David Anders, embedded systems developer at Texas Instruments, explains how to work with I2C in Linux based embedded systems at ELCE 2012.
Abstract:
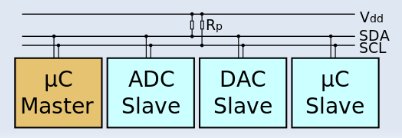
Board bring up is one of the most under documented aspects of embedded development. I2C is such a powerful, low-cost, and ubiquitous method of communication, that a basic understanding of it’s usage is essential to the embedded linux developer to quickly bring up and debug embedded designs. This presentation will look at the various software and hardware aspects of working with I2C using simple case studies highlighting the implementation of an EEPROM and a GPIO Expander. Most embedded Linux developers at some point in their career will be handed a piece of hardware that is untested. This presentation intends to provide some information about core tools and methods for bring up of I2C interfaces and assorted I2C based peripheral devices. David Anders has previously presented at Embedded Linux Conference 2012 with “Board Bringup: LCD and Display Interfaces“.
The talk is divided into 3 main parts:
- Communication Principles – Asynchronous (e.g. RS232) and Synchronous (e.g. I2C) communication
- Drivers and Software Tools – Bootloaders & Linux kernel GPIO bit-bang & I2C chardev, and I2C tools (i2cdetect, i2cdump,. i2cget, i2cset)
- Board Bringup Use Cases:
- I2C GPIO expanders
- I2C EEPROMs
You can also download the slides for this presentation.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress