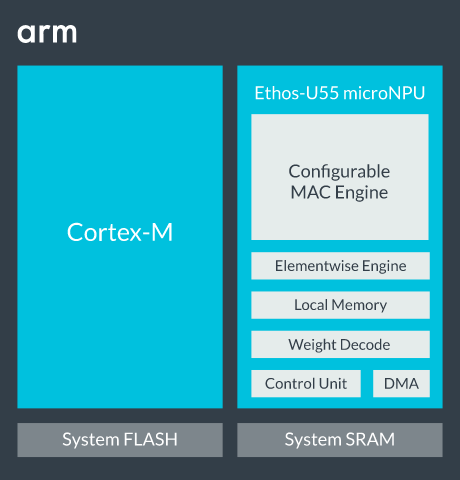
Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things often go hand in hand with AIoT being a new buzz word that came up last year or so. But for AIoT to scale we need ultra-low-cost, low-power solutions capable of doing inference at the sensor node level, and this is only possible with microcontrollers.
To achieve this goal, Arm has just unveiled the Arm Cortex-M55 microcontroller core optimized for artificial intelligence workloads that delivers up to a 15x uplift in ML performance and a 5x uplift in DSP performance with greater efficiency, as well as Ethos-U55 microNPU designed for Cortex-M microcontrollers that need even more AI performance (up to 480 times faster), while consuming as little power as possible.
Arm Cortex-M55
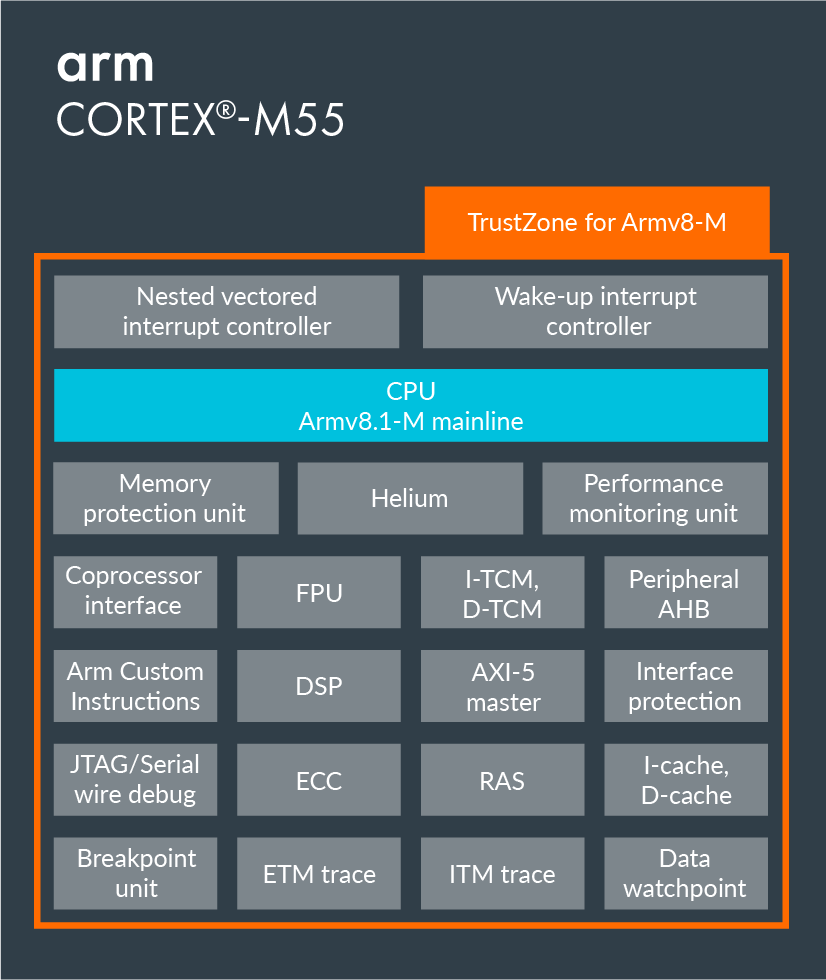
Key features and specifications:
- Architecture – Armv8.1-M
- Bus interface – AMBA 5 AXI5 64-bit master (compatible to AXI4 IPs)
- Pipeline – 4-stage (for main integer pipeline)
- Security – Arm TrustZone technology (optional)
- DSP extension – 32-bit DSP/SIMD extension
- M-Profile Vector Extension (MVE) – Helium (optional)
- Optional Floating-point Unit (FPU)
- Coprocessor interface – 64-bit (optional)
- Instruction cache – Up to 64KB with ECC (optional)
- Data cache – Up to 64KB with ECC (optional)
- Instruction TCM (ITCM) – Up to 16MB with ECC (optional)
- Data TCM (DTCM) – Up to 16MB with ECC (optional)
- Interrupts – Up to 480 interrupts + Non-maskable interrupt (NMI)
- Wake-up Interrupt Controller (WIC) – Internal and/or external (optional)
- Multiply-accumulate (MAC) / cycle – Up to: 2 x 32-bit MACs/cycle, 4 x 16-bit MACs/cycle, 8 x 8-bit MACs/cycle
- Sleep modes – Multiple power domains, Sleep modes (sleep and deep sleep), Sleep-on-exit, Optional retention support for memories and logic
- Debug – Hardware and software breakpoints, Performance Monitoring Unit (PMU)
- Trace – Optional Instruction trace with Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM), Data Trace (DWT) (selective data-trace), and Instrumentation Trace (ITM) (software trace)
- Arm Custom Instructions – Optional (available in 2021)
- Robustness – ECC on instruction cache, data cache, instruction TCM, data TCM (optional); Bus interface protection (optional); PMC-100 (Programmable MBIST Controller, optional); Reliability, availability, and serviceability (RAS) extension
The faster ML performance is due to Helium technology and corresponding M-Profile Vector Extension (MVE) that were announced by Arm and covered on CNX Software in February 2019. Arm Cortex-M55 is just the first core to leverage the technology.
Arm Ethos-U55 microNPU
Arm Cortex-M55 cores and future compatible Cortex-M cores can be further extended with Ethos U55 microNPU with the following key features:
- Performance (At 1 GHz) – 64 to 512 GOP/s
- MACs (8×8) – 32, 64, 128, 256
- Utilization on popular networks – Up to 85%
- Data Types – Int-8 and Int-16
- Network Support – CNN and RNN/LSTM
- Winograd Support – No
- Sparsity – Yes
- Memory System
- Internal SRAM – 18 to 50 KB
- External on Chip SRAM – KB to Multi-MB
- Compression – Weights only
- Memory Optimizations – Extended compression, layer/operator fusion
- Debug and Profile – Layer-by-layer visibility with PMUs
- Evaluation and Early Prototyping – Performance Model, Cycle Accurate Model, or FPGA evaluations
Arm Ethos-U55 microNPU is compatible with TensorFlow Lite Micro framework and works on bare-metal Cortex-M55 platforms or ones running an RTOS. Arm provides several software components for the new IP including a TensorFlow Lite Micro runtime, CMSIS-NN, Optimizer, and a driver.
IoT platform Corstone-300
You’ll find more information in the announcement, and respective product pages for Arm Cortex-M55 and Arm Ethos-U55 here and there.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress