Several server SoCs with a large number of ARMv8 cores have been announced in the past with products such as Cavium ThunderX featuring 48 64-bit ARM cores and EZTile TILE-Mx100 with 100 ARM Cortex A53 cores. Phytium Technology, a Chinese startup funded in 2012, has showcased its work on Mars processor with 64 custom design ARMv8 cores at Hotchips 2015 conference.
 Charles Zhang, director of research for Phytium, made the presentation entitled “Mars: A 64-Core ARMv8 Processor” at the conference, and a PDF version is available on Hotchips 2015 website (Conf. Day 1 section) but unfortunately it’s password-protected and only accessible by attendees. Last year, they made all presentations publicly downloadable in December, so hopefully it will be the same this year. In the meantime, I relied on an articles published on EETimes and Golem.de, the latter reproduced some of the slides, to get some of the specs and features:
Charles Zhang, director of research for Phytium, made the presentation entitled “Mars: A 64-Core ARMv8 Processor” at the conference, and a PDF version is available on Hotchips 2015 website (Conf. Day 1 section) but unfortunately it’s password-protected and only accessible by attendees. Last year, they made all presentations publicly downloadable in December, so hopefully it will be the same this year. In the meantime, I relied on an articles published on EETimes and Golem.de, the latter reproduced some of the slides, to get some of the specs and features:
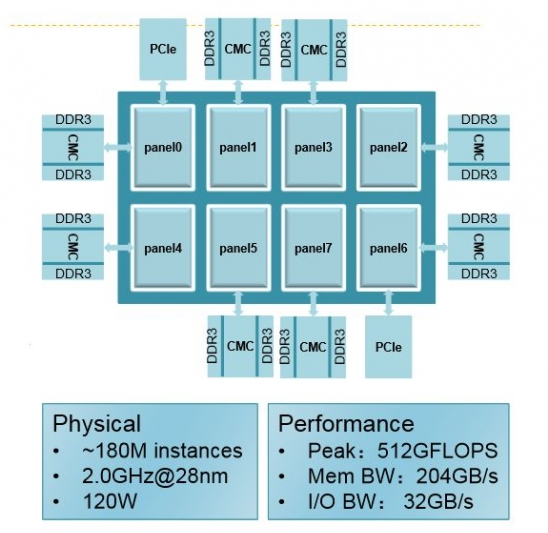
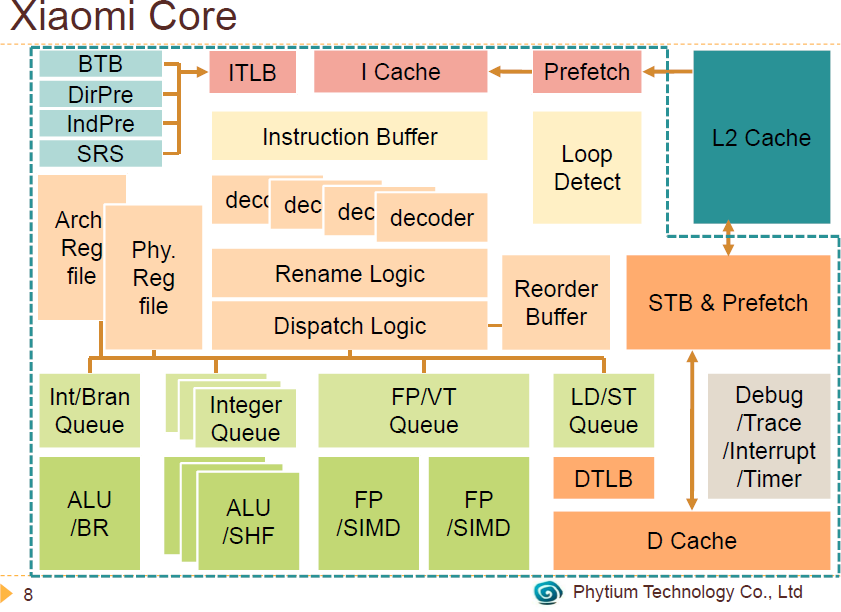
- 64 custom designed ARMv8 “Xiaomi” core up to 2.0 GHz
- Cache – L1 I-Cache and D-Cache, 32MB L2 cache, 128MB L3 Cache
- Memory – 16 DDR3-1600 channels
- ECC and memory protection on all caches, tags and TLBs
- Expansion – 2x 16-lane PCIe 3.0 interfaces
- Performance – 512GFLOPS, 204 GB/s memory bandwidth, 32GB/s I/O bandwidth
- Manufacturing process – 28 nm
- Die size / Package – 640 mm2; FCBGA package with ~3,000 pins
- TDP – 120 Watts
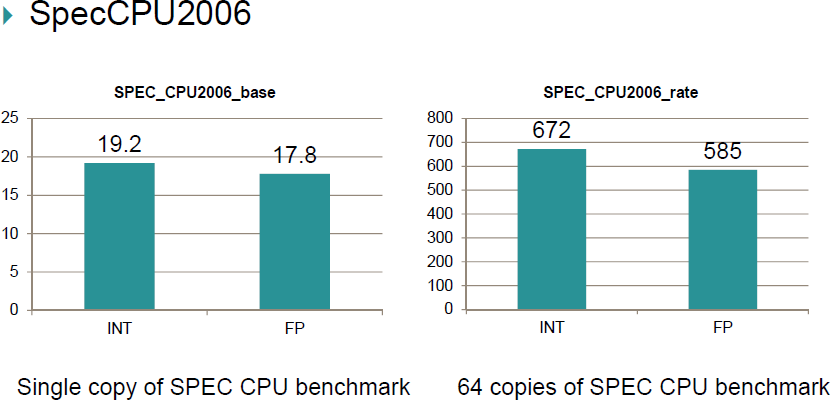
Mars design has not yet taped out, but the company perform some simulations with SpecCPU 2006 base and rate benchmark, where the chip achieved 672 points and 585 points for respectively integer and floating-point performance.
Here are some background between the base and rate benchmark to make it clearer to what is actually tested here:
The SPEC CPU 2006 benchmark has several different ways to measure computer performance. One way is to measure how fast the computer completes a single task; this is a speed measurement. Another way is to measure how many tasks a computer can accomplish in a certain amount of time; this is called a throughput, capacity or rate measurement.
- The SPECspeed metrics (e.g., the SPECint 2006 benchmark) are used for comparing the ability of a computer to complete single tasks.
- The SPECrate metrics (e.g., the SPECint_rate 2006 benchmark) measure the throughput or rate of a machine carrying out a number of tasks.
If we check published integer rate benchmarks results, Phytium Mars would have roughly the performance of four AMD Opteron 6174 deca-core processors (Max TDP: 115 Watt / processor) or two Intel Xeon E5-2643 v3 deca-core processors (135 W TDP / processor).
No date was provided for the launch of Mars SoC.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress