While 5G is ramping up, 4G LTE handsets will still be dominant in terms of market demand for a few more years. So Qualcomm has unveiled three new mobile SoC for mid-range smartphones with Snapdragon 720G, Snapdragon 622, and Snapdragon 460 that also happen to be one of the first processors to support Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC).
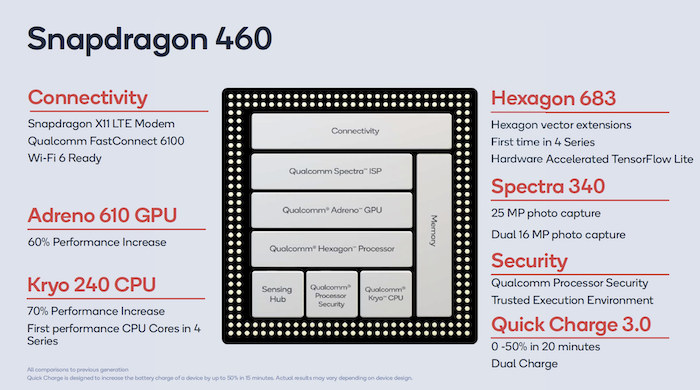
Snapdragon 460
Key features:
- CPU – 8x Kryo 240 cores up to 2.3GHz
- GPU – Adreno 610 GPU
- DSP – Hexagon 683 with vector extensions, hardware-accelerated TensorFlow Lite
- ISP – Spectra 340 ISP supporting 25MP camera, or dual 16MP camera
- Connectivity
- Cellular – Snapdragon X11 LTE modem
- WiFi 6 ready
- Bluetooth 5.1 with advanced audio via the Qualcomm FastConnect 6100 platform
- GNSS – Dual-Frequency (L1 and L5) GNSS for GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, Beidou, NavIC
- Quick Charge 3.0 – 0 to 50% in 20 minutes
- Process – 11nm
Snapdragon 460 is an update to the Arm Cortex-A53 based Snapdragon 450 processor with the custom Kryo 240 processor delivering up to 60% extra performance, while Adreno 610 GPU delivers up to 70% performance increase over Adreno 506.
Snapdragon 662
Highlights:
- CPU – Octa-core “Kryo 260” processor with four Cortex-A73 cores @ up to 2.0 GHz, and four Cortex-A53 cores @ up to 1.8 GHz
- GPU – Adreno 610 GPU
- DSP – Hexagon 683 with vector extensions, hardware-accelerated TensorFlow Lite
- ISP – Spectra 340T ISP supporting 48MP cameras, HEIF capture, and triple cameras
- Connectivity
- Cellular – Snapdragon X11 LTE modem
- WiFi 6 ready
- Bluetooth 5.1 with advanced audio via the Qualcomm FastConnect 6100 platform
- GNSS – Dual-Frequency (L1 and L5) GNSS for GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, Beidou, NavIC
- Quick Charge 3.0 – 0 to 50% in 20 minutes
- Process – 11nm
Snapdragon 662 looks very similar to Snapdragon 665, but with a slower modem, and better ISP. It also shares many features of Snapdragon 460, but with more powerful Cortex-A73 CPU cores, and better camera support.
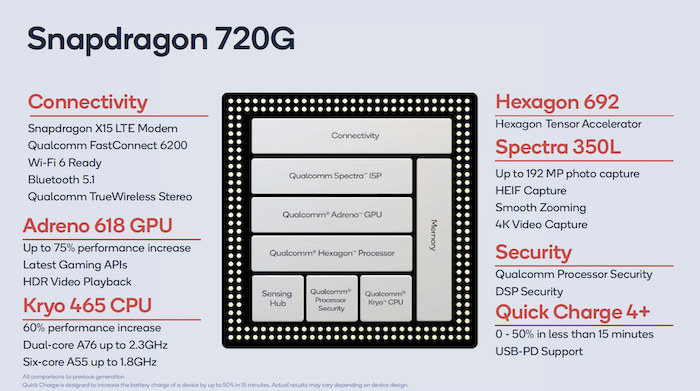
Snapdragon 720G
Key features and specifications:
- CPU – Octa-core “Kryo 465” processor with 2x Cortex-A76 cores @ up to 2.3 GHz, and 6x Cortex-A55 cores @ up to 1.8 GHz
- GPU – Adreno 618 GPU
- DSP – Hexagon 692 Hexagon Tensor Accelerator
- ISP – Spectra 350L ISP supporting 192MP cameras, HEIF capture, and 4K video capture
- Connectivity
- Cellular – Snapdragon X15 LTE modem
- WiFi 6 ready
- Bluetooth 5.1 with advanced audio via the Qualcomm FastConnect 6200 platform
- GNSS – Dual-Frequency (L1 and L5) GNSS for GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, Beidou, NavIC
- Fast Charging – Quick Charge 4+ allowing 0 to 50% charge in less than 15 minutes; USB PD support
- Process – 8nm
Snapdragon 720G looks to be an upgrade to Snapdragon 712 with the processor delivering a 60% performance increase, and the GPU providing 75% better improve and support for HDR video playback.
Availability
Snapdragon 720G based phones will come to market soon as the first devices are slated for Q1 2020, but we’ll need to wait a little longer for Snapdragon 662 and Snapdragon 460 based smartphones which are scheduled for the end of 2020.
Via Press Release

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress