Yesterday I wrote about using 3G on Raspberry Pi board, and one of the commenter mentioned higher traffic than expected when connecting to 3G to just send a few bytes before disconnecting. One of the reasons are the extra data needed if you transmit data over a secure connection, for example establishing a PPP connection, connect to the board over SSH, and disconnect, results in the transmission & reception of a few kilobytes on my board:
|
1 2 |
Connect time 1.9 minutes. Sent 5815 bytes, received 6972 bytes. |
But if you get much more traffic than that, you may want to investigate if another package may transfer data when it detects the connection is up. To analyze traffic, tcpdump and Wireshark are good options, especially if you want to look into the packets data, however such tools do not tell you which process is sending or receiving the data.
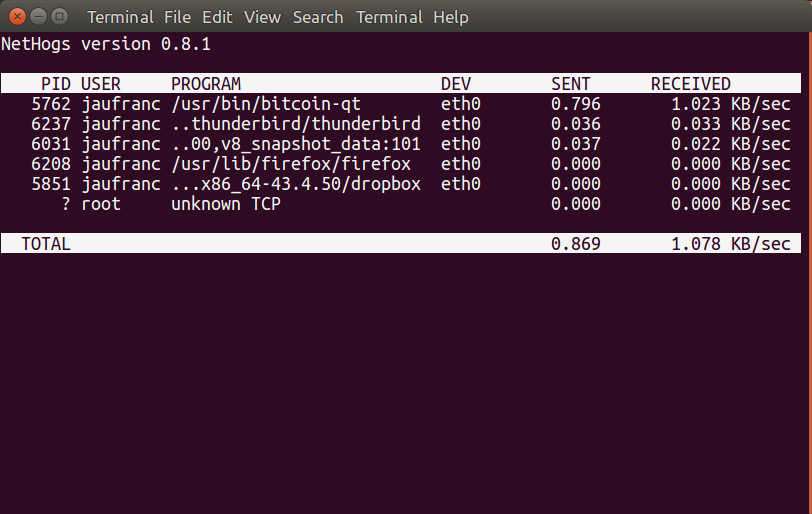
So I searched whether I could find a program that would do just that, and a thread on Ask Ubuntu discussing how to display network traffic in the terminal, mentions some interesting utilities like bmon, iftop, tcptrack, etc… which all show info about the connections, but the utility that does exactly what I I want is called nethogs. Installing it in Ubuntu/Debian is very easy.
|
1 |
sudo apt install nethogs |
Now run it as root, as you should get a list of processes that send and received data over a specific interface:
|
1 |
sudo nethogs |
The full options can be found with -h:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
nethogs -h usage: nethogs [-V] [-h] [-b] [-d seconds] [-v mode] [-c count] [-t] [-p] [-s] [ device [device [device ...]]] -V : prints version. -h : prints this help. -b : bughunt mode - implies tracemode. -d : delay for update refresh rate in seconds. default is 1. -v : view mode (0 = KB/s, 1 = total KB, 2 = total B, 3 = total MB). default is 0. -c : number of updates. default is 0 (unlimited). -t : tracemode. -p : sniff in promiscious mode (not recommended). -s : sort output by sent column. -a : monitor all devices, even loopback/stopped ones. device : device(s) to monitor. default is all interfaces up and running excluding loopback When nethogs is running, press: q: quit s: sort by SENT traffic r: sort by RECEIVE traffic m: switch between total (KB, B, MB) and KB/s mode |

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress