway would need GPS support, RAK Wireless explains CNX Software it’s for precise time syncing and stamping, not location services:
The GPS is for precise time syncing of the rx/tx windows for Class B and to precise time-stamping in case of asset tracking.
Since the company focuses their efforts on Raspberry Pi support, and none of the Raspberry Pi foundation board currently come with a mini PCIe socket, there’s also a Raspberry Pi for this purpose: RAK2287 Pi HAT.
RakWireless RAK2287 mini PCIe LPWAN concentrator module can be purchased on the company’s online store for $89 plus shipping, and the optional Pi HAT adding $27.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress