When developing software for embedded systems, you may need to support multiple architectures such as arm, mips, x86, powerpc, alpha etc.. but you may not have the hardware required on hand to test them.
This is where QEMU – a processor emulator – comes to the rescue. In a way, QEMU is similar to VirtualBox, VMWare or Citrix Xendeskop except it can support multiple architectures.
I’ll show how to run Debian Lenny ARMEL in QEMU on a computer running Ubuntu 10.10 (aka Ubuntu Maverick Meerkat).
QEMU (Qemu-kvm) Installation
First install qemu-kvm and qemu-kvm-extras (the latter contains qemu-system-arm):
sudo apt-get install qemu-kvm qemu-kvm-extras
Let’s check qemu version:
jaufranc@CNX-TOWER:~/edev$ qemu –version
QEMU PC emulator version 0.12.5 (qemu-kvm-0.12.5), Copyright (c) 2003-2008 Fabrice Bellard
Debian ARM Installation in QEMU
Create a directory to store the required files for the emulator and download the Debian Lenny ARMEL kernel (vmlinuz) and debian installer rootfs (initrd.gz):
mkdir ~/arm-emul
cd ~/arm-emul
wget ftp://ftp.debian.org/debian/dists/lenny/main/installer-armel/current/images/versatile/netboot/vmlinuz-2.6.26-2-versatile
wget ftp://ftp.debian.org/debian/dists/lenny/main/installer-armel/current/images/versatile/netboot/initrd.gz
Create a raw virtual hard disk large enough (e.g. 2GB) for Debian:
qemu-img create -f raw hda.img 2G
Run the ARM virtual machine and follow the instructions to install Debian. This may take several hours, since all instructions are decoded by software:
qemu-system-arm -m 256 -M versatilepb -kernel ~/arm-emul/vmlinuz-2.6.26-2-versatile -initrd ~/arm-emul/initrd.gz -hda ~/arm-emul/hda.img -append “root=/dev/ram”
After the system reboots, close QEMU.
Running Debian ARM in QEMU
Once the installation is complete, mount the first disk partition of the QEMU disk image with a loop device (offset 32256) in order to copy the initrd (rootFS) (mount QEMU images):
mkdir mount
sudo mount -o loop,offset=32256 ~/arm-emul/hda.img ~/arm-emul/mount
cp ~/arm-emul/mount/boot/initrd.img-2.6.26-2-versatile ~/arm-emul/
sudo umount ~/arm-emul/mount
Then run Debian ARMEL in QEMU as follows:
qemu-system-arm -m 256 -M versatilepb -kernel ~/arm-emul/vmlinuz-2.6.26-2-versatile -initrd ~/arm-emul/initrd.img-2.6.26-2-versatile -hda ~/arm-emul/hda.img -append “root=/dev/sda1”
That’s it, you now have a running ARM virtual machine. You can cross-compile your application or library in your host PC (compiling them in the emulator would be very slow), copy them to the VM (via NFS for example) and run them in your ARM emulator. As long as those are not graphics intensive or processor intensive, they should work just fine.
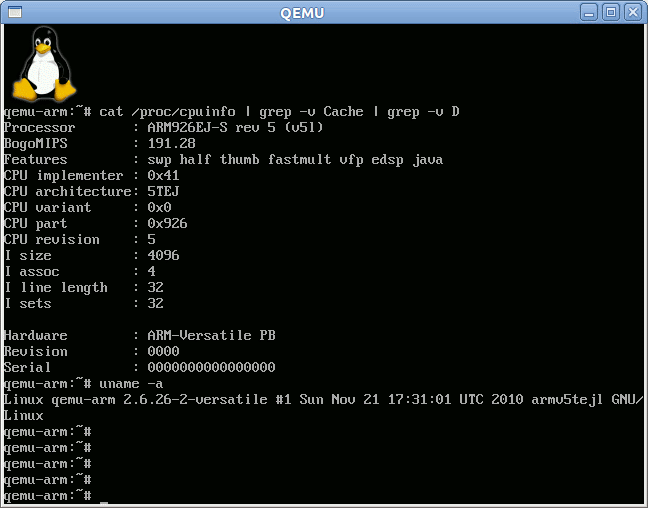
Once the emulator is running you can check the emulated CPU is an ARM926E-JS Core.
I got most of the instructions from http://blog.troyastle.com/2010/07/building-arm-powered-debian-vm-with.html

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress