Qualcomm Snapdragon processors are mainly used in smartphones manufactured in high volume, and in the past if you contacted the company to use their processor for your custom project with a target yearly production of a few thousands pieces, they’d just ignore you.
This started to change in late 2016 with the launch of Snapdragon 410E and 600E processors based on mobile version of Snapdragon 410 and 600 processors minus the modem, but instead targeting the embedded space and the Internet of Things, which anybody could purchase easily through Arrow Electronics, and offering a 10-year life cycle. Those are good if you are satisfied with entry-level or mid-range processor, but the company has now announced the launch of Snapdragon 820E for customers requiring better performance for their application.
Snapdragon 820E specifications appears to be moslty the same as Snapdragon 820 except for the lack of X12 cellular modem:
- CPU – 4x Qualcomm 64-bit Kryo CPU cores @ up to 2.35 GHz
- GPU – Qualcomm Adreno 530 GPU with support for Path Rendering, OpenCL 2.0 Full, RenderScript-Next, OpenGL ES GEP, GL4.4, DX11.3/4, OpenGL ES 3.1, OpenGL ES 3.0
- DSP – Qualcomm Hexagon 680 DSP
- Memory I/F – Dual-Channel LPDDR4 up to 1866MHz
- Storage I/F – eMMC 5.1, UFS 2.0, SD 3.0 (UHS-I)
- Display – MIPI DSI I/F; Up to 3 displays (2 panels + external) with 3840×2400 max. resolution @ 60 fps
- Audio – I²S, PCM
- Camera – MIPI CSI interface; Up to 28 MP camera sensor; 2x 14-bit Image Sensor Processor (ISP)
- Video – Capture and Playback up to 4K UHD @ 60 fps; H.264 and H.265 video codecs
- Connectivity – Dual band 802.11ac 2×2 MU-MIMO Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.2
- Location – GPS, GLONASS
- USB – USB 3.0, USB 2.0
- Other Peripherals – SLIMbus, TSIF, PCIe 2.0
- Security – Secure code signing service, Secure Boot
- Package – 994-pin NSP package (15.6 x 15 x 0.64mm; 0.4mm Pitch)
- Process Technology – 14 nm FinFET
The company expects the processor to be used for Industrial IoT applications, digital signage, UAVs and robotics, smart glasses, and virtual/augmented reality headsets. There’s no mention of software support, but according to the press release, the long awaited 96Boards compliant DragonBoard 820c development board features Snapdragon 820E SoC, and based on recent info from 96Boards community, the board supports Linux (Debian, Open Embedded, Yocto Project) as well as Android.
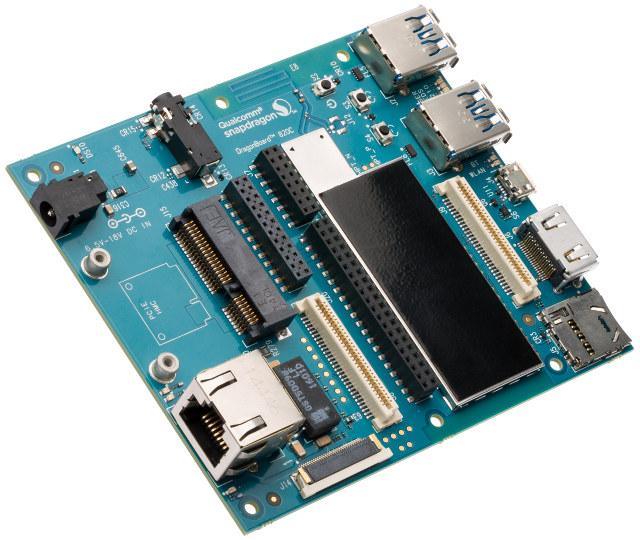
Snapdragon 820E SoC (they call it “embedded platform”) will be made available through Arrow Electronics and other distributors for 10 years from commercial sample (until 2025) together with the following companion chips for power management (PM8996/PMI8996 PMUs), audio (WCD9335 codec), and GPS & Glonass (WGR7640 RF Receiver). Arrow Electronics is also selling DragonBoard 820c development board to help end customers and ecosystem participants getting started with Snapdragon 820E embedded platform. Somehow there’s no price on Arrow website (quote request only), but based on DB820c page on 96Boards website, the price should be $199 for the “basic kit”. More details may be found on Qualcomm 820E’s product page, and developer website.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress





